Abstract
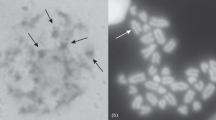
The meiosis of the diploidPaeonia tenuifola and the allotetraploidP. officinalis was studied after conventional methanol/acetic acid-fixation and synaptonemal complex (SC) spreading. Meiosis inP. tenuifolia (2n = 10) is normal with five bivalents in metaphase I, and the SCs in pachytene show regular features. InP. officinalis (2n = 4x = 20) univalents, bivalents and multivalents are found in metaphase I. The SCs reveal several abnormalities: a high number of unpaired lateral elements, partner exchanges between three and four lateral elements, loops and lateral element thickenings. These characteristics are compared with the situations found in other polyploid and hybrid species. It is noteworthy that the abnormalities in meiosis ofP. officinalis are not reflected in its somatic karyotype. Its features were analysed after silver staining and fluorescent staining with chromomycin and compared with those ofP. tenuifolia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Church, K., 1976: Arrangement of chromosome ends and axial core formation during early meiotic prophase in the male grasshopperBrachystola magna by 3 D, E.M. reconstruction. — Chromosoma58, 365–376.
Dark, S. O. S., 1936: Meiosis in diploid and tetraploidPaeonia species. — J. Genet.32, 353–372.
Friebe, B., 1976: Spezifische Giemsa-Färbung von heterochromatischen Chromosomensegmenten beiVicia faba, Allium cepa andPaeonia tenuifolia. — Theor. Appl. Genet.47, 275–283.
Gillies, C. B., 1973: Ultrastructural analysis of maize pachytene karyotypes by three dimensional reconstruction of the synaptonemal complexes. — Chromosoma43, 145–176.
—, 1981: Electron microscopy of spread maize pachytene synaptonemal complexes. — Chromosoma83, 575–591.
—, 1984: The synaptonemal complex in higher plants. — Crit. Rev. Plant Sci.2, 81–116.
Goodpasture, C., Bloom, S. E., 1975: Visualization of nucleolar organizer regions in mammalian chromosomes using silver staining. — Chromosoma53, 37–50.
Harte, C., 1956: Die Variabilität der Chiasmenbildung beiPaeonia tenuifolia. — Chromosoma8, 152–182.
Hasenkampf, C. A., 1984: Longitudinal axis thickenings in whole-mount spreads of synaptonemal complexes fromTradescantia. — Chromosoma90, 285–288.
Hobolth, P., 1981: Chromosome pairing in allohexaploid wheat var. Chinese Spring. Transformation of multivalents into bivalents, a mechanism for exclusive bivalent formation. — Carlsberg Res. Commun.46, 129–173.
Jenkins, G., 1985: Synaptonemal complex formation in hybrids ofLolium temulentum ×L. perenne (L.) I. High chiasma frequency diploid. — Chromosoma92, 81–88.
Jones, G. H., 1973: Light and electron microscope studies of chromosome pairing in relation to chiasma localisation inStethophyma grossum (Orthoptera:Acrididiae). — Chromosoma42, 145–162.
Kehlhoffner, J. L., Dietrich, J., 1983: Synaptonemal complex and a new type of nuclear polycomplex in three higher plants:Paeonia tenuifolia, Paeonia delavayi, andTradescantia paludosa. — Chromosoma88, 164–170.
Kodama, Y., Yoshida, M. C., Sasaki, M., 1980: An improved silver staining technique for nucleolus organizer regions by using nylon cloth. — Japan. J. Hum. Genet.25, 229–233.
La Cour, L. F., Wells, B., 1973: Abnormalities in synaptonemal complexes in pollen mother cells of a lily hybrid. — Chromosoma42, 137–144.
Loidl, J., Greilhuber, J., 1983: Structural changes of Ag-stained nucleolus organizing regions and nucleoli during meiosis inAllium flavum. — Canad. J. Genet. Cytol.25, 524–529.
Marquardt, H., 1952: Über die spontanen Aberrationen in der Anaphase der Meiosis vonPaeonia tenuifolia. — Chromosoma5, 81–112.
Menzel, M. Y., Price, J. M., 1966: Fine structure of synapsed chromosomes in F 1Lycopersicon esculentum ×Solanum lycopersicoides and its parents. — Amer. J. Bot.53, 1079–1086.
