Abstract
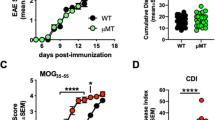
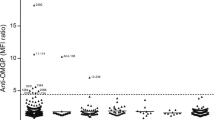
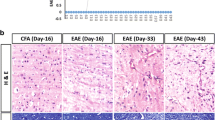
Multiple sclerosis (MS), an autoimmune disease of the central nervous system (CNS) characterized by primary demyelination, is believed to result from an autoimmune attack against myelin components. In view of their ability to induce experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), an animal model for MS, the quantitatively major myelin proteins — myelin basic protein (MBP) and proteolipid protein (PLP) — have been extensively studied as the relevant primary antigens in MS, and therapeutic approaches have been targeted to counteract autoimmune reactivity to MBP and PLP. Accordingly, copolymer 1, a random synthetic amino acid copolymer cross-reactive with MBP and highly protective against the induction of EAE with MBP or PLP, is now being extensively tested in clinical studies as a therapeutic agent for MS. However, increasing evidence suggests that autoimmune reactivity against other CNS-specific myelin proteins could also be involved in the pathogenesis of MS. In this context, we have demonstrated that peripheral blood lymphocytes from patients with MS respond predominantly to myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) rather than to MBP or PLP, suggesting an important role for cell reactivity against MOG in the pathogenesis of MS. We have demonstrated that T-cell reactivity to MOG can also be pathogenic by inducing neurological disease in H-2u and H-2b mice with the same peptide of MOG, pMOG 35–55. Most interestingly, the expression of the disease differed with the different MHC backgrounds. Induction of a differentially expressed disease in different strains of mice with the same myelin antigen makes this new model particularly relevant to MS, where different expression of the disease is seen in different patients. Therefore, notwithstanding the importance of the autoimmune reactivity to MBP and PLP in MS, the potentially pathogenic autoimmune reactivity to MOG must now also be taken into consideration in therapeutic approaches to MS. In this context, we have investigated the possible effect of copolymer 1 treatment on autoimmune reactivity to MOG and on the development of EAE induced by MOG. Copolymer 1 was found to inhibit the binding of MOG peptides to MHC molecules, as well as the proliferation of MOG-reactive T cells, in a dose-dependent manner. In parallel, injection of copolymer 1 concomitantly with the encephalitogenic MOG peptide exerted a strong protective effect against the development of EAE. These preliminary data on the effect of copolymer 1 on the autoimmune response to MOG in mice indicate that copolymer 1 may also be effective in cases of MS where the autoimmune response to MOG prevails, and should therefore be further investigated in this context.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abo S, Bernard CCA, Webb M, et al (1993) Preparation of highly purified human myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein in quantities sufficient for encephalitogenicity and immunogenicity studies. Int Biochem Mol Immunol 30:945–958
Amiguet P, Gardinier M V, Zanetta JP, et al (1992) Purification and partial structural and functional characterization of mouse myelin/oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG). J Neurochem 58:1676–1682
Amor S, Groome N, Linington C, et al (1994) Identification of epitopes of myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein for the induction of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in SJL and Biozzi AB/H mice. J Immunol 153:4349–4356
Ben-Nun A, Wekerle H, Cohen IR (1981) The rapid isolation of clonable antigen-specific T lymphocyte lines capable of mediating autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Eur J Immunol 11:195–199
Birling M-C, Roussel G, Nussbaum F, et al (1993) Biochemical and immunohistochemical studies with specific polyclonal antibodies directed against bovine myelin/oligodendrocyte glycoprotein. Neurochem Res 18:937–945
Brunner C, Lassmann H, Waehneldt TV, et al (1989) Differential ultrastructural localization of myelin basic protein, myelin/oligodendroglial glycoprotein, and 2′, 3′-cyclic nucleotide 3′-phosphodiesterase in the CNS of adult rats. J Neurochem 52:296–304
Burger D, Steck AJ, Bernard CCA, et al (1993) Human myelin/oligodendrocyte glycoprotein: a new member of the L2/HNK-1 family. J Neurochem 61:1822–1827
