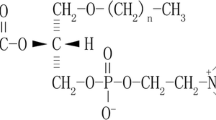
Abstract
In this review, evidence is summarized for the production of PAF in brain, in response to stimulation associated with pathology. As well, there is a growing literature on the duality of actions of this lipid autocoid upon nervous tissue, indicated by extracellular and intracellular actions and binding sites for PAF in brain. The metabolic routes to PAF can be divided into the de novo and remodelling pathways of synthesis. The de novo route consists of 1-alkyl glycerophosphate acetyltransferase, and the subsequent actions of distinct phosphohydrolase and cholinephosphotransferase activities. This acetyltransferase can be activated by phosphorylation, and inhibited by MgATP and fatty acyl CoA thioesters, inhibitions which have particular relevance to brain ischemia. There is also evidence that the cholinephosphotransferase is controlled by phosphorylation, and regulated by levels of CDP-choline. The remodelling pathway to PAF relies upon the actions of phospholipase A2 or CoA-independent transacylases to generate the l-alkyl glycerophosphorylcholine, as substrate for a distinct acetyltransferase. Following stimulation, rising intracellular calcium may trigger arachidonate selective cytosolic phospholipase activity which leads to increased PAF synthesis. The l-alkyl glycerophosphocholine acetyltransferase activity is quite small in brain in comparison with the de novo acetyltransferase activity, and is also controlled by phosphorylation. Evidence has been presented for the actions of both pathways in brain, in response to biologically relevant stimulation pertinent to the disease state.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yoshida, J. I., Tokumura, A., Fukuzawa, K., Terao, M., Takauchi K., and Tsukatani, H. 1986. A platelet aggregating and hypotensive phospholipid isolated from bovine brain. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 38:878–882.
Tokomura, A., Kamiyasu, K., Takashi, K., and Tsukatani, H., 1987. Evidence for the existence of various homologues and analogues of platelet activating factor in a lipid extract of bovine brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 145:415–425.
Domingo, M. T., Spinnewyn, B., Chabrier, P. E., and Braquet, P. 1994. Changes in [3H]PAF binding and PAF concentrations in gerbil brain after bilateral carotid artery occlusion: a quantitative autoradiographic study. Brain Res. 640:268–276.
Lindsberg, P. J., Yue, T.-L., Frerichs., K. U., Hallenbeck, J. M., and Feuerstein, G. 1990. Evidence for platelet, activating factor as a novel mediator in experimental stroke in rabbits. Stroke 21: 1452–57.
Kumar, R., Harvey, S. A. K., Hanahan, D. J., and Olsen, M. S. 1988. Production and effects of platelet activating factor in the rat brain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 963:375–383.
Yue, T. L., Lysko, P. G., and Feuerstein, G. 1990. Production of platelet activating factor from rat cerebellar cells in culture. J. Neurochem. 54:1809–1811.
Bussolino, F., Gremo, F., Tatta, C., Pescarmona, G. P., and Camussi, G. 1986. Production of platelet activating factor by chick retina. J. Biol. Chem. 261:16502–08.
Sogos, V., Bussolino, F., Pilia, E., Torelli, S., and Gremo, F. 1990. Acetylcholine-induced production of platelet activating factor by human fetal brain cells in culture. J. Neurosci. Res. 27:706–711.
Kunievsky, B., and Yavin, E. 1994. Production and metabolism of platelet activating factor in the normal and ischemic fetal rat brain. J. Neurochem. 63:2144–2151.
Domingo, M. T., Spiniewyn B., Chabrier, P. E., and Braquet, P.. 1988. Presence of specific binding sites for platelet activating factor in the brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 151:730–736.
Bito, H., Nakamura, M., Honda, Z., Izumi, T., Iwatsubo, T., Seyama, Y., Ogura, A., Kudo, Y., and Shimizu, T. 1992. Platelet activating factor receptor in rat brain: PAF mobilizes intracellular Ca2+ in hippocampal neurons. Neuron 9:285–294.
Braquet P., Spinnewyn, B., Blavet, N., Marcheselli, V., Rossawska M., and Bazan, N. G. 1988. Platelet activating factor as a mediator in cerebral ischemia and related disorders 1988. Biomed. Biochim. Acta 47:195–218.
Dray, F., Wisner, A., Bommelaer-Bayet, M. C., Tiberghien, C., Gerozissis, K., Saadi, M., Junier M. P., and Rougeot, C. 1989. Prostaglandin E2, leukotriene C4 and platelet activating factor receptor sites in the brain. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 559:100–111.
Bazan, N. G., Squinto, S. P., Braquet, P., Panetta, T., and Mercheselli, V. L. 1991. Platelet activating factor and polyunsaturated fatty acids in cerebral ischemia or convulsions: Intracellular PAF binding sites and activation of a fos/jun/AP-1 transcriptional signalling system. Lipids 26:1236–1242.
