Summary
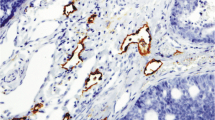
Pseudocysts are unique structures found in adenoid cystic carcinomata of human salivary glands. They were studied in 13 such cases by histochemical and immunohistochemical means. The pseudocysts contained an abundance of mucoid materials which reacted strongly with both Alcian Blue and dialysed iron ferrocyanide. The mucoid material was digested with chondroitinase ABC and heparitinase, but was resistant toStreptomyces hyaluronidase. The inner surfaces of the pseudocysts were strongly reactive for laminin, whereas the interface between the tumour cell nests and the outer stromal area was intensely reactive for fibronectin. Numerous fibronectin-reactive fibrils and blood coagulation factor XIII (F-XIII)-positive cells were distributed extensively in the outer stromal area. The F-XIII-positive cells were also found within some pseudocysts. The results obtained in the present study have shown that the pseudocysts represent a peculiar structure consisting of basement membrane components; laminin, fibronectin, heparan sulphate and chondroitin sulphate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrechtsen, R., Nielsen, M., Wewer, U., Engvall, E. &Ruoslahti, E. (1981). Basement membrane changes in breast cancer detected by immunohistochemical staining for laminin.Cancer Res. 41, 5076–81.
Anderson, W. (1968) InBoyd's Pathology for the Surgeon, 8th edn, pp. 144–69. Philadelphia, London, W. B. Saunders.
Azzopardi, J. G. &Smith, O. D. (1959) Salivary gland tumours and their mucins.J. Path. Bact 77, 131–40.
Bloom, G. D., Carlsöö, B., Gustafsson, H. &Henriksson, R. (1977) Distribution of mucosubstances in adenoid cystic carcinoma. A light and electron microscopic study.Virchows Arch. path. Anat. 375, 1–12.
Burns, J., Dixon, A. J. &Woods, J. C. (1980). Immunoperoxidase localisation of fibronectin in glomeruli of formalin fixed paraffin processed renal tissue.Histochemistry 67, 73–8.
Chen, S. Y. (1976) Adenoid cystic carcinoma of minor salivary gland. Histochemical and electron microscopic studies of cystlike spaces.Oral Surg. 42, 606–19.
Chomette, G., Auriol, M., Tranbaloc, P. &Vaillant, J. M. (1982). Adenoid cystic carcinoma of minor salivary glands. Analysis of 86 cases. Clinico-pathological, histoenzymological and ultrastructural studies.Virchows Arch. path. Anat 395, 289–301.
Cohn, R. H., Banerje, S. D. &Bernfield, M. R. (1977) Basal lamina of embryonic salivary epithelia. Nature of glycosaminoglycan and organization of extracellular materials.J. Cell Biol. 73, 464–78.
Filipe, M. I. &Lake, B. D. (1983) Immunohistochemical methods. InHistochemistry in Pathology (edited byFilipe, M. I. &Lake, B. D.), pp. 333–8 Edinburgh, London, Melbourne, New York: Churchill Livingstone.
Gusterson, B. A., Lucas, R. B., &Ormerod, M. G. (1982) Distribution of epithelial membrane antigen in benign and malignant lesions of the salivary glands.Virchows Arch. path. Anat. 397, 227–33.
Harrison, J. D. (1974) Cystic adenoma of a minor salivary gland: A histochemical, study.J. Path. 114, 29–38.
Holborow, E. J. (1983) The value of immunohistochemistry in diagnosis. InHistochemistry in Pathology (edited byFilipe, M. I. &Lake, B. D.), pp. 26–33. Edinburgh, London, Melbourne, New York: Churchill Livingstone.
Hoshino, M. &Yamamoto, I. (1970) Ultrastructure of adenoid cystic carcinoma.Cancer 25, 186–98.
Iwabuchi, S. (1983) Hepatic fibrosis and coagulation factor XIII.Jap. J. Gastroenterol. 80, 2229–39.
Keski-Oja, J., Mosher, D. F. &Vaheri, A. (1976) Cross-linking of a major fibroblast surface-associated glycoprotein (fibronectin) catalyzed by blood coagulation factor XIII.Cell. 9, 29–35.
Laurie, G. W., Leblond, C. P. &Martin, G. R. (1982) Localization of type IV collagen, laminin, heparan sulfate proteoglycan, and fibronectin to the basal lamina of basement membranes.J. Cell Biol. 95, 340–4.
Lillie, R. D. &Fullmer, H. M. (1976)Histopathologic Technic and Practical Histochemistry 4th edn, pp. 25–68, New York: McGraw-Hill.
