Abstract
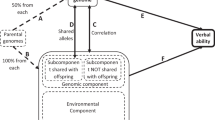
A multivariate path model of genetic and environmental transmission was fitted to specific cognitive abilities data (verbal, spatial, perceptual speed, and visual memory) and evaluated using a maximum-likelihood estimation procedure. In this first multivariate behavioral genetic analysis of adoption data, cultural transmission was modeled via parental phenotypes, each parental phenotype being allowed to affect all traits in the offspring, and assortative mating and cross-assortative mating were accommodated. Results of a preliminary analysis indicated that selective placement is absent in this study. When the full model was fitted to the data, it was found that assortative mating is more important than cross-assortative mating but is substantial only for verbal ability. Genetic transmission parameters are modest in size, whereas cultural transmission is both small and nonsignificant. A simplified model in which cultural transmission and genotype-environment correlation are constrained to be zero provided a good fit to the data. Analyses of the structures of genetic and environmental correlation matrices indicated a strong genetic general factor and a similar, but weaker, environmental factor. Inspection of the genetic transmission parameters suggests that genetic continuity between early childhood and adulthood may be substantial for verbal ability, spatial ability, and perceptual speed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bock, R. D., and Vandenberg, S. G. (1968). Components of heritable variation in mental test scores. In Vandenberg, S. G. (ed.),Progress in Human Behavior Genetics, Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, pp. 233–260.
CERN (1977).MINUIT: A System for Function Minimization and Analysis of Parameter Errors and Correlations, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland.
DeFries, J. C., and Fulker, D. W. (1986). Multivariate behavioral genetics and development.Behav. Genet. 16:1–10.
DeFries, J. C., Johnson, R. C., Kuse, A. R., McClearn, G. E., Polovina, J., Vandenberg, S. G., and Wilson, J. R. (1979). Familial resemblance for specific cognitive abilities.Behav. Genet. 9:23–43.
DeFries, J. C., Plomin, R., Vandenberg, S. G., and Kuse, A. R. (1981). Parent-offspring resemblance for cognitive abilities in the Colorado Adoption Project: Biological, adoptive, and control parents and one-year-old children.Intelligence 5:245–277.
Eaves, L. J., and Gale, J. S. (1974). A method for analyzing the genetic basis of covariation.Behav. Genet. 4:253–267.
Eaves, L. J., Long, J., and Heath, A. C. (1986). A theory of developmental change in quantitative phenotypes applied to cognitive development.Behav. Genet. 16:143–162.
Fulker, D. W., and DeFries, J. C. (1983). Genetic and environmental transmission in the Colorado Adoption Project: Path analysis.Br. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 36:175–188.
Fulker, D. W., Baker, L. A., and Bock, R. D. (1983). Estimating components of covariance using LISREL.Data Anal. 1(3):5–8.
Heath, A. C., and Eaves, L. J. (1985). Resolving the effects of phenotypic and social background on mate selection.Behav. Genet. 15:15–30.
Martin, N. G., and Eaves, L. J. (1977). The genetical analysis of covariance structure.Heredity 38:79–95.
Plomin, R., (1986). Multivariate analysis and developmental behavioral genetics: Developmental change as well as continuity.Behav. Genet. 16:25–43.
Plomin, R., and DeFries, J. C. (1980). Genetics and intelligence: Recent data.Intelligence 4:15–24.
Plomin, R., and DeFries, J. C. (1985).Origins of Individual Differences in Infancy: The Colorado Adoption Project, Academic Press, Orlando, Fla.
Plomin, R., DeFries, J. C., and Loehlin, J. C. (1977). Genotype-environment interaction and correlation in the analysis of human behavior.Psychol. Bull. 84:309–322.
Rice, T., Corley, R., Fulker, D. W., and Plomin, R. (1985). The development and validation of a test battery measuring specific cognitive abilities in four-year-old children.Educ. Psychol. Measure. (in press).
Singer, S., Corley, R., Guiffrida, C., and Plomin, R. (1984). The development and validation of a test battery to measure differentiated cognitive abilities in three-year-old children.Educ. Psychol. Measure. 44:703–713.
Vandenberg, S. G. (1965) Multivariate analysis of twin differences. In Vandenberg, S. G. (ed.),Methods and Goals in Human Behavior Genetics, Academic Press, New York, pp. 29–43.
Vogler, G. (1985). Multivariate path analysis of familial resemblance.Genet. Epidemiol. 2:35–53.
Vogler, G., and DeFries, J. C. (1986). Multivariate path analysis of cognitive abilities in reading-disabled and control nuclear families and twins.Behav. Genet. 16:89–106.
Wilson, R. S. (1983). The Louisville Twin Study: Developmental synchronies in behavior.Child Dev. 54:298–316.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported in part by grants from the NSF (BNS-7826204 and BNS-8200310) and from the NICHD (HD-10333).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rice, T., Fulker, D.W. & DeFries, J.C. Multivariate path analysis of specific cognitive abilities in the colorado adoption project. Behav Genet 16, 107–125 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01065482
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01065482