Abstract
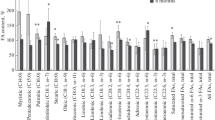
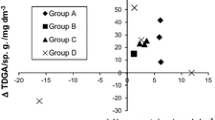
Brain, liver, and adipose lipids were studied in the postmortem tissues of four adrenoleukodystrophy patients who had been treated with a mixture of glyceryl trioleate and trierucate olis (“Lorenzo's Oil”) and compared to 7 untreated ALD patients and 3 controls. The dietary therapy appeared to reduce the levels of saturated very long chain fatty acids in the plasma, adipose tissue and liver; in the brain they were reduced in only one of the four patients. While substantial amounts of erucic acid were present in some of the tissues even 12 months after therapy had been discontinued, the levels in brain did not exceed those in controls at any time. The failure of erucic acid to enter the brain in significant quantity may be a factor in the disappointing results of dietary therapy for adrenoleukodystrophy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moser, H. W., and Moser, A. B. 1989. X-Linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Pages 1511–1532,in Scriver, C. R., Beaudet, A. L., Sly, W. S., Valle, D. (eds.) The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease. Sixth Edition ed. New York: McGraw Hill.
Lazo, O., Contreras, M., Hashmi, M., Stanley, W., Irazu, C., and Singh, I. 1988. Peroxisomal lignoceroyl-CoA ligase deficiency in childhood adrenoleukodystrophy and adrenomyeloneuropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 85:7647–7651.
Mosser, J., Douar, A. M., Sarde, C. O., Kioschis, P., Feil, R., Moser, H., Poustka, A. M., Mandel, J. M., and Aubourg, P. 1993. Putative X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy gene shares unexpected homology with ABC transporters. Nature. 361:726–730.
Moser, H. W., Moser, A. B., Smith, K. D., Bergin, A., Borel, J., Shankroff, J., Stine, O. C., Merette, C., Ott, J., Krivit, W., and Shapiro, E. 1992. E. Adrenoleukodystrophy: Phenotypic variability: Implications for therapy. J Inher Metab Dis. 15:645–664.
Igarashi, M., Schaumburg, H. H., Powers, J., Kishimoto, Y., Kolodny, E., and Suzuki, K. 1976. Fatty acid abnormality in adrenoleukodystrophy. J Neurochem. 26:851–860.
Theda, C., Moser, A. B., Powers, J. M., and Moser, H. W. 1992. Phospholipids in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy white matter. Fatty acid abnormalities before the onset of demyelination. J Neurol Sci. 110:195–204.
Kishimoto, Y., Moser, H. W., Kawamura, N., Platt, M., Pallante, B., and Fenselau, C. 1980. Evidence that abnormal very long chain fatty acids of brain cholesterol esters are of exogenous origin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 96:69–76.
Van Duyn, M. A., Moser, A. B., Brown III, F. R., Sacktor, N., Liu, A., and Moser, H. W. 1984. The design of a diet restricted in saturated very long chain fatty acids: Therapeutic application in adrenoleukodystrophy. Am J Clin Nutr. 40:277–284.
Brown III, F. R., Van Duyn, M. A., Moser, A. B., Schulman, J. D., Rizzo, W. B., Snyder, R. D., Murphy, J. V., Kamoshita, S., Migeon, C. J., and Moser, H. W. 1982. Adrenoleukodystrophy: Effects of dietary restriction of very long chain fatty acids and of administration of carnitine and clofibrate on clinical status and plasma fatty acids. Johns Hopkins Med J. 151:164–172.
Bourre, J. M., Daudu, O., and Baumann, N. 1976. Nervonic acid biosynthesis by erucyl-CoA elongation in normal and quaking mouse brain microsomes. Elongation of other unsaturated fatty acyl-CoAs (mono and polyunsaturated). Biochim Biophys Acta. 424:1–7.
Tsuji, S., Sano-Kawamura, T., Ariga, T., and Miyatake, T. 1985. Metabolism of (17,18-3H2) hexacosanoic acid and (15,16–3h2) lignoceric acid in cultured skin fibroblasts from patients with adrenolcukodystrophy (ALD) and adrenomyeloneuropathy (AMN). J Neurol Sci. 71:359–367.
Rizzo, W. B., Watkins, P. A., Phillips, M. W., Cranin, D., Campbell, B., and Avigan, J. 1986. Adrenoleukodystrophy: Oleic acid lowers fibroblast saturated C22–C26 fatty acids. Neurology. 36:357–361.
Rizzo, W. B., Phillips, M. W., Dammann, A. L., Leshner, R. Y., and Jennings, S. V. K. 1987. Adrenoleukodystrophy: Dietary oleic acid lowers hexacosanoate levels. Ann Neurol. 21:232–239.
Moser, A. B., Borel, J., Odone, A., Naidu, S., Cornblath, D., Sanders, D. B., and Moser, H. W. 1987. A new dietary therapy for adrenoleukodystrophy: Biochemical and preliminary clinical results in 36 patients. Ann Neurol. 21:240–249.
Moser, H. W., Aubourg, P., Cornblath, D., Borel, J., Wu, Y. W., Bergin, A., Naidu, S., and Moser, A. B. The Therapy for X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy. Desnick, R. J. Treatment of Genetic Diseases. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 1991(Chapter 7):111–129.
Rizzo, W. B., Leshner, R. T., Odone, A., Dammann, A. L., Craft, D. A., Jensone, M. E., Jennings, S. S., Davis, S., Jaitly, R., and Sgro, J. A. 1989. Dietary erucic acid therapy for X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Neurology. 39(11):1415–1422.
Odone, A., and Odone, M. 1989. Lorenzo's oil. A new treatment for adrenoleukodystrophy. J. Pediatr Neurosci. 5:55–61.
