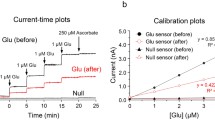
Abstract
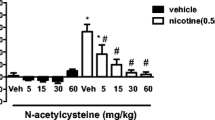
Ten minutes after a single injection of 0.8 mg/kg nicotine SC (free base) the level of substance P-like immunoreactivity (SPLI) was reduced by 61–73% in rat caudate-putamen, nucleus accumbens, and olfactory tubercle, with smaller and not significant reductions in the frontal cortex, substantia nigra, and ventral tegmental area. The nicotinic receptor antagonist mecamylamine (1.0 mg/kg IP) prevented the reductions in SPLI. The rapidity and the degree of the changes in SPLI after nicotine exceed those previously reported for other agents and implicate substance P neurotransmission as a major component of nicotinic action.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Naftchi, N. E., Lapin, E. P., Maker, H., Sleis, J., Hurd, Y., and Leeman, S. 1986. Acute reduction of brain substance P induced by nicotine. Trans. Amer. Soc. Neurochem. 17:291.
Lapin, E. P., Maker, H. S., Cohen, G., Hurd, Y., Sershen, H., and Lajtha, A. 1985. Interaction of nicotine with rat brain dopamine neurons. Trans. Amer. Soc. Neurochem. 16:133.
Lapin, E. P., Maker, H., Sershen, H., Hurd, Y., and Lajtha, A. 1987. Dopamine-like action of nicotine: Lack of tolerance and reverse tolerance. Brain Res. 407:351–363.
Andersson, K., Fuxe, K., and Agnati, L. F. 1981. Effects of single injections of nicotine on the ascending dopamine pathways in the rat. Evidence for increases of dopamine turnover in the nigrostriatal and mesolimbic dopamine neurons. Acta Physiol. Scand. 112:345–347.
Andersson, K., Fuxe, K., Eneroth, P., and Agnati, L. F. 1984. Differential effects of mecamylamine on the nicotine induced changes in amine levels and turnover in hypothalamic dopamine and noradrenaline nerve terminal systems and in the secretion of adenohypophyseal hormones in the castrated female rat. Evidence for involvement of cholinergic nicotine-like receptors. Acta. Physiol. Scand. 120:489–498.
Fuxe, K., Agnati, L., Eneroth, P., Gustafsson, P., Hokfelt, T., Lofstrom, A., Skett, B., and Skett, P. 1977. The effect of nicotine on central catecholamine neurons and gonadotropin secretion. 1. Studies in the male rat. Med. Biol. 55:148–157.
Lichtensteiger, W., Hefti, F., Felix, D., Huwyler, T., Melamed, E., and Schlumpf, M. 1982. Stimulation of nigrostriatal dopamine neurons by nicotine. Neuropharmacology 21:963–968.
Sukarai, Y., Kohjimoto, Y., Honda, K., and Kamiya, H. O. 1982. Effect of [3H]dopamine release and its [3H]metabolites by nicotine drugs. Brain Res. 242:99–102.
Brownstein, M. J., Mroz, E. A., Kizer, S. J., Palkovits, M., and Leeman, S. 1976. Substance P. Brain Res. 116:299–305.
Cuello, A. C., Priestly, J. V., and Matthews, M. R. 1981. Localization of substance P in neuronal pathways. Ciba Foundation Symposium, London 91:65–79.
Glowinski, J., Torrens, Y., and Beaujcuan, J. C. 1981. The strionigral substance P pathway and dopaminergic mechanisms. Ciba Foundation Symposium, London 91:281–295.
Hong, J. S., Yang, H. Y., Racagni, G., and Costa, E. 1977. Projections of substance P containing neurons from neostriatum to substantia nigra. Brain Res. 122:541–544.
Kohno, J., Shinoda, S., Inagaki, S., and Tohyana, M. 1984. Two distinct strio-nigral substance P pathways in the rat: An experimental immunohistochemical study. Brain Res. 308:309–311.
Pettibone, P. J. and Wurtman, R. J. 1980. D-amphetamine reduces striatal substance P concentrations by presynaptic release of dopamine. Brain Res. 186:409–418.
Bannon, M. J. and Goedert, M. 1984. Changes in substance P concentrations after protein synthesis inhibition provide an index of substance P utilization. Brain Res. 301:184–186.
Hanson, G. R., Alphs, L., Wolf, W., and Levone, R. 1981. Haloperidol-induced reduction of nigral substance P-like immunoreactivity: A probe for the interaction between dopamine and substance P neuronal systems. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 218:568–574.
Sansella, P. K., Gibbs, J. W., and Hanson, G. R. 1984. Opposite responses in the striato-nigral substances P system to D1 and D2 receptor activation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 105:185–188.