Honda, Z., Nakamura, M., Miki, I., Minami, M., Watanabe, T., Seyama, Y., Okado, H., Toh, H., Ito, K., Miyamoto, T., and Shimizu, T. 1991. Nature 349:342–346.
Catalan, R. E., Martinez, A. M., Aragones, M. D., Fernandez I., Lombardia, M., and Miguel, B. G. 1992. Platelet activating factor induced activation of polyphosphoinositide hydrolyzing phospholipase C in cerebral cortex. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 183:300.
Kunievsky, B., and Yavin, E. 1992. Platelet activating factor stimulates arachidonic acid release and enhances thromboxane B2 production in intact fetal rat brain ex vivo. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 263:562–568.
Kornecki, E., and Ehrlick, Y. H. 1988. Neuroregulatory and neuropathological actions of ether phospholipid platelet activating factor. Science 240:1792–1794.
Yue, T. L., Gleason, M. M., Hallenbeck, J., and Feuerstein, G. Z. 1991. Characterization of platelet activating factor-induced elevation of cytosolic free calcium in neurohybrid NCB-20 cells. Neuroscience 41:177–185.
Yue, T. L., Gleason, M. M., Gu, J. L., Lysko, P. G., Hallenbeck, J., and Feuerstein, G. Z. 1991. Platelet activating factor receptor mediated calcium mobilization and phosphoinositide turnover in hybrid NG 108-15 cells: Studies with BN 50739, a new PAF antagonist. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 257:374–381.
Yue, T. L., Jeffrey, M. S., Sarau, H. M., and Feuerstein, G. Z. 1992 Platelet activating factor stimulates phosphoinositide turnover in neurhybrid N6B-20 cells: Involvement of pertussis toxin sensitive guanine nucleotide binding proteins and inhibition by protein kinase C. Mol. Pharmacol. 41:281–289.
Petroni, A., Salami, M., Blasevich, M., Papini, N., Galello, G., Colombo, C., and Galli, C. 1994 Eicosanoid and inositol phosphate response to platelet activating factor and to PAF antagonists in rat astroglial cells. Dev. Brain Res. 78:169–174.
Spinnewyn, B., Blavet, N., Clostre, F., Bazan, N., and Braquet, P. 1987. Involvement of platelet activating factor in cerebral ischemic phase in Mongolian gerbils Prostaglandins 34:337–349.
Panetta, T., Marcheselli, V. L., Braquet, P., and Bazan, N. G. 1989. Arachidonic acid metabolism and cerebral bloodflow in the normal, ischemic and reperfused gerbil brain: Inhibition of ischemic-reperfusion induced cerebral injury by PAF antagonist BN 52021. Ann N.Y. Acad. Sci. 559:340–351.
Kochanek, P. M., Dutka, A. J., Kumaroo, K. M., and Hallenbeck, J. M. 1987. Platelet activating factor receptor blockade enhances recovery after multifocal brain ischemia. Life Sci. 41:2639–2644.
Bielenberg, G. W., Wagener, G., and Beck, T. 1992. Infarct reduction by the platelet activating factor antagonist apafant in rats. Stroke 23:98.
Bazan, H. E. P., Tao, Y., and Bazan, N. G. 1993. Platelet activating factor induces collagenase expression in corneal epithelial cells. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 90:8678–8682.
Bazan, H. E. P., Tao, Y., and Bazan, N. G. 1993. Platelet activating factor induces collagenase expression in corneal epithelial cells. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 90:8678–8682.
Bazan, N. G., Fletcher, B. S., Herschman, H. R. and Mukherjee, P. K. 1994. Platelet activating factor and retinoic acid synergistically activate the inducible prostaglandin synthase gene. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 91:5252–5256.
Marcheselli, V. L. and Bazan, N. G. 1994 Platelet activating factor is a messenger in the electroconvulsive shock-induced transcriptional activation of c-fos and zif-268 in hippocampus. J. Neurosci. Res. 37:54–61.
Kato, K., Clark, G. D., Bazan, N. G., and Zorumski, F. 1994. Platelet activating factor as a potential retrograde messenger in CAl hippocampal long term potentiation. Nature 367:175–179.
Snyder, F. 1987. The significance of dual pathways for the biosynthesis of platelet activating factor: 1-alkyl-2-lyso-sn-glycero-3-phosphate as a branchpoint. Pages 13–25,in Wislow, C. M. and Lee, M. L. (eds.) New Horizons in Platelet Activating Factor Research, Wiley and Sons, New York.
