Summary
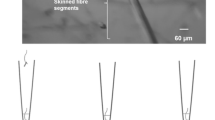
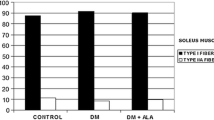
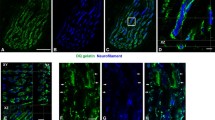
The activity of four lysosomal proteases in soleus and extensor digitorum longus muscles was studied in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats using newly developed fluorescence histochemical and biochemical techniques. The results indicate that the content of lysosomal protease in skeletal muscle cells was decreased three weeks after the induction of diabetes. The reduction was most pronounced in the extensor digitorum longus for all the proteases tested, but in the soleus only cathepsin B and dipeptidyl peptidase II showed a decrease. Biochemical assays on total muscle homogenates and muscle extracts confirmed the histochemical observations that protease activity was significantly lower in diabetic muscles. This decrease in activity varied with the duration of diabetes beginning as early as 48 h for the soleus. In conclusion, myofibre-specific decreases in lysosomal proteases occur following diabetes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beyler, A. L. &Szego, C. M. (1954) Correlation of ovarian cholesterol levels with changes in β-glucuronidase activity of reproductive tract during estrous cycle and pregnancy.Endocrinology 54, 323–33.
Bird, J. W. C. (1975) Skeletal muscle lysosomes. InLysosomes in Biology and Pathology, Vol. 4 (edited byDingle, J. T. andDean, R. T.), pp. 75–109. Amsterdam: North Holland Publishing Company.
Bond, J. S. (1980). Failure to demonstrate increased protein turnover and intracellular proteinase activity in livers of mice with streptozotocin-induced diabetes.Diabetes 29, 648–54.
Dahlmann, B. &Reinauer, H. (1981) Proteolytic activities in skeletal muscle of streptozotocin-diabetic rats. InStrentozotocin: Fundamentals and Therapy (edited byAgarwal, M. K.), pp. 123–40. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Dahlmann, B., Schroeter, H., Herbertz, L. &Reinauer, H. (1979). Myofibrillar protein degradation in normal and diabetic rats.Biochem. Med. 21, 33–9.
Dolbeare, F. &Smith, R. E. (1977) Flow cytometric measurement of peptidases with the use of 5-nitrosalicylaldehyde and 4-methoxy-2-naphthylamine derivatives.Clin. Chem. 23, 1485–91.
Graf, M., Leemann, U., Ruch, F. &Strauli, P. (1979) The fluorescence and bright field microscopic demonstration of cathepsin B in human fibroblasts.Histochemistry 64, 319–22.
Iodice, A. A., Chin, S., Perker, S. &Weinstock, I. M. (1972) Cathepsins A, B, C, D and autolysis during development of breast muscle of normal and dystrophic chickens.Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 152. 166–74.
Kar, N. C. &Pearson, C. M. (1977) Early elevation of cathepsin B1 in human muscle disease.Biochem. Med. 18, 126–9.
Kar, N. C. &Pearson, C. M. (1979). Muscular dystrophy and activation of proteinases.Muscle Nerve 1, 308–13.
Katunuma, N., Sanada, E., Kominami, E., Kobayashi, K. &Banno, Y. (1977) Intracellular protein catabolism and new serine proteases.Acta biol. med. Germ. 36, 1537–46.
Kaiunuma, N., Yasogawa, N., Kito, K., Sanada, H., Kawai, H. &Miyoshi, K (1978) Abnormal expression of a serine protease in human dystrophic muscle.J. Biochem. 83, 625–8.
Lowry, O. H., Rosenbrough, N. J., Farr, A. L. &Randall, R. J. (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent.J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–75.
McElligott, M. A. &Bird, J. W. C. (1981) Muscle proteolytic enzyme activities in diabetic muscles.Amer. J. Physiol. (Endocrinol. Metab. 4) 241, E378–84.
Noguchi, I. &Kandatsu, U. (1966) Proteolytic activity in the myofibrillar fractions of rat skeletal muscle.Agr. Biol. Chem. 30, 199–201
Park, D. C., Parsons, M. E. &Pennington, R. J. T. (1973) Evidence for mast cell origin of proteinase in skeletal muscle homogenates.Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1, 730–3.
Peters, T. J., Muller, M. &DeDuve, C. (1972) Lysosomes of the arterial wall. I. Isolation and subcellular fractionation of cells from normal rabbit aorta.J. expl Med. 136, 1117–39.
Schwartz, W. N. &Bird, J. W. C. (1977) Degradation of myofibrillar proteins by cathepsins B and D.Biochem. J. 167, 811–20.
Skoza, L., Giacomelli, F. &Wiener, J. (1980) Lysosomal enzymes in the heart of the genetically diabetic mouse.Lab. Invest. 43, 443–8.
Stauber, W. T. (1981) Lysosomes and skeletal muscle atrophy. InMechanism of Muscle Adaptation to Eunctional Requirements (edited byGuba, F., Marechal, G., andTakacs, O.), pp. 171–7. Budapest: Akademiai Kiado.
Stauber, W. T. &Ong, S. H. (1981a) Fluorescence demonstration of dipeptidyl peptidase II in skeletal, cardiac and vascular smooth muscles.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 29, 672–7.
Stauber, W. T. &Ong, S. H. (1981b) Fluorescence demonstration of cathepsin B in skeletal, cardiac and vascular smooth muscle.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 29, 866–9.
Stauber, W. T. &Ong, S. H. (1982a) Fluorescence demonstration of dipeptidyl peptidase I (Cathepsin C) in skeletal, cardiac and vascular smooth muscle.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 30, 162–4.
Stauber, W. T. &Ong, S. H. (1982b) Fluorescence demonstration of cathepsin H-like enzyme in cardiac, skeletal, and vascular smooth muscle.Histochem. J. 14, 585–91.
Wolinsky, M., Goldfischer, S., Capron, L., Capron, F., Coltoff-Schiller, B. &Kasak, L. (1978) Hydrolase activities in the rat aorta. I. Effects of diabetes mellitus and insulin treatment.Circ. Res. 42, 821–31.
Woodbury, R. G., Everitt, M., Sanada, Y., Katunuma, N., Lagunoff, D. &Neurath, M. (1978) A major serine protease in rat skeletal muscle: Evidence for its mast cell origin.Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. USA 75, 5311–3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stauber, W.T., Fritz, V.K. Decreased lysosomal protease content of skeletal muscles from streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: a biochemical and histochemical study. Histochem J 17, 613–622 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01003201
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01003201