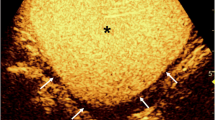
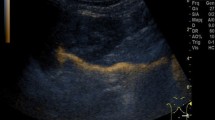
Abstract
Purpose
Although contrast-enhanced urosonography (ceVUS) has shown capable diagnostic accuracy for the diagnosis of vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) in children, the ability of ceVUS to detect intrarenal reflux (IRR) is considered limited. The purpose of our study is to assess the ability of ceVUS to detect IRR as well as its association with age, gender, and the grade of VUR.
Methods
This study included 5153 children who were referred to our clinic for ceVUS. All children underwent sonographic examinations, which were performed on a LOGIQ S8 machine equipped with dedicated software for contrast-enhanced studies with harmonic imaging. Standard ultrasound of the urinary tract was followed by bladder catheterisation and instillation of physiological normal saline and the US contrast medium (SonoVue®, Bracco).
Results
VUR was diagnosed by ceVUS in 1959 out of 5153 children (38%), of whom IRR was found in 233 of 1959 children (11.9%). A total of 285 ureteral units showing IRR were found. High grades of VUR (IV + V) with IRR were found in a total of 235 of 285 (82.81%) renal units. Bilateral IRR was found in 53 patients, usually with a high-grade VUR on both sides. Most children had VUR grade IV, predominantly those < 12 months. The younger the child, the higher the likelihood of higher-grade VUR (p = 0.02).
Conclusion
ceVUS, combined with harmonic imaging and second-generation ultrasound contrast media, enabled IRR detection in almost 12% of our patients with VUR. IRR is most commonly found in children under 1 year of age with VUR grades IV and V.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Hannerz L, Wikstad I, Johansson L, Broberger O, Aperia A (1987) Distribution of renal scars and intrarenal reflux in children with a past history of urinary tract infection. Acta radiologica (Stockholm, Sweden: 1987) 28(4):443–446
Hodson CJ, Edwards D (1960) Chronic pyelonephritis and vesico-ureteric reflex. Clin Radiol 11:219–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0009-9260(60)80047-5
Hodson CJ (1981) Neuhauser lecture. Reflux nephropathy: a personal historical review. AJR Am J Roentgenol 137(3):451–462. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.137.3.451
Bailey RR (1973) The relationship of vesico-ureteric reflux to urinary tract infection and chronic pyelonephritis-reflux nephropathy. Clin Nephrol 1(3):132–141
Schneider KO, Lindemeyer K, Kammer B (2019) Intrarenal reflux, an overlooked entity—retrospective analysis of 1166 voiding cysturethrographies in children. Pediatr Radiol 49(5):617–625. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-018-04330-z
Colleran GC, Barnewolt CE, Chow JS, Paltiel HJ (2016) Intrarenal reflux: diagnosis at contrast-enhanced voiding urosonography. J Ultrasound Med Off J Am Inst Ultrasound Med 35(8):1811–1819. https://doi.org/10.7863/ultra.15.09056
Fukui S, Watanabe M, Yoshino K (2013) Intrarenal reflux in primary vesicoureteral reflux. Int J Urol Off J Jpn Urol Assoc 20(6):631–636. https://doi.org/10.1111/iju.12015
Darge K, Trusen A, Gordjani N, Riedmiller H (2003) Intrarenal reflux: diagnosis with contrast-enhanced harmonic US. Pediatr Radiol 33(10):729–731. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-003-1050-2
Gotoh T, Asano Y, Nonomura K, Togashi M, Koyanagi T (1991) Intrarenal reflux in children with vesicoureteral reflux. Nihon Hinyokika Gakkai Zasshi 82(9):1480–1486
Cremin BJ (1979) Observations on vesico-ureteric reflux and intrarenal reflux: a review and survey of material. Clin Radiol 30(6):607–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0009-9260(79)80003-3
Ključevšek D, Battelino N, Tomažič M, Kersnik Levart T (2012) A comparison of echo-enhanced voiding urosonography with X-ray voiding cystourethrography in the first year of life. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway: 1992) 101(5):e235–e239. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1651-2227.2011.02588.x
Darge K (2002) Diagnosis of vesicoureteral reflux with ultrasonography. Pediatr Nephrol (Berlin, Germany) 17(1):52–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004670200010
Papadopoulou F, Anthopoulou A, Siomou E, Efremidis S, Tsamboulas C, Darge K (2009) Harmonic voiding urosonography with a second-generation contrast agent for the diagnosis of vesicoureteral reflux. Pediatr Radiol 39(3):239–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-008-1080-x
Kis E, Nyitrai A, Várkonyi I, Máttyus I, Cseprekál O, Reusz G, Szabó A (2010) Voiding urosonography with second-generation contrast agent versus voiding cystourethrography. Pediatr Nephrol (Berlin, Germany) 25(11):2289–2293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-010-1618-7
von Rohden L, Bosse U, Wiemann D (1995) Reflux sonography in children with ultrasound contrast media in comparison to voiding cystourethrography (in German). Paediatr Prax 49:49–58
Darge K, Troeger J (2002) Vesicoureteral reflux grading in contrast-enhanced voiding urosonography. Eur J Radiol 43(2):122–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0720-048x(02)00114-6
Ransley PG (1976) Opacification of the renal parenchyma in obstruction and reflux. Pediatr Radiol 4(4):226–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02461530
