Abstract
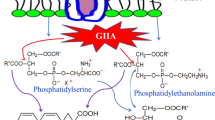
The influence of quercetin, chlorpromazine, aristolochic acid, and indomethacin on group I phospholipase A2 (PLA2) from porcine pancreas and on group II PLA2 fromVipera russelli was compared. Quercetin and chlorpromazine were found to inhibit PLA2 activity in lower concentrations (< 100μM), while aristolochic acid and indomethacin were inhibitory only in higher concentrations (> 100μM). The order of potency againstVipera PLA2 was: quercetin >chlorpromazin aristolochic acid > indomethacin, while the order of potency against pancreatic PLA2 was: chlorpromazine > aristolochic acid > indomethacin> quercetin. Thus, quercetin was a potent inhibitor towards group II PLA2 (IC50=2μM), but a very weak inhibitor against group I PLA2, with maximum 30% inhibition. Aristolochic acid and indomethacin were three to four times more potent towards group II PLA2 than towards group I PLA2, while chlorpromazine was equally potent towards the two PLA2 types. Quercetin and chlorpromazine were also tested against two PLA2 fractions purified from the plasma of septic shock patients; chlorpromazine was then equally potent towards the two PLA2 fractions, whereas quercetin was a potent inhibitor of only one of the two PLA2 fractions (IC50=4μM). Together, these results indicate that (1) different PLA2 inhibitors have different potency depending on which type of PLA2 they are used against, (2) quercetin selectively inhibits group II PLA2 and may therefore be used to discriminate between different PLA2 forms in biological materials, and (3) both PLA2 of group I and group II are present in septic shock plasma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang, J., J. H. Musser, andH. McGregor. 1987. Phospholipase A2: Function and pharmacological regulation.Biochem. Pharmacol. 36:2429–2436.
Pruzanski, W., E. C. Keystone, B. Sternby, C. Bombardier, K. M. Snow, andP. Vadas. 1988. Serum phospholipase A2 correlates with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis.J. Rheumatol. 15:1351–1355.
Vadas, P., W. Pruzanski, andE. Stefanski. 1988. Extracellular phospholipase A2: Causative agent in circulatory collapse of septic shock?Agents Actions 24:320–325.
Crowl, R. M., T. J. Stoller, R. R. Conroy, andC. R. Stoner. 1991. Induction of phospholipase A2 gene expression in human hepatoma cells by mediators of the acute phase response.J. Biol. Chem. 266:2647–2651.
Pruzanski, W., andP. Vadas. 1991. Phospholipase A2-a mediator between proximal and distal effectors of inflammation.Immunol. Today 12:143–146.
Davidson, F. F., andE. A. Dennis. 1990. Evolutionary relationships and implications for the regulation of phospholipase A2 from venom to human secreted forms.J. Mol. Evol. 31:228–238.
Kramer, R. M., C. Hession, B. Johansen, G. Hayes, P. McGray, E. P. Chow, R. T. Tizard, andR, B. Pepinsky. 1989. Structure and properties of a human nonpancreatic phospholipase A2.J. Biol. Chem. 264:5768–5774.
Ono, T., H. Tojo, S. Kuramitsu, H. Kagamiyama, andM. Okamoto. 1988. Purification and characterization of a membrane-associated phospholipase A2 from rat spleen. Its comparison with a cytosolic phospholipase A2 S-1.J. Biol. Chem. 263:5732–5738.
Nakano, T., andH. Arita. 1990. Enhanced expression of group II phospholipase A2 gene in the tissues of endotoxin shock rats and its suppression by glucocorticoid.FEBS Lett. 273:23–26.
Matsuda, Y., M. Ogawa, T. Shibata, K. Nakaguchi, J.-I. Nishijima, C. Wakasugi, andT. Mori. 1987. Distribution of immunoreactive pancreatic phospholipase A2 (IPPL-2) in various human tissues.Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 58:281–284.
Wright, G. W., C. E. Ooi, J. Weiss, andP. Elsbach. 1990. Purification of a cellular (granulocyte) and extracellular (serum) phospholipase A2 that participate in the destruction ofEscherichia coli in a rabbit inflammatory exudate.J. Biol. Chem. 265:6675–6681.
Minami, T., H. Tojo, Y. Shinomura, S. Tarui, andM. Okamoto. 1992. Raised serum activity of phospholipase A2 immunochemically related to group II enzyme in inflammatory bowel disease: Its correlation with disease activity of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.Gut 33:914–921.
Vadas, P., K. Scott, G. Smith, I. Rajkovic, E. Stefanski, B. D. Schouten, R. Singh, andW. Pruzanski. 1992. Serum phospholipase A2 enzyme activity and immunoreactivity in a prospective analysis of patients with septic shock.Life Sci. 50:807–811.
Kitigawa, M., T. Hayakawa, T. Kondo, T. Shibata, Y. Sakai, H. Sobajima, H. Ishiguro, M. Tanikawa, Y. Nakae, S. Kameya, andA. Noda. 1991. Elevation of serum phospholipase A2 in patients at an intensive care unit.Int. J. Pancreatol. 10:279–286.
