Abstract
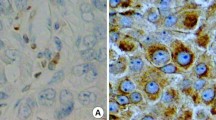
Bcl-2 and Bax proteins are coded by a family of genes that take part in the manteinance of the balance between cell proliferation rate and programmed cell death in multicellular organisms. TheBax gene acts as promoter of cell death by opposing the death protector effect of theBcl-2 gene. Expression of the Bcl-2 and Bax proteins has been investigated in 58 cases of duct carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and duct invasive and invasive lobular carcinomas (IC) of the breast. While both proteins were expressed at the same time in normal and benign epithelium, different staining patterns were observed according to the degree of differentiation of the neoplastic epithelium. In well-differentiated DCIS and grade I IC there was a predominance of Bcl-2 protein staining. Grade II lesions co-expressed both proteins. Poorly differentiated DCIS displayed a predominantly Bax protein staining pattern. Therefore, it appears that Bax protein expression, especially in DCIS, relates to more aggressive neoplasms while Bcl-2 protein expression is associated with less aggressive malignant lesions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bargou RC, Daniel PT, Mapara MY, Bommert K, Wagener C, Kallinich B, Royer HD, Dorken B (1995) Expression of thebcl-2 gene family in normal and malignant breast tissue:low bax-alfa expression in tumour cells correlates with resistance towards apoptosis. Int J Cancer 60:854–859
Barinaga M (1994) Cell suicide: by ICE, not fire. Science 263:754–756
Bhargava V, Kell DL, Van de Rijn M, Warnke RA (1994) Bcl-2 immunoreactivity in breast carcinoma correlates with hormone receptor positivity. Am J Pathol 145:535–540
Bobrow LG, Happerfield LC, Gregory WM, Springall RD, Millis RR (1994) The classification of ductal carcinoma in situ and its association with biological markers. Semin Diagn Pathol 11:199–207
Cerroni L, Soyer HP, Kerl H (1995) Bcl-2 protein expression in cutaneous malignant melanoma and benign melanocytic nevi. Am J Dermatopathol 17:7–11
Colombel M, Symmans F, Gil S, O'Toole KM, Chopin D, Benson M, Olsson CA, Korsmeyer S, Buttyan R (1993) Detection of the apoptotis-suppressing oncoprotein bcl-2 in hormone-refractory human prostate cancers. Am J Pathol 143:390–400
Doglioni C, Dei Tos AP, Laurino L, Chiarelli C, Barbareschi M, Viale G (1994) The prevalence of Bcl-2 immunoreactivity in breast carcinomas and its clinicopathological correlates, with particular reference to estrogen receptor status. Virchows Arch 424:47–51
Elston CW, Ellis IO (1991) Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology 19:403–410
Eusebi V, Feudale E, Foschim MP, Micheli A, Conti A, Riva C, Di Palma S, Rilke F (1994) Long-term follow-up of in situ carcinoma of the breast. Semin Diagn Pathol 11:223–235
Gee JMW, Robertson JFR, Ellis IO, Willsher P, McClelland RA, Hoyle HB, Kyme SR, Finlay P, Blarney RW, Nicholson RI (1994) Immunocytochemical localization of bel-2 protein in human breast cancers and its relationship to a series of prognostic markers and response to endocrine therapy. Int J Cancer 59:619–628
Hockenbery DM, Zutter M, Hickey W, Nahm M, Korsmeyer SJ (1991) Bcl-2 protein is topographically restricted in tissues characterized by apoptotic cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:6961–6965
Holland R, Peterse JL, Millis RR, Eusebi V, Faverly D, Van de Vijver MJ, Zafrani B (1994) Ductal carcinoma in situ: a proposal for a new classification. Semin Diagn Pathol 11:167–180
Hurlimann J, Larrinaga B, Vala DLM (1995) Bcl-2 protein in invasive ductal breast carcinomas. Virchows Arch 426:163–168
Joensuu H, Pylkkanen L, Toikkanen S (1994) Bcl-2 protein expression and long-term survival in breast cancer. Am J Pathol 145:1191–1198
Krajewski S, Krajewska M, Shabaik A, Miyashita T, Wang HG, Reed JC (1994) Immunohistochemical determination of in vivo distribution of Bax, a dominant inhibitor of Bcl-2. Am J Pathol 145:1323–1336
