Abstract
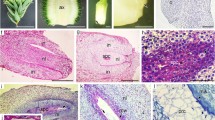
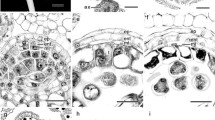
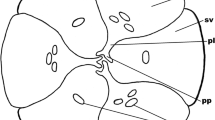
Development of pollen and female gametophyte inEpipogium roseum (D. Don)Lindl. has been investigated. The embryo sac conforms to the Apinagia type. The taxonomic position ofEpipogium within the family is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe, K., 1972: Contributions to the embryology of the familyOrchidaceae, VII. A comparative study of the orchid embryo sac. — Sci. Rep. Tohoku Univ. Ser. IV (Biol.)36, 179–201.
—, 1976: A reinvestigation of the development of the embryo sac inGastrodia elata Blume (Orchidaceae). — Ann. Bot.40, 99–102.
Afzelius, K., 1954: Embryo sac development inEpipogium aphyllum. — Svensk Botanisk Tidskrift48 (2), 513–520.
Battaglia, E., 1971: The embryo sac ofPodostemaceae—an interpretation. — Caryologia24, 403–420.
Carlson, M. C., 1945: Megasporogenesis and development of the embryo sac ofCypripedium parviflorum. — Bot. Gaz.107, 107–114.
Dressler, R. L., 1974: Classification of the Orchid Family. — Proc. 7th World Orchid Conference, 259–279.
—, 1960: Classification and Phylogeny in theOrchidaceae. — Ann. Missouri Bot. Gard.47, 25–68.
Garay, L. A., 1964: A phylogenetic study of theOrchidaceae. — 299 pp. Doctoral thesis, Tufts University.
Geitler, L., 1956: Zur Fortpflanzungsbiologie, Embryologie und mechanistischen Deutung der Embryogenese vonEpipogium aphyllum. — Österr. Bot. Z.103, 312–335.
Kimura, Chugai., 1968: On the embryo sac ofCypripedium debile Reichb. f. — Sci. Rep. Tohoku Univ. Ser. IV (Biol.)34, 67–74.
Nagendran, C. R., Subramanyam, K., Arekal, G. D., 1976: Development of the female gametophyte inHydrobryum griffithii (Podostemaceae). — Ann. Bot.40, 511–513.
Pace, L., 1914: Two species ofGyrostachys. — Baylor. Univ. Bull.17, 1–16.
Prosina, M. N., 1930: Über die vomCypripedium-Typus abweichende Embryosackentwicklung vonCypripedium guttatum Sw. — Planta12, 532–544.
Savina, G. L., 1978: Certain peculiarities in the embryology of orchids. — Proc. Indian Nat. Sci. Acad.B 44, 141–145.
Schnarf, K., 1929: Embryologie der Angiospermen. — InLinsbauer, K., (Ed.): Handbuch der PflanzenanatomieII/2. — Berlin: Gebr. Borntraeger.
Swamy, B. G. L., 1949: Embryological studies in theOrchidaceae: 1: Gametophyte. — Amer. Midl. Natur.41, 184–201.
Tohda, H., 1967: An embryological study ofHetaeria skikokiana, a saprophytic orchid in Japan. — Sci. Rep. Tohoku Univ. Ser. IV (Biol.)33, 83–95.
Vermeulen, P., 1965: The place ofEpipogium in the system ofOrchidales. — Acta Bot. Neerl.14, 230–241.
Withner, C. L., (Ed.), 1959: The Orchids: A Scientific Survey. — New York: The Ronald Press Company.
Ziegenspeck, H., 1928–1936:Orchidaceae. — InKirchner, O., Loew, E., Schroeter, C.: Lebensgeschichte der Blütenpflanzen Mitteleuropas,1/4. — Stuttgart.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arekal, G.D., Karanth, K.A. The embryology ofEpipogium roseum (Orchidaceae). Pl Syst Evol 138, 1–7 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00984604
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00984604