Marshall, L. A., J. Bauer, M. L. Sung, andJ. Y. Chang. 1991. Evaluation of antirheumatic drugs for their effect in vitro on purified human synovial fluid phospholipase A2.J. Rheumatol. 18:59–65.
Mobilio, D., andL. A. Marshall. 1989. Recent advances in the design and evaluation of inhibitors of phospholipase A2.Annu. Rep. Med. Chem. 24:157–166.
Patriarca, P., S. Beckerdite, andP. Elsbach. 1972. Phospholipase and phospholipid turnover inEscherichia coli spheroplasts.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 260:593–600.
Lindahl, M., C. de Wit, B. Weström, H. von Schenck, andC. Tagesson. 1991. Demonstration of a phospholipase A2 inhibitor in human plasma and in plasma from the european hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus).Int. J. Biochem. 23:287–292.
Vadas, P., E. Stefanski, andW. Pruzanski. 1986. Potential therapeutic efficacy of inhibitors of human phospholipase A2 in septic shock.Agents Actions 19:194–202.
Lindahl, M., H. von Schenck, andC. Tagesson. 1989. Isolation and characterization of phospholipase A2 from rat lung with affinity chromatography and two-dimensional gel electrophoresis.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1005:282–288.
Nicholson, D. P. 1983. Corticosteroids in treatment of septic shock and the adult respiratory distress syndrome.Med. Clin. North Am. 67:717–724.
Chang, J., M. D. Skowronek, M. L. Cherney, andA. J. Lewis. 1984. Differential effects of putative lipoxygenase inhibitors on arachidonic acid metabolism in cell-free and intact cell preparations.Inflammation 8:143–155.
Vishwanath, B. S., R. M. Kini, andT. V. Gowda. 1987. Characterization of three edemainducing phospholipase A2 enzymes from habu (Trimeresurus flavoviridis) venom and their interaction with the alkaloid aristolochic acid.Toxicon 25:501–515.
Vishwanath, B. S., A. G. A. Rao, andT. V. Gowda. 1987. Interaction of phospholipase A2 fromVipera russelli venom with aristolochic acid: A circular dichroism study.Toxicon 25:939–946.
Rosenthal, M. D., B. S. Vishwanath, andR. C. Franson. 1989. Effects of aristolochic acid on phospholipase A2 activity and arachidonate metabolism of human neutrophils.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1001:1–8.
Waite, M. 1987. Pancreatic and snake venom phospholipases A2.In The Phospholipases. Handbook of Lipid ReseArch. Vol. 5. D. J. Hanahan, editor. Plenum Press, New York. 155–190.
Lindahl, M. 1990. Phospholipase A2 activation and inflammatory reactions in the lung. Linköping University Medical Dissertations No. 323, Linköping, Sweden.
Calhoun, W., J. Yu, A. Sung, T. T. Chau, L. A. Marshall, B. M. Weichman, andR. P. Carlson. 1989. Pharmacologic modulation of D-49 phospholipase A2-induced paw edema in the mouse.Agents Actions 27:418–421.
Lanni, C., andE. L. Becker. 1985. Inhibition of neutrophil phospholipase A2 by p-bromophenacyl bromide, nordihydroguaiaretic acid, 5,8,11,14-eicostetetrayenoic acid and quercetin.Int. Arch. Allergy. Appl. Immun. 76:214–217.
Fawzy, A. A., B. S. Vishwanath, andR. C. Franson. 1988. Inhibition of human nonpancreatic phospholipase A2 by retinoids and flavonoids. Mechanism of action.Agents Actions 25:394–400.
Baur, M., T. O. Schmid, andB. Landauer. 1989. Role of phospholipase A in multiorgan failure with special reference to ARDS and acute renal failure (ARF).Klin. Wochenschr. 67:196–202.
Hoffmann, G. E., andW. G. Guder. 1989. Serum phospholipase-regulatory and pathophysiological aspects.Klin. Wochenschr. 67:144–148.
Vadas, P., W. Pruzanski, E. Stefanski, andB. Sternby. 1990. Compartmental heterogeneity of soluble phospholipase A.Inflammation 14:173–183.
Eskola, J. U., T. J. Nevalainen, andP. Kortesuo. 1988. Immunoreactive pancreatic phospholipase A2 and catalytically active phospholipase A2 in serum from patients with acute pancreatitis.Clin. Chem. 34:1052–1054.
Pruzanski, W., S. Saito, E. Stefanski, andP. Vadas. 1991. Comparison of group I and II soluble phospholipase A2 activities on phagocytic functions of human polymorphonuclear and mononuclear phagocytes.Inflammation 15:127–135.
Hanasaki, K., andH. Arita. 1992. Characterization of a high affinity binding site for pancreatic-type phospholipase A2 in the rat. Its cellular and tissue distribution.J. Biol. Chem. 267:6414–6420.
Murakami, M., I. Kudo, andK. Inoue. 1991. Eicosanoid generation from antigen-primed mast cells by extracellular mammalian 14-kDa group II phospholipase A2.FEBS Lett. 294:247–251.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lindahl, M., Tagesson, C. Selective inhibition of group II phospholipase A2 by quercetin. Inflammation 17, 573–582 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00914195
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00914195