Abstract
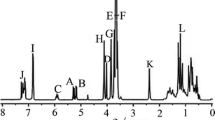
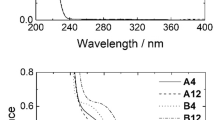
Original associating systems have been obtained by mixing hydrophobically end-capped polyethylene oxide and water soluble β-cyclodextrin polymers in aqueous solutions. The hydrophobic ends of the PEO polymers, naphtyl and adamantyl groups, have been chosen in order to match the β-cyclodextrin cavities. Inclusion complex formation between the PEO terminal groups and β-cyclodextrin are at the origin of polymolecular associations. Complexation constants have been determined by fluorescence methods, using a fluorescent probe 1-8 ANS as a competitor for complexation against the adamantyl groups or directly checking the fluorescence of the naphtytl groups by fluorescence anisotropy measurements. The onsets of the polymolecular associations have been monitored by viscosimetry.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Glass, J. E., Polymers in Aqueous Media: performance through associations, Advances in Chemistry Series 223, (American Chemical Society, Washington DC, 1989).
Renard, E., Deratani, A., Sebille, B., Preparation and characterization of water soluble high molecular weight β-cyclodextrin - epichloridrin polymers,European Polymer Journal, in press.
Amiel, C., Sandier, A., Sebille, B., Valat, P., Wintgens, V., Associations between hydrophobically end-capped polyethylene oxide and water soluble β-cyclodextrin polymers,Int. J. Polymer Analysis & Characterization,1, 289–300 (1995).
Lakowitcz, J. R., Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy, Plenum Press, New York (1983).
Nakashima, K., Anzai, T., Fujimoto, Y.,Langmuir,10, 658 (1994).
Park, J. W., Song, H. J.,J. Phys. Chem.,93, 6454–6458 (1989).
Catena, G. C., Bright, F. V.,Analytical Chemistry,61, 905–909 (1989).
Pitchumani, K., Vellayappan, M., Complex formation of nitrobenzoic acids and some naphtalene derivatives with β-cyclodextrin,Journal of Inclusion Phenomena and Molecular Recognition in Chemistry,14 157–162 (1992).
Annable, T., Buscall, R., Ettelaie, R., Whittlestone, D., The rheology of solutions of associating polymers: comparison of experimental behavior with transient network theory, J. Rheol.,37, 695–726 (1993).
Ekberg, B., Sellergren, B., Olsson, L., Mosbach, K.,Carbohydrate Polymers,10, 183 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amiel, C., Sebille, B. New associating polymer systems involving water soluble β-cyclodextrin polymers. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 25, 61–67 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01041537
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01041537