Miller, D. A., Dev, V. G., Tantravahi, R., Miller, O. J., 1976: Suppression of human nucleolus organizer activity in mouse-human somatic hybrid cells. — Exp. Cell Res.101, 235–243.
Moens, P. B., 1968: Synaptonemal complexes ofLilium tigrinum (triploid) sporocytes. — Canad. J. Genet. Cytol.10, 799–807.
—, 1970: The fine structure of meiotic chromosome pairing in natural and artificialLilium polyploids. — J. Cell Sci.7, 55–63.
Moses, M. J., Poorman, P. A., 1981: Synaptonemal complex analysis of mouse chromosomal rearrangements II. Synaptic adjustment in a tandem duplication. — Chromosoma81, 519–535.
—, —, 1982: Synaptonemal complex analysis of mouse chromosomal rearrangements IV. Synapsis and synaptic adjustment in two paracentric inversions. — Chromosoma84, 457–474.
Rasmussen, S. W., 1977: Chromosome pairing in triploid females ofBombyx mori analyzed by three dimensional reconstructions of synaptonemal complexes. — Carlsberg Res. Commun.42, 163–197.
—, 1979: Chromosome pairing in autotetraploidBombyx females. Mechanism for exclusive bivalent formation. — Carlsberg Res. Commun.44, 101–125.
—, —, 1980: Mechanics of meiosis. — Hereditas93, 187–216.
Schwarzacher, H. G., Wachtler, F., 1983: Nucleolus organizer regions and nucleoli. — Hum. Genet.63, 89–99.
Schwarzacher, T., 1984: Untersuchungen zur Organisation der synaptonemalen Komplexe in Oberflächen-gespreiteten Meiocyten einiger Angiospermen- und Säuger-Arten. — Ph.D. thesis, University of Vienna, Austria.
—, 1980: Application of Giemsa banding to orchid karyotype analysis. — Pl. Syst. Evol.134, 293–297.
Schwarzacher-Robinson, T., Schweizer, D., 1986: Synaptonemal complex spreading in plants: Technical aspects and preliminary observations on the synaptonemal complex inPaeonia andOrnithogalum. — Pl. Syst. Evol.154, 129–136.
Schweizer, D., 1980: Fluorescent chromosome banding in plants: applications, mechanisms, and implications for chromosome structure. — InDavies, D. R., Hopwood, R. A., (Eds.): Proc. 4th John Innes Symposium, Norwich 1979: The Plant Genome, pp. 61–72. — Norwich: John Innes Charity.
—, 1981: Counterstain-enhanced chromosome banding. — Hum. Genet.57, 1–14.
—, 1983: Cytogenetics of the parthenogenetic grasshopperWarramaba virgo and its bisexual relatives. X. Patterns of fluorescent banding. — Chromosoma88, 227–236.
Sears, E. R., 1976: Genetic control of chromosome pairing in wheat. — Ann. Rev. Genet.10, 31–51.
Sinclair, J. H., Brown, D. D., 1971: Retention of common nucleotide sequences in the ribosomal deoxyribonucleic acid of eukaryotes and some of their physical characteristics. — Biochemistry10, 2761–2769.
Solari, A. J., Moses, M. J., 1977: Synaptonemal complexes in a tetraploid mouse spermatocyte. — Exp. Cell Res.108, 464–467.
Stebbins, Jr., G. L., 1938: Cytogenetic studies inPaeonia II: The cytology of the diploid species and hybrids. — Genetics23, 83–110.
Wahrman, J., 1981: Synaptonemal complexes — origin and fate. Chromosomes Today7, 105–113.
Westergaard, M., Wettstein, von D., 1972: The synaptinemal complex. — Ann. Rev. Genet.6, 71–110.
Wettstein, von D., Rasmussen, S. W., Holm, P. B., 1984: The synaptinemal complex in genetic segregation. — Ann. Rev. Genet.18, 331–413.
Zickler, D., Sage, J., 1981: Synaptonemal complexes with modified lateral elements inSordaria humana: development of and relationship to the “recombination nodules”. — Chromosoma84, 305–318.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Synaptonemal Complex Spreading in Plants2; for part1 see Pl. Syst. Evol.154, 129–136 (1986).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwarzacher-Robinson, T. Meiosis, SC-formation, and karyotype structure in diploidPaeonia tenuifolia and tetraploidP. officinalis . Pl Syst Evol 154, 259–274 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00990128
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00990128