Abstract
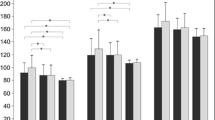
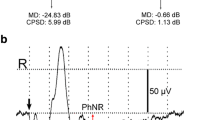
A total of 20 patients with unilateral acute optic neuritis were studied. Each patient had experienced the recent onset of a decrease in visual acuity, a relative afferent papillary defect, a relative or absolute central scotoma and a colour-vision defect. The pattern-reversal electroretinogram (PERG) of each patient was analysed with regard to the amplitude of the positive and negative components. During the acute stage the amplitude of the positive component was reduced in all patients and that of the negative, in 18 of 20 cases. Parallel to clinical recovery, a steady increase was observed in the amplitude of the positive component to normal values; no statistical differences between affected and fellow eyes was found. In contrast, the amplitude of the negative component remained significantly reduced after clinical recovery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arden GB, Vaegan (1983) Electroretinograms evoked in man by local uniform or patterned stimulation. J Physiol 341:85–104
Arden GB, Carter RM, Macfarlan A (1984) Pattern and Ganzfield electroretinograms in macular disease. Br J Ophthalmol 68:878–884
Berdjis H, Gedeon B, Staerk N, Jacobi G (1984) Muster-ERG und -VECP nach Optikusneuritis im Kindesalter. Klin Monatsbl Augenheilkd 184:533–535
Berninger TA (1986) The pattern electroretinogram and its contamination. Clin Vis Sci 1:185–190
Berninger TA, Arden GB (1989) The pattern electroretinogram (PERG). Eye 2 [Suppl]:257–283
Berninger TA, Heider W (1989) Electrophysiology and perimetry in acute retrobulbar neuritis. Doe Ophthalmol 71:293–305
Berninger TA, Schuurmans RP (1985) Spatial tuning of the pattern ERG across temporal frequency. Doc Ophthalmol 61:17–25
Bobak P, Bodis-Wollner I, Harnois C, Maffei L, Mylin L, Podos S, Thornton J (1983) Pattern electroretinograms and visualevoked potentials in glaucoma and multiple sclerosis. Am J Ophthalmol 96:72–83
Celesia GG, Kaufman D (1985) Pattern ERG's and visual evoked potentials in maculopathies and optic nerve diseases. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 26:726–735
Dawson WW, Maida T, Rubin M (1982) Human pattern evoked retinal responses are altered by optic atrophy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 22:796–803
Drasdo N, Cox W, Thompson DA (1987) Defects of image degradation on retinal illuminance and pattern responses to checkerboard stimuli. Doc Ophthalmol 66:267–273
Fiorentini A, Maffei L, Pirchio M, Spinelli D, Porciatti V (1981) The ERG in response to alternating gratings with disease of the peripheral visual pathways. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 21:490–493
Groneberg A, Teping C (1980) Topodiagnostik von SehstSehstörungenörungen durch Ableitung retinaler und kortikaler Antworten auf Umkehr-Kontrastmuster. Ber Dtsch Ophthalmol Ges 77:409–417
Harrison JM, O'Connor PS, Young SL, Kincaid M, Bentley R (1984) The pattern ERG in man following surgical resection of the optic nerve. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 28:492–499
Hess RF, Baker CL Jr (1984) Human pattern-evoked electroretinogram. J Neurophysiol 51:939–951
Holder GE (1987) Significance of abnormal pattern electroretinogram in anterior visual pathway dysfunction. Br J Ophthalmol 71:166–171
Holländer H, Bisti S, Maffei L, Hebel R (1984) Electroretinographic responses and retrograde changes of retinal morphology after intracranial optic nerve section: a quantitative analysis in the cat. Exp Brain Res 55:483–493
Korth M (1983) Pattern-evoked responses and luminance responses in human electroretinogram. J Physiol 337:451–469
Lightman S, McDonald WI, Bird AC, Francis DA, Hoskins A, Batchelor JR, Halliday AM (1987) Retinal venous sheathing in optic neuritis. Brain 110:405–414
Maffei L, Fiorentini A, Bisti S, Hollander H (1985) Pattern ERG in the monkey after section of the optic nerve. Exp Brain Res 59:423–425
Persson HE, Wanger P (1984) Pattern-reversal electroretinograms and visual evoked cortical potentials in multiple sclerosis. Br J Ophthalmol 68:760–764
Plant GT, Hess RF, Thomas SJ (1986) The pattern evoked electroretinogram in optic neuritis. Brain 109:469–481
Porciatti V, Berger GP von (1984) Pattern electroretinogram and visually evoked cortical potentials in optic nerve disease: early diagnosis and prognosis. Doc Ophthalmol Proc Ser 40:117–123
Regan D, Milner BA, Heron JR (1976) Delayed visual evoked perception and delayed visual evoked potentials in the spinal form of multiple sclerosis and in retrobulbar neuritis. Brain 99:43–66
Rucker W (1945) Sheathing of the retinal veins in multiple sclerosis. J Am Med Assoc 127:970–973
Ryan S, Arden GB (1988) Electrophysiological discrimination between retinal and optic nerve disorders. Doc Ophthalmol 68:247–253
Seiple W, Price MJ, Kupersmith M, Siegel IM, Carr ER (1983) The pattern electroretinogram in optic nerve disease. Ophthalmology 90:1127–1132
Trick GL (1985) Retinal potentials in patients with primary open angle glaucoma: physiological evidence for temporal frequency tuning of pattern reversal retinal potentials. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 23:1750–1758
Weinstein GW, Arden GB, Hitchings RA, Ryan S, Calthorpe CM, Odom JV (1988) The pattern electroretinogram (PERG) in ocular hypertension. Arch Ophthalmol 106:923–931
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berninger, T.A., Heider, W. Pattern electroretinograms in optic neuritis during the acute stage and after remission. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 228, 410–414 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00927252
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00927252