Linker, A. &Hovingh, P. (1972) Heparinase and heparitinase from flavobacteria.Meth. Enzym. 28, 902–11.
McManus, J. F. A. (1946) Histological demonstration of mucin after periodic acid.Nature, Lond. 158, 202.
Mepham, B. L., Frater, W. &Mitchell, B. S. (1979) The use of proteolytic enzymes to improve immunoglobulin staining by the PAP technique.Histochem. J. 11, 345–57.
Mosher, D. F. (1976) Cross-linking of cold-insoluble globulin by fibrin-stabilizing factor.J. biol. Chem. 250, 6614–21.
Mosher, D. F., Schad, P. E. &Kleinman, H. K. (1979). Cross-linking of fibronectin to collagen by blood coagulation factor XIIIa.J. clin. Invest. 64, 781–7.
Mosher, D. F., Schad, P. E. &Vann, J. M. (1980) Cross-linking of collagen and fibronectin by factor XIIIa. Localization of participating glutaminyl residues to a tryptic fragment of fibronectin.J. biol. Chem. 255, 1181–8.
Mowry, R. W. (1960) Revised method producing improved coloration of acidic polysaccharides with alcian blue 8GX supplied currently.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 8, 323–4.
Mowry, R. W. (1963) The special value of methods that color both acidic and vicinal hydroxyl groups in the histochemical study of mucins. With revised directions for the colloidal iron stain, the use of alcian blue 8GX and their combinations with the periodic acid-Schiff reaction.Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 106, 402–23.
Sainte-Marie, G. (1962) A paraffin embedding technique for studies employing immunofluorescence.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 10, 250–6.
Sternberger, L. A. (1979)Immunocytochemistry, 2nd edn, pp. 96–9 and 122–9. New York: John Wiley.
Takeuchi, J., Sobue, M., Katoh, Y., Esaki, T., Yoshida, M. &Miura, K. (1976) Morphologic and biologic characteristics of adenoid cystic carcinoma cells of the salivary gland.Cancer 38, 2349–56.
Takeuchi, J., Sobue, M., Yoshida, M., Esaki, T. &Katoh, Y. (1975) Pleomorphic adenoma of the salivary gland with special references to histochemical and electron microscopic studies and biochemical analysis of glycosaminoglycansin vivo andin vitro Cancer 36, 1771–84.
Takeuchi, J., Sobue, M., Yoshida, M. &Sato, E. (1978) Glycosaminoglycan-synthetic activity of pleomorphic adenoma, adenoid cystic carcinoma and nonneoplastic tubuloacinar cells of the salivary gland.Cancer 42, 202–8.
Tandler, B. (1971) Ultrastructure of adenoid cystic carcimoma of salivary gland originLab. Invest. 24, 504–12.
Thackray, A. C. &Lucas, R. B. (1960) The histology of cylindroma of mucous gland origin.Br. J. Cancer 14, 612–20.
Timpl, R. &Martin, G. R. (1982) Components of basement membranes. InImmunochemistry of the Extracellular Matrix, Vol. 2 (edited byFurthmayr, H.), pp. 119–50. Boca Raton, Florida: Chemical Rubber Company Press.
Toida, M., Takeuchi, J., Hara, K., Sobue, M., Tsukidate, K., Goto, K. &Nakashima, N. (1984) Histochemical studies of intercellular components of salivary gland tumors with special reference to glycosaminoglycan, laminin and vascular elements.Virchows Arch. path. Anat. 403, 15–26.
Trelstad, R. L., Hayashi, K. &Toole, B. P. (1974) Epithelial collagens and glycosaminoglycans in the embryonic cornea. Macromolecular order and morphogenesis in the basement membrane.J. Cell. Biol. 62, 815–30.
Yamada, K. (1973) The effect, of digestion withStreptomyces hyaluronidase upon certain histochemical reactions of hyaluronic acid-containing tissues.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 21, 794–803.
Yamada, K. (1974) The effect of digestion with chondroitinase upon, certain histochemical reactions of mucosaccharide-containing tissues.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 22, 266–75.
Yamada, K., Fujita, Y. &Shimizu, S. (1982) The effect of digestion with keratanase (Pseudomonas sp.) on certain histochemical reactions for glycosaminoglycans in cartilaginous and corneal tissues.Histochem. J. 14, 897–910.
Yamada, K. &Hirano, K. (1973) The histochemistry of hyaluronic acid-containing mucosubstances.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 21, 469–72.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toida, M., Takeuchi, J., Sobue, M. et al. Histochemical studies on pseudocysts in adenoid cystic carcinoma of the human salivary gland. Histochem J 17, 913–924 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01004186
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01004186