Abstract
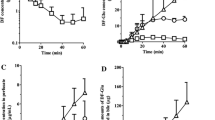
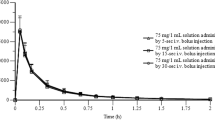
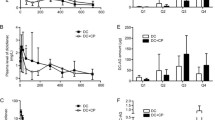
Diclofenac sodium is a widely used drug with interesting absorption and disposition features when administered to laboratory animals. The present study was undertaken to assess the pharmacokinetics of the drug after iv and gastrointestinal dosing to rats. Renal excretion of unchanged drug was negligible, but biliary excretion of the drug (unchanged and conjugated) was detected in bile duct-cannulated rats; it accounted for 27.2 and 31.2% of the total dose following iv and intraduodenal administration, respectively. Most of the drug excreted in the bile was conjugated diclofenac; unchanged drug accounted for only 4.7 and 5.4% of total diclofenac excreted in the bile after iv and intraduodenal dosing, respectively. In normal animals, intestinal absorption of the drug excreted in the bile resulted in higher drug concentrations in plasma than those obtained in bile duct-cannulated rats, but only after 60 min of dosing. When administered directly into the duodenum, diclofenac absorption was extremely fast and the maximum plasma diclofenac concentration was reached within 2 min. After oral dosing, an early peak was also observed, but it was lower than that obtained after intraduodenal dosing: 71% diclofenac hioavailability was found in bile duct-cannulated rats intraduodenally dosed, whereas in normal animals dosed by mouth a bioavailability of 79% was obtained. In normal animals intraduodenally dosed, an apparent bioavailability of 106% was observed. All of these features, particularly the influence of enterohepatic circulation on drug bioavailability, are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Degen, J. W. Faigle, A. Gerardin, J. Moppert, A. Sallmann, K. Schmid, A. Schweizer, M. Sulc, W. Theobald, and J. Wagner. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of the antiinflammatory agent voltaren.Scand. J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 22:17–29 (1978).
H. Stierlin, J. W. Faigle, A. Sallmann, and W. Kung. Biotransformation of diclofenac sodium (Voltaren) in animals and in man. I. Isolation and identification of principal metabolites.Xenobiotica 9:601–610 (1979).
V. A. John. The pharmacokinetics and metabolism of diclofenac sodium (Voltarol) in animals and man.Rheumatol. Rehabil. Suppl. 2:22–37 (1979).
T. Tsuchiya, M. Terakawa, K. Ishibasho, H. Noguchi, and R. Kato. Disposition and enterohepatic circulation of diclofenac in dogs.Arzneim. Forsch. Drug Res. 30:1650–1653 (1980).
P. D. Fowler. Voltarol: diclofenac sodium.Clin. Rheumat. Dis. 5:427–464 (1979).
J. V. Willis, M. J. Kendall, R. M. Flinn, D. P. Thornhill, and P. G. Welling. The pharmacokinetics of diclofenac sodium following intravenous and oral administration.Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 16:405–410 (1979).
J. V. Willis, M. J. Kendall, and D. B. Jack. A study of the effect of aspirin on the pharmacokinetics of oral and intravenous diclofenac sodium.Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 18:415–418 (1980).
S. Yamashita, H. Saitoh, K. Nakanishi, M. Masada, T. Nadai, and T. Kimura. Effects of diclofenac sodium and disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetate on electrical parameters of the mucosal membrane and their relation to the permeability enhancing effects in the rat jejunum.J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 39:621–626 (1987).
U. P. Geiger, P. H. Degen, and A. Sioufi. Quantitative assay of diclofenac in biological material by gas-liquid chromatography.J. Chromatogr. 111:293–298 (1975).
J. G. Wagner. Pharmacokinetic absorption plots from oral data alone or oral/intravenous data and an exact Loo-Riegelman equation.J. Pharm. Sci. 72:838–842 (1983).
D. P. Vaughan and M. Dennis. Mathematical basis of point-area deconvolution method for determining “in vivo” input functions.J. Pharm. Sci. 67:663–665 (1978).
A. Martin-Villodre, J. M. Plá-Delfina, J. Moreno, D. Pérez-Buendía, J. Miralles, E. F. Collado, E. Sánchez-Moyano, and A. del Pozo. Studies on the reliability of a bihyperbolic functional absorption model. I. Ring-substituted anilines.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 14:615–633 (1986).
V. G. Casabó, E. Núñez-Benito, A. Martinez-Coscollá, E. Miralles-Loyola, A. Martín-Villodre, and J. M. Plá-Delfina. Studies on the reliability of a bihyperbolic functional absorption model. II. Phenylalkylamines.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 15:633–643 (1987).
E. F. Collado, S. Fabra-Campos, J. E. Peris-Ribera, V. G. Casabó, A. Martín-Villodre, and J. M. Plá-Delfina.Int. J. Pharm. 44:187–196 (1988).
F. L. S. Tse, F. Ballard, and J. Skinn. Estimating the fraction reabsorbed in drugs undergoing enterohepatic circulation.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 10:455–461 (1982).
K. Yamaoka, M. Kanba, Y. Toyoda, Y. Yano, and T. Nakagawa. Analysis of enterohepatic circulation of ceflxime in rat by fast inverse Laplace Transform (FILT).J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 18:545–559 (1990).
T. A. Shepard and R. H. Reuning. An equation for the systemic availability of drugs undergoing simultaneous enterohepatic cycling, first-pass metabolism, and intestinal elimination.Pharm. Res. 4:195–199 (1987).
T. A. Shepard, R. H. Reuning, and L. J. Aarons. Interpretation of area under the curve measurements for drugs subject to enterohepatic cycling.J. Pharm. Sci. 74:227–228 (1985).
K. S. Pang and J. R. Gillette. A theoretical examination of the effects of gut wall metabolism, hepatic elimination, and enterohepatic recycling on estimates of bioavailability and of hepatic blood flow.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 6:355–367 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The present work is part of a research project developed with a grant for the “Plan Nacional de I + D (FAR 90-0092)” of the Ministry of Industry and Energy of Spain.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peris-Ribera, JE., Torres-Molina, F., Garcia-Carbonell, M.C. et al. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of diclofenac in the rat. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 19, 647–665 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01080872
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01080872