Ritter, J. K., Schmidt, C. J., Gibo, J. W., and Hanson, G. R. 1984. Increase of substance P-like immunoreactivity within striatal-nigral structures after subacute metamphetamine treatment. J. Pharmacol. Exper. Ther. 229:487–492.
Hanson, G., Alphs, L., Pradham, S., and Lowenberg, W. 1981. Response of striatonigral substance P system to a dopamine receptor agonist and antagonist. Neuropharmacology. 20:541–548.
Pongdhana, K., Ogawa, N., Hirose, Y., Ono, T., Kosaka, F., and Amori, A. 1987. Effects of ketamine on the cholecystokinin, somatostatin, Substance P, thyrotropin releasing hormone in discrete regions of rat brain. Neurochem. Res. 12:73–77.
Oblin, A., Zikouic, B., and Bartholini, G. 1984. Involvement of the D-2 dopamine receptor in the neuroleptic-induced decrease in nigral substance P. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 105:175–178.
Hong, J. S., Yang, H. Y., and Costa, E. 1978. Substance P content of substantia nigra after chronic treatment with antischizophrenic drugs. Neuropharmacology 17:83–88.
Fuxe, K., Siegel, R. A., Andersson, K., Eneroth, P., Maseagni, F., and Agnati, L. F. 1985. Acute continuous exposure to cigarette smoke produces discrete changes in cholecystokinin and substance P levels in the hypothalamus and preoptic are of the male rat. Acta Physiol. Scand. 125:437–443.
Iversen, L. L., Jessell, T., and Kanazawa, I. 1976. Release and metabolism of substance P in rat hypothalamus. Nature 264:81–83.
Schenker, C., Mroz, E. A., and Leeman, S. 1976. Release of substance P from isolated nerve endings. Nature 264:790–792.
Floor, E. 1983. Substance P release from K+-depolarized rat brain synaptosomes at one second resolution. Brain Res. 279:321–324.
Cheramy, A., Nieoullon, A., Michelot, R., and Glowinski, J. 1977. Effects of intranigral application of dopamine and substance P on the in vivo release of newly synthesized [3H]dopamine in the ipsilateral caudate nucleus of the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 4:105–109.
Cheramy, A., Michelot, R., Leviel, R., Nieoullon, A., Glowinski, J., and Kerdelhue, B. 1978. Effect of immunoneutralization of substance P in the rat substantia nigra on the release of dopamine from dendrites and terminals of dopaminergic neurons. Brain Res. 155:404–408.
Davies, J. and Dray, A. 1976. Substance P in the substantia nigra. Brain Res. 107:623–627.
Waldmeier, P. C., Kam, R., and Stocklin, K. 1978. Increased dopamine metabolism in the rat striatum after infusions of substance P into the substantia nigra. Brain Res. 159:223–227.
Dames, T. A. and Starr, M. S. 1977. Behavioral and biochemical effects of substance P injected into the substantia nigra of the rat. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 29:181–183.
Kelley, A. E. and Iversen, S. D. 1978. Behavioral response to bilateral injection of substance P into the substantia nigra of the rat. Brain Res. 158:474–478.
Stinus, L., Kelley, A., and Iversen, S. D. 1978. Increased spontaneous activity following substance P infusion into A10 dopaminergic area. Nature 276:616–617.
Olpe, R. and Koella, W. P. 1977. Rotating behavior in rats by intranigral application of substance P and an eledroisin fragment. Brain Res. 126:576–579.
Iversen, S. D. 1982. Behavioral effects of substance P through dopaminergic pathways in the brain. Ciba Foundation Symposium, Pitman, London 91:307–324.
Pinnock, R. D., Woodruff, G. N., and Turnbull, M. J. 1983. Actions of substance P, MIF, TRH, and related peptides in the substantia nigra, caudate nucleus, and nucleus accumbens. Neuropharmacology 22:687–696.
Naranjo, J. R. and Del Rio, J. 1984. Locomotor activation induced in rodent by substance P and analogues. Blockade of the effect of substance P by met-enkephalin antiserum. Neuropharmacology 23:1169–1171.
Kelley, A. E., Cador, M., and Stinus, L. 1985. Behavioral analysis of the effect of substance P injected into the ventral mesencephalon on investigatory and spontaneous motor behavior in the rat. Psychopharmacology 85:37–46.
Godwin-Austin, R. B., Lee, P. N., Marnot, M. G., and Stern, G. H. 1982. Smoking and Parkinson's disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat. 45:577–581.
Ward, C. D., Duvoisin, R. L., Ince, S. E., Nutt, J. D., Eldridge, R., and Calle, D. 1983. Parkinson's disease in 65 pairs of twins and in a set of quadruplets. Neurology 33:815–824.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naftchi, N.E., Maker, H., Lapin, E. et al. Acute reduction of brain substance P induced by nicotine. Neurochem Res 13, 305–309 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00972478
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00972478