Rizzo, W. B., Leshner, R. T., Odone, A., Craft, D. A., Jennings, S. S., Jaitly, R., and Segro, J. A. 1990. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: Biochemical and clinical efficacy of dietary erucic acid therapy. Pages 149–162.in: Uziel, G., Wanders, R. J. A., Cappa, M. Adrenoleukodystrophy and other peroxisomal disorders. Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica; (International Congress Series 898).
Uziel, G., Bertini, E., Rimoldi, M., and Gambetti, M. 1990. Italian multicentric dietary therapeutical trial in adrenoleukodystrophy. Pages 163–180.in Uziel, G., Wanders, R. J. A., and Cappa, M. (eds.), Adrenoleukodystrophy and Other Peroxisomal Disorders: Clinical, Biochemical, Genetic and Therapeutic Aspects. International Congress Series 898 ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers.
Kaplan, P. W., Tusa, R. J., Shankroff, J., Heller, J. E., and Moser, H. W. 1993. Visual evoked potentials in adrenoleukodystrophy: A trial with Lorenzo oil. Ann Neurol. 34(2):169–174.
Aubourg, P., Adamsbaum, C., Lavallard-Rousseau, M. C., Rocchiccioli, F., Cartier, N., Jambaque, I., Jakobezak, C., Lemaitre, A., Boureau, F., Wolf, C., and Bougneres, P. F. 1993. A twoyear trial of oleic and erucic acids (“Lorenzo's oil”) as treatment for adrenoleukodystrophy. N Engl J Med. 329:745–752.
Moser, H. W. 1993. Lorenzo oil therapy for adrenoleukodystrophy: A prematurely amplified hope. Ann Neurol. 34(2):121–122.
Rizzo, W. B. 1993. Lorenzo's oil–Hope and disappointment. N Engl J Med. 329(11):801–802.
Moser, H. W. 1993. Lorenzo's oil. Film Review. Lancet. 341:544.
Stephen, A. M., and Wald, N. J. 1990. Trends in individual consumption of dietary fat in the United States. Am J Clin Nutr. 52:457–469.
Simopoulos, A. P. 1989. Executive summary, in Dietary Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids-Biological Effects and Nutritional Essentiality. Galli, C., and Simopoulos, A. P. (Eds). New York: Plenum; 391–404.
Borel, J. S. 1992. Adrenoleukodystrophy and Related Peroxisomal Disorders. In: Ekvall, S. (Ed.). Pediatric Nutrition in Developmental Disorders and Chronic Diseases. : Oxford University; 1992(in press).
Borel, J., and Cohen, J. 1990. Editors. ALD/AMN Diet Cookbook. Second Edition ed. DeKalb; Baltimore: United Leukodystrophy Foundation and The Kennedy Institute; 1–274.
Folch, J., Lees, M., and Stanley, S. 1957. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 226:497–509.
Vance, D. E., and Sweely, C. C. 1967. J Lipid Res. 8:621–630.
Moser, H. W., and Moser, A. B. 1991. Measurements of Saturated Very Long Chain Fatty Acids in Plasma. Pages 177–191.in: Hommes, F. (ed). Techniques in Diagnostic Human Biochemical Genetics. Chapter 12: New York: Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Taketomi, T., Hara, A., Kitazawa, N., Takada, K., and Nakamura, H. 1987. An adult case of adrenoleukodystrophy with features of olivo-ponto-cerebellar atrophy: 2. lipid abnormalities. Jpn J Exp Med. 57:59–70.
Reinecke, C. J., Knoll, D. P., Pretorius, P. J., Steyn, H. S., and Simpson, R. H. W. 1985. The correlation between biochemical and histopathological findings in adrenoleukodystrophy. J Neurol Sci. 70:21–38.
Foote, S., Vollrath, D., Hilton, A., and Page, D. C. 1992. The human Y chromosome: Overlapping DNA clones spanning the euchromatic region. Science. 258:60–66.
Bourre, J. M., Dumont, O., Pascal, G., and Durand, G. 1993. Dietary alpha-linolenic acid at 1.3 g/kg maintains maximal docosahexaenoic acid concentration in brain, heart and liver of adult rats. J Nutr. 123:1313–1319.
Li, J., Wetzel, M. G., and O'Brien, P. J. 1992. Transport of n-3 fatty acids from the intestine to the retina in rats. J Lipid Res. 33:539–548.
Nilsson, A., Hjelte, L., and Strandvik, B. 1992. Incorporation of dietary [14C]arachidonic acid and [3H]eicosapentaenoic acid into tissue lipids during absorption of a fish oil emulsion. J Lipid Res. 33:1295–1305.
Scott, B. L., and Bazan, N. G. 1989. Membrane docosahexaenoate is supplied to the developing brain and retina by the liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 86:2093–2097.
Zinkham, W. H., Kickler, T., Borel, J., and Moser, H. W. 1993. Lorenzo's oil and thrombocytopenia in patients with adrenoleukodystrophy. N Engl J Med. 328(15):1126–1127.
Moser, H. W., Kok, F., Neumann, S., Borel, J., Bergin, A., Darwish, Mostava S., Panoscha, R., Davoli, C. T., Shankroff, J., and Smith, K. D. Adrenoleukodystrophy update: Genetics and effect of Lorenzo's oil therapy in asymptomatic patients. Int Pediatr, in press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Special issue dedicated to Dr. Marjorie B. Lees.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rasmussen, M., Moser, A.B., Borel, J. et al. Brain, liver, and adipose tissue erucic and very long chain fatty acid levels in adrenoleukodystrophy patients treated with glyceryl trierucate and trioleate oils (Lorenzo's Oil). Neurochem Res 19, 1073–1082 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00968719
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00968719