Boubnova J, Sergent-Alaoui A, Deschênes G, Audry G (2011) Evolution and prognosis value of intrarenal reflux. J Pediatr Urol 7(6):638–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpurol.2010.09.015
Hellström M, Jacobsson B, Mårild S, Jodal U (1989) Voiding cystourethrography as a predictor of reflux nephropathy in children with urinary-tract infection. AJR Am J Roentgenol 152(4):801–804. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.152.4.801
Rolleston GL, Maling TM, Hodson CJ (1974) Intrarenal reflux andthe scarred kidney. Arch Dis Child 49:531–539
Kim SW, Im YJ, Hong CH, Han SW (2010) The clinical significance of intrarenal reflux in voiding cystourethrography (VCUG). Korean J Urol 51(1):60–63. https://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2010.51.1.60
Rose JS, Glassberg KI, Waterhouse K (1975) Intrarenal reflux and its relationship to renal scarring. J Urol 113(3):400–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-5347(17)59492-6
Kanumakala S, Kalidasan V, Kenney I (2004) Intra-renal reflux. Arch Dis Child 89(7):692. https://doi.org/10.1136/adc.2003.041517
Lebowitz RL (1986) The detection of vesicoureteral reflux in the child. Invest Radiol 21(7):519–531. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004424-198607000-00003
Perisinakis K, Raissaki M, Damilakis J, Stratakis J, Neratzoulakis J, Gourtsoyiannis N (2006) Fluoroscopy-controlled voiding cystourethrography in infants and children: are the radiation risks trivial? Eur Radiol 16(4):846–851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-005-0072-6
Ward VL (2006) Patient dose reduction during voiding cystourethrography. Pediatr Radiol 36(Suppl 2):168–172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-006-0213-3
Ward VL, Barnewolt CE, Strauss KJ, Lebowitz RL, Venkatakrishnan V, Stehr M, McLellan DL, Peters CA, Zurakowski D, Dunning PS, Taylor GA (2006) Radiation exposure reduction during voiding cystourethrography in a pediatric porcine model of vesicoureteral reflux. Radiology 238(1):96–106. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2381041433
Schneider K, Krüger-Stollfuss I, Ernst G, Kohn MM (2001) Paediatric fluoroscopy–a survey of children’s hospitals in Europe. I. Staffing, frequency of fluoroscopic procedures and investigation technique. Pediatr Radiol 31(4):238–246. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002470100429
Darge K (2008) Voiding urosonography with ultrasound contrast agents for the diagnosis of vesicoureteric reflux in children. I. Procedure. Pediatr Radiol 38(1):40–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-007-0529-7
Darge K (2008) Voiding urosonography with US contrast agents for the diagnosis of vesicoureteric reflux in children. II. Comparison with radiological examinations. Pediatr Radiol 38(1):54–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-007-0528-8
Jequier S, Jequier JC (1989) Reliability of voiding cystourethrography to detect reflux. AJR Am J Roentgenol 153(4):807–810. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.153.4.807
Joaquim AI, de Godoy MF, Burdmann EA (2015) Cyclic direct radionuclide cystography in the diagnosis and characterization of vesicoureteral reflux in children and adults. Clin Nucl Med 40(8):627–631. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLU.000000000000079
Papadopoulou F, Tsampoulas C, Siomou E, Tzovara J, Siamopoulou A, Efremidis SC (2006) Cyclic contrast-enhanced harmonic voiding urosonography for the evaluation of reflux. Can we keep the cost of the examination low? Eur Radiol 16(11):2521–2526
Kenda RB, Kenig A, Novljan G, Ponikvar R, Ponikvar JB (2001) Cyclic voiding urosonography for detecting vesicoureteric reflux in renal transplant recipients. Nephrol Dial Transpl 16(11):2229–2231
Novljan G, Kenig A, Rus R, Kenda RB (2003) Cyclic voiding urosonography in detecting vesicoureteral reflux in children. Pediatr Nephrol (Berlin, Germany) 18(10):992–995. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-003-1228-8
Funding
The authors declare that they did not receive any funding for this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AC-R was responsible for data, conceptualized the study, carried out analyses, drafted the initial manuscript, revised, and approved the final manuscript. DT carried out the statiscial analysis and interpretation of data, revised, and approved the final manuscript. DM conceptualized the study, revised and approved the final manuscript. IP collected and revised the data. GR conceptualized and designed the study, carried out the analyses, drafted the initial manuscript and approved the final manuscript as submitted.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This retrospective study has been approved by the Ethics committee of the Helena Clinic for Pediatric Medicine which waved the requirement for informed consent.
Consent to participate
Both parents/guardians and older children were informed in detail of the entire procedure before the examination. They were also provided with a written leaflet describing the whole procedure.
Consent for publication
The authors agree to publish this manuscript in the Journal of Ultrasound.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cvitkovic-Roic, A., Turudic, D., Milosevic, D. et al. Contrast-enhanced voiding urosonography in the diagnosis of intrarenal reflux. J Ultrasound 25, 89–95 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-021-00568-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-021-00568-w