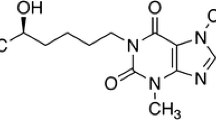
Abstract
A blood flow rate-limited pharmacokinetic model was developed to study the effect of sulfonamide on the plasma elimination and tissue distribution of14C -tolbutamide (TB) in rats. The sulfonamides (SA) used were sulfaphenazole (SP), sulfadimethoxine (SDM), and sulfamethoxazole (SMZ). The tissue-to-plasma partition coefficients (Kp) of all tissues studied, i.e., lung, liver, heart, kidney, spleen, G.I. tract, pancreas, brain, muscle, adipose tissue, and skin, increased in the presence of SA, but except for brain, liver, and spleen, the tissue-to-plasma unbound concentration ratio (Kp, f) of other tissues did not show a significant alteration. This suggested that the tissue binding of TB is not affected by SA and that the increase of Kp is due mainly to the displacement of plasma protein-bound TB by SA. The concentrations of TB in several tissues and plasma were predicted by a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model using in vitro plasma binding and metabolic parameters, the plasma-to-blood concentration ratio and the tissue-to-plasma unbound concentration ratios having been determined from both the tissue and plasma concentrations of TB at the β-phase after intravenous administration of TB and the plasma free fraction. The predicted concentration curves of TB in each tissue and in plasma showed good agreement with the observed values except for the brain, for which the predicted concentrations were lower than the observed values in the early time period. In the SP- and SDM-treated rats, the predicted free concentration of TB in the target organ, the pancreas, at 6 h was six times higher than that of the control rats. From these findings, it is suggested that physiologically based pharmacokinetic analysis could be generally useful to predict approximate plasma and tissue concentrations of a drug in the presence of drug-drug interaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- V :
-
volume of tissue, ml
- Q :
-
blood flow rate through tissue, ml/min
- C :
-
tissue or blood concentration of tolbutamide, μg/ml
- Kp :
-
tissue-to-plasma partition coefficient of tolbutamide
- Kp B :
-
tissue-to-blood partition coefficient of tolbutamide
- Kp,f :
-
tissue-to-plasma unbound concentration ratio of tolbutamide
- S :
-
plasma-to-blood concentration ratio of tolbutamide
- f p :
-
plasma free fraction of tolbutamide
- n :
-
number of binding site
- (p):
-
concentration of plasma protein, mM
- K d :
-
dissociation constant of plasma protein binding, mM
- v :
-
oxidative metabolic rate of tolbutamide, μmol tolbutamide metabolized/min/12.4 g of liver
- V max :
-
maximum velocity, μmol tolbutamide metabolized/min/12.4 g of liver
- K m :
-
Michaelis constant, mM
- λ :
-
reciprocal of the injection time, min/s-1
- B :
-
blood
- P :
-
plasma
- Li :
-
liver
- K :
-
kidney
- G.I. :
-
gastrointestinal tract
- Lu :
-
lung
- H :
-
heart
- M :
-
muscle
- Br :
-
brain
- Pa :
-
pancreas
- Sp :
-
spleen
- Ad :
-
adipose
- Sk :
-
skin
- Ar :
-
arterial blood
- Ve :
-
venous blood
References
R. L. Dedrick and K. B. Bischoff. Pharmacokinetics in application of the artificial kidney.Chem. Eng. Prog. Symp. Ser. 64:32–44 (1968).
H. S. G. Chen and J. F. Gross. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic models for anticancer drugs (general review).Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2:85–94 (1979).
K. J. Himmelstein and R. J. Lutz. A review of the application of physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 7:127–145 (1979).
N. Benowitz, R. P. Forsyth, K. L. Melmon, and M. Rowland. Lidocaine disposition kinetics in monkey and man I. Prediction by a perfusion model.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 16:87–98 (1974).
N. Benowitz, R. P. Forsyth, K. L. Melmon, and M. Rowland. Lidocaine disposition kinetics in monkey and man II. Effects of hemorrhage and sympathomimetic drug administration.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 16:99–109 (1974).
L. I. Harrison and M. Gibaldi. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic model for digoxin disposition in dogs and its preliminary application to humans.J. Pharm. Sci. 66:1679–1683 (1977).
K. B. Bischoff and R. L. Dedrick. Thiopental pharmacokinetics.J. Pharm. Sci. 57:1346–1351 (1968).
K. B. Bischoff, R. L. Dedrick, D. S. Zaharko, and J. A. Longstreth. Methotrexate pharmacokinetics.J. Pharm. Sci. 60:1128–1133 (1971).
R. L. Dedrick, D. D. Forrester, J. N. Cannon, S. M. E. Dareer, and L. B. Mellett. Pharmacokinetics of 1-β-arabinofuranosylcytosine (ARA-C) deamination in several species.Biochem. Pharmacol. 22:2405–2417 (1973).
B. Montadon, R. J. Roberts, and L. J. Fischer. Computer simulation of sulfobromophthalein kinetics in the rat using flow-limited models with extrapolation to man.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 3:277–290 (1975).