Lee, T.-C., Malone, B., and Snyder, F. 1986. A newde novo pathway for the formation of 1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerols, precursors of platelet activating factor: Biochemical characterization of 1-alkyl-2-lyso-sn-glycero-3-P: acetyl CoA acetyltransferase in Rat Spleen. J. Biol. Chem. 261:5373–5377.
Fernandez-Gallardo, S., Gijon, M. A., Garcia, M., Cano, E., and Sanchez-Crespo, M. 1988 Biosynthesis of platelet activating factor in glandular gastric mucosa. Biochem. J. 254:707–714.
Baker, R. R., and Chang, H.-Y. 1993. The potential for platelet activating factor synthesis in brain: properties of cholinephosphotransferase and 1-alkyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate acetyltransferase in microsomal fractions of immature rabbit cerebral cortex. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1170:157–164.
Baker, R. R., and Chang, H.-Y. 1994. MgATP inhibits the synthesis of 1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate by microsomal acetyltransferase of immature rabbit cerebral cortex. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1213:27–33.
Baker, R. R., and Chang H.-Y. 1995. Fatty acyl CoA inhibits 1-alkyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate acetyltransferase in microsomes of immature rabbit cerebral cortex: Control of the first committed step in the de novo pathway of platelet activating factor synthesis. J. Neurochem. 64:364–370.
Lee, T.-C., Malone, B., and Snyder, F. 1988. Formation of 1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerols via the de novo biosynthetic path for platelet activating factor: Characterization of 1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate phosphohydrolase in rat spleens. J. Biol. Chem. 263:1755–1760.
Renooij, W., and Snyder, F. 1981. Biosynthesis of 1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (platelet activating factor and a hypotensive lipid) by cholinephosphotransferase in various rat tissues. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 663:545–556.
Woodward, D. S., Lee, T.-C., and Snyder, F. 1987. The final step in the de novo biosynthesis of platelet activating factor: Properties of a unique CDP-choline: 1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol choline phosphotransferase in microsomes from the renal inner medulla of rats. J. Biol. Chem. 262:2520–2527.
Francescangeli, E., and Goracci, G. 1989. The de novo biosynthesis of platelet activating factor in rat brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 161:107–112.
Goracci, G., and Francescangeli, E. 1995. Modulation of platelet activating factor biosynthetic pathways in nervous tissue. J. Neurochem. 64S:S37D.
Goracci, G. 1990. PAF in the nervous system: biochemistry and pathophysiology pp. 377–390,in Krieglstein, J., and Oberpichler, H. (eds.) Pharmacology of Cerebral Ischemia. Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft, Stuttgart.
Van de Bosch, H., Sturk, A., ten Cate, J. W., and Aarsman, A. J. 1991. Studies of the selectivity of enzymes, involved in platelet activating factor formation in stimulated cells. Lipids 26:967–973.
Wong, B., Tang W., and Ziboh, V. A. 1992. Identification of a membrane-associated 1-O-alkyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine hydrolyzing phospholipase A2 in guinea pig epdermis. FEBS Lett. 305:213–216.
Clark, J. D., Lin, L.-L., Kriz, R. W., Ramesha, C. S., Sultzman, L. A., Lin, A. Y., Milona, N., and Knopf, J. L. 1991. A novel arachidonic acid-selective cytosolic PLA2 contains a Ca2+-dependent translocation domain with homology to PKC and GAP. Cell 65:1043–1051.
Lin, L.-L., Wartmann, M., Lin, A. Y., Knopf, J. L., Seth, A., and Davis, R. J. 1993. cPLA2 is phosphorylated and activated by MAP kinase. Cell 72:269–278.
Yoshihara, Y., Yamaji, M., Kawasaki, M., and Watanabe, Y. Ontogeny of cytosolic phospholipase A2 in rat brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 185:350–355.
Fujimori, Y., Murakami, M., Kim, D. Y., Hara, S., Takayana, K., Kudo, I., and Inoue, K. 1992. Immunochemical detection of arachidonoyl-preferential phospholipase A2. J. Biochem. 111:54–60.
Edgar, A. D., Strosznajder, J., and Horrocks, L. A. 1982. Activation of ethanolamine phospholipase A2 in brain during ischemia. J. Neurochem. 39:1111–1116.
Rodorf, G., Uemura, Y., and Bonventre, J. V. Characterization of phospholipase A2 activity in gerbil brain: Enhanced activities of cytosolic, mitochondrial and microsomal forms after ischemia and reperfusion. J. Neurosci. 11:1829–1836.
Chilton, F. H., Cluzel, M., and Triganni M. 1991. Recent advances in our understanding of the biochemical interaction between platelet activating factor and arachidonic acid. Lipids 26: 1021–1027.
Venable, M. E., Zimmerman, G. A., McIntyre, T. M., and Prescott, S. M. 1993. J. Lipid Res. 34:691–702.