Krajewski S, Blomqvist C, Franssila K, Krajewska M, Wasenius VM, Niskanen E, Nordling S, Reed JC (1995) Reduced expression of proapoptotic gene BAX is associated with poor response rates to combination chemotherapy and shorter survival in women with metastatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res 55:4471–4478
Leek RD, Kaklamanis L, Pezzella F, Gatter KC, Harris AL (1994) Bcl-2 in normal human breast and carcinoma, association with oestrogen receptor-positive, epidermal growth factor receptor-negative tumours and in situ cancer. Br J Cancer 6:135–139
Lu QL, Abel P, Foster CS, Lalani EN (1996) Bcl-2: role in epithelial differentiation and oncogenesis. Hum Pathol 27:102–110
Manetto V, Lorenzini R, Cordon-Cardo C, Krajewski S, Rosai J, Reed JC, Eusebi V (1996) Relationship of Bel-2 and Bax expression with differentiation in thyroid tumors: an immunohistochemical and western blot analysis. Virchows Arch (in press)
Miyashita T, Reed JC (1995) Tumor suppressor p53 is a direct transcriptional activator of the human bax gene. Cell 80:293–299
Nathan B, Anbazhagan R, Clarkson P, Bartkova J, Gusterson B (1994) Expression of Bcl-2 in the developing human fetal and infant breast. Histopathology 24:73–76
Ngan BY, Chen-Levy Z, Weiss LM, Warnke RA, Cleary ML (1988) Expression in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of the bcl-2 protein associated with the t(14;18) chromosomal translocation. N Engl J Med 318:1638–1644
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL, Korsmeyer SJ (1993) Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell 74:609–619
Pezzella F, Gatter K (1995) What is the value of bcl-2 protein detection for histopathologists? Histopathology 26:89–93
Pezzella F, Tse AGD, Cordell JL, Pulford KAF, Gatter KC, Mason DY (1990) Expression of the bcl-2 oncogene protein is not specific for the 14;18 chromosomal translocation. Am J Pathol 137:225–232
Pezzella F, Morrison H, Jones M, Gatter KC, Lane D, Harris AL, Mason DY (1993) Immunohistochemical detection of p53 and bcl-2 in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Histopathology 22:39–44
Pezzella F, Turley H, Kuzu I, Tungekar MF, Dunnill MS, Pierce CB, Harris A, Gatter KC, Mason DY (1993) Bcl-2 protein in non-small-cell lung carcinoma. N Engl J Med 329:690–694
Sabourin JC, Martin A, Baruch J, True JB, Gompel A, Poitout P (1994) Bcl-2 expression in normal breast tissue during the menstrual cycle. Int J Cancer 59:1–6
Silvestrini R, VeneroniS, Daidone MG, Benim E, Boracchi P, Mezzetti M, Di Fronzo G, Rilke F, Veronesi U (1994) The Bcl-2 protein: a prognostic indicator strongly related to p53 protein in lymph node-negative breast cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst 86:499–504
Siriaunkgul S, Tavassoli FA (1993) Invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast. Mod Pathol 6:660–662
Siziopikou KP, Prioleau J, Schnitt S (1996) MIB-1 proliferation index (PI) in ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS): relationship to bcl-2 and p53 protein. Lab Invest 126:25A
Takayama S, Sato T, Krajewski S, Kochel K, Irie S, Millan JA, Reed JC (1995) Cloning and functional analysis of Bag-1: a novel Bcl-2-binding protein with anti-cell death activity. Cell 80:279–284
Vaux DL (1993) Toward an understanding of the molecular mechanisms of physiological cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:786–789
Yang E, Zha J, Jockel J, Boise LH, Thompson CB, Korsmeyer SJ (1995) Bad, a heterodimeric partner for Bcl-xL and Bcl-2, displaces Bax and promotes cell death. Cell 80:285–291
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kapucuoglu, N., Losi, L. & Eusebi, V. Immunohistochemical localization of Bcl-2 and Bax proteins in in situ and invasive duct breast carcinomas. Virchows Archiv 430, 17–22 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01008011
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01008011