P. A. Harris and J. F. Gross. Preliminary pharmacokinetic model for adriamycin (NSC-123127).Cancer Chemother. Rep. Part I,59:819–825 (1975).
L. I. Harrison and M. Gibaldi. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic model for digoxin distribution and elimination in the rat.J. Pharm. Sci. 66:1138–1142 (1977).
R. H. Smith, D. H. Hunt, A. B. Seifen, A. Ferrari, and D. S. Thompson. Pharmacokinetic model for procaine in humans during and following intravenous infusion.J. Pharm. Sci. 68:1016–1024 (1979).
R. H. Luecke and W. D. Wosilait. Drug elimination interactions: analysis using a mathematical model.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 7:629–641 (1979).
E. Schulz and F. H. Schmidt. Abbauhemmung von tolbutamid durch sulfaphenazol beim menschen.Pharmacol. Clin. 2:150–154 (1970).
M. Kristensen and L. K. Christensen. Drug induced changes of the blood glucose lowering effect of oral hypoglycemic agents. In C. A. Loubatieres and A. E. Rengold (eds.),Pharmacology and Mode of Oral Hypoglycemic Agents, Vol. VI. Casea Editrice “Li Ponte”, Milano, 1969 pp. 116–136.
M. Rowland and S. B. Matin. Kinetics of drug-drug interactions.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 1:553–567 (1973).
S. M. Pond, D. J. Birkett, and D. N. Wade. Mechanisms of inhibition of tolbutamide metabolism: phenylbutazone, oxyphenbutazone, sulfaphenazole.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 22:573–579 (1977).
J. Shibasaki, R. Konishi, and K. Yamasaki. Tolbutamide-sulfaphenazole interaction in rabbits.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 5:277–290 (1977).
J. J. Thiessen and M. Rowland. Kinetics of drug-drug interactions in sheep; tolbutamide and sulfadimethoxine.66:1063–1070 (1977).
Y. J. Lin, S. Awazu, and M. Hanano. Inhibitory mechanism of sulfaphenazole on tolbutamide elimination from plasma in rats.J. Pharm. Dyn. 2:273–285 (1979).
O. Sugita, Y. Sawada, Y. Sugiyama, T. Iga, and M. Hanano. Prediction of drug-drug interaction fromin vitro plasma protein binding and metabolism. A study of tolbutamide-sulfonamides interaction in rats.Biochem. Pharmacol. 30:3347–3354 (1981).
M. Hanano. Library program (D2/TC/RKM) of the University of Tokyo Computer Center, Tokyo, Japan (1980).
R. L. Dedrick. Animal scale-up.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 1:435–461 (1973).
Y. Sasaki and H. N. Wagner. Measurement of the distribution of cardiac output in unanesthetized rats.J. Appl. Physiol. 30:879–884 (1971).
R. L. Dedrick, D. S. Zaharko, and R. J. Lutz. Transport and binding of methotrexatein vivo. J. Pharm. Sci. 62:882–890 (1973).
R. J. Lutz, R. L. Dedrick, H. B. Matthews, T. E. Eling, and M. W. Anderson. A preliminary pharmacokinetic model for several chlorinated biphenyls in the rat.Drug Metab. Dispos. 5:386–396 (1977).
H. S. G. Chen and J. F. Gross. Estimation of tissue-to-plasma partition coefficients used in physiological pharmacokinetic models.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 7:117–125 (1979).
J. R. Gillette. InHandbook of Experimental Pharmacology, Vol. 28, Concepts in Biochemical Pharmacology, Part 3. chap. 60, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1975, Chap. 60, pp. 35–85.
H. Y. Yu, Y. Sawada, Y. Sugiyama, T. Iga, and M. Hanano. Effect of sulfadimethoxine on thiopental distribution and elimination in rats.J. Pharm. Sci. 70:323–326 (1981).
B. Fichtl, H. Kurz, I. Wachter, and A., Ziegler. Binding of drugs to muscle tissue: drug interactions.Naunyn-Schmideberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 302:R2 (1978).
W. M. Wardell. Drug displacement from protein binding: source of the sulphadoxine liberated by phenylbutazone.Br. J. Pharmacol. 43:325–334 (1971).
A. Roos and W. F. Boron. Intracellular pH.Physiol. Rev. 61:296–434 (1981).
R. Spector and A. V. Lorenzo. The effects of salicylate and probenecid on the cerebrospinal fluid transport of penicillin, aminosalicyclic acid and iodide.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 183:55–65 (1974).
J. Sehlin. Evidence of specific binding of tolbutamide of the plasma of pancreatic β-cells.Acta Disbetol. Lat. 10:1052–1060 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by a grant-in-aid for Scientific Research provided by the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture of Japan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sugita, O., Sawada, Y., Sugiyama, Y. et al. Physiologically based pharmacokinetics of drug-drug interaction: A study of tolbutamide-sulfonamide interaction in rats. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 10, 297–316 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01059263
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01059263