Bazan, N. G. 1995 (in press). Signals, messages and genes in cerebral ischemia: Novel sites for neuroprotection, pages x-x,in Kriegelstein, J., and Oberpichler-Schwenk, H. (eds.). Pharmacology of Cerebral Edema, Wissenschaftliach Verlagsgesellschaft, Stuttgart.
Snyder F., Lee, T.-C., and Blank, M. L. 1992. The role of transacylases in the metabolism of arachidonate and platelet activating factor. Prog. Lipid Res. 31:65–86.
Ojima, A., Nakagawa, Y., Sugiura, T., and Waku K. 1987. Selective transacylation of 1-O-alkylglycerophosphoethanolamine by docosahexaenoate and arachidonate in rat brain microsomes. J. Neurochem. 48:1403–1410.
Masuzawa, Y., Sugiura, T., Sprecher H., and Waku, K. 1989. Selective transfer in the reacylation of brain glycerophospholipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1005:1–12.
Ninio, E., Mencia-Huerta, J. P., and Benveniste, J. 1983. Biosynthesis of platelet activating factor: Enhancement of acetyltransferase activity in murine peritoneal cells by calcium ionophore A23187. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 751:298–304.
Joly, F., Beauvais, F., and Ninio, E., 1992. Biosynthesis of PAF-acether in cultured-mouse mast cells: The role of calcium and G proteins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 184:1425–1431.
Lenihan, D. J., and Lee, T.-C. 1984. Regulation of platelet activating factor synthesis: Modulation of 1-alkyl-2-lyso-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine: acetyl CoA acetyltransferase by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation in rat spleen microsomes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 120:834–839.
Gomez-Cambronero, J., Velasco, S., Mato, J. M., and Sanchez-Crespo. 1985. Modulation of lyso PAF: acetyl CoA acetyltransferase from rat spleen microsomes. The role of cyclic AMP dependent protein kinase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 845:516–519.
Domenech, C., Machado-De, Domenech, and Soling, H.-D. 1987. Regulation of acetyl CoA: 1-alkyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine O-acetyltransferase in exocrine glands: Evidence for an activation via phosphorylation by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 262:5671–5676.
Garcia, C., Montero, M., alvarez, J., and Sanchez Crespo, M. 1993. Biosynthesis of platelet activating factor induced by chemotactic peptide is modulated at the lyso PAF: acetyl CoA acetyltransferase level by calcium transient and phosphatidic acid. J. Biol Chem. 268:4001–4008.
Bussolino, F., Arese, M., Silvestro, L., Soldi, R., Benfenati, E., Sanavio, F., Aglietta, M., Bosia, A., and Camussi, G. 1994. Involvement of a serine protease in the synthesis of platelet activating factor by endothelial cells stimulated by tumor necrosis factor-α or interleukin-1α. Eur. J. Immunol. 24:3131–3139.
Holland, M. R., Venable, M. E., Whatley, Zimmerman, G. A., McIntyre, T. M., and Prescott, S. M. 1992. Activation of the acetyl CoA: lysoplatelet activating factor acetyltransferase regulates platelet activating factor synthesis in human endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 267:22883–22890.
Bussolino, F., Pescarmona, G., Camussi, G., and Gremo, F. 1988. Acetylcholine and dopamine promote the production of platelet activating factor in immature cells of chick embryonic retina. J. neurochem. 51:1755–1759.
Heller, R., Bussolino, F., Ghigo, D., Garbarino, G., Pescarmona, G., Till, U., and Bosia, A. 1991. Stimulation of platelet activating factor synthesis in human endothelial cells by activation of the de novo pathway: Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate activates 1-alkyl-2-lyso-sn-glycero-3-phosphate: acetyl CoA acetyltransferase and dithiothreitol-insensitive 1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol: CDP-choline cholinephosphotransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 266:21358–21361.
Blank, M. L., Lee, Edgar, Cress, E. A., and Snyder, F. 1988. Stimulation of the de novo pathway for the biosynthesis of platelet activating factor via cytidylyltransferase activation in cells with minimal endogenous PAF production. J. Biol. Chem. 263:5656–5661.
Whatley R. E., Fennell, D. F., Kurrus, J. A., Zimmerman, G. A., McIntyre, T. M., and Prescott, S. M. 1990. Synthesis of platelet activating factor by endothelial cells: the role of G proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 265:15550–15559.
McManus, L. M., Woodward, D. S., Deavers, S. I., and Pinckard, R. N. 1993. Biology of disease: PAF molecular heterogeneity: pathobiological implications. Lab. Invest 69:639–650.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Special issue dedicated to Dr. Leon S. Wolfe.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baker, R.R. Enzymes of platelet activating factor synthesis in brain. Neurochem Res 20, 1345–1351 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00992510
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00992510