Fridkis-Hareli M, Teitelbaum D, Gurevich E, et al (1994) Direct binding of myelin basic protein and synthetic copolymer 1 to class II major histocompatibility complex molecules on living antigen-presenting cells — specificity and promiscuity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:4872–4876
Gardinier MV, Amiguet P, Linington C, et al (1992) Myelin/oligodendrocyte glycoprotein is a unique member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. J Neurosci Res 33:177–187
Glynn P, Linington C (1989) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of autoimmune demyelination in the central nervous system. Crit Rev Neurobiol 4:367–385
Gunn C, Suckling AJ, Linington C (1989) Identification of a common idiotype on myelin-oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-specific autoantibodies in chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 23:101–108
Kerlero de Rosbo N, Bernard CCA (1989) Multiple sclerosis brain immunoglobulins stimulate myelin basic protein degradation in human myelin: a new cause of demyelination. J Neurochem 53:513–518
Kerlero de Rosbo N, Honegger P, Lassmann H, et al (1990) Demyelination induced in aggregating brain cell cultures by a monoclonal antibody against myelin/oligodendrocyte glycoprotein. J Neurochem 55:583–587
Kerlero de Rosbo N, Milo R, Lees MB, et al (1993) Reactivity to myelin antigens in multiple sclerosis: peripheral blood lymphocytes respond predominantly to myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein. J Clin Invest 92:2602–2608
Kerlero de Rosbo N, Mendel I, Ben-Nun A (1995) Chronic relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis with a delayed onset and an atypical clinical course, induced in PL/J mice by myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG)-derived peptide: preliminary analysis of MOG T cell epitopes. Eur J Immunol 25:985–993
Kuchroo VK, Sobel RA, Yamamura T, et al (1991) Induction of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by myelin proteolipid protein-specific T cell clones and synthetic peptides. Pathobiology 59:305–312
Lassmann H, Linington C (1987) The role of antibodies against myelin surface antigens in demyelination in chronic EAE. In: Crescenzi GS (ed) A multidisciplinary approach to myelin diseases. Plenum Press, New York, pp 219–225
Lassmann H, Brunner C, Bradl M, et al (1988) Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: the balance between encephalitogenic T lymphocytes and demyelinating antibodies determines size and structure of demyelinated lesions. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 75:566–576
Lebar R, Boutry J-M, Vincent C, et al (1976) Studies on autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the guinea pig. II. An in vitro investigation on the nature, properties and specificities of the serum-demyelinating factor. J Immunol 116:1439–1446
Lebar R, Vincent C, Fischer-Le Boubennec E (1979) Studies on autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the guinea pig. II. A comparative study of two autoantigens of central nervous system. J Neurochem 32:1451–1460
Lebar R, Lubetzki C, Vincent C, et al (1986) The M2 autoantigen of central nervous system myelin, a glycoprotein present in oligodendrocyte membrane. Clin Exp Immunol 66:423–443
Linington C, Lassmann H (1987) Antibody responses in chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: correlation of serum demyelinating activity with antibody titre to the myelin/oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG). J Neuroimmunol 17:61–69
Linington C, Webb M, Woodhams PL (1984) A novel myelin-associated glycoprotein defined by a mouse monoclonal antibody. J Neuroimmunol 6: 387–396
Linington C, Bradl M, Lassmann H, et al (1988) Augmentation of demyelination in rat acute allergic encephalomyelitis by circulating mouse monoclonal antibodies directed against a myelin/oligodendrocyte glycoprotein. Am J Pathol 130:443–454
Mendel I, Kerlero de Rosbo N, Ben-Nun A (1995) A myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein peptide induces typical chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in H-2b mice: fine specificity and T cell receptor V beta expression of encephalitogenic T cells. Eur J Immunol 25:1951–1959
Mohktarian F, McFarlin DE, Raine CS (1984) Adoptive transfer of myelin basic protein-specific T cells produces chronic relapsing demyelinating disease in mice. Nature 309:356–358
Pham-Dinh D, Mattei M-G, Nussbaum J-L, et al (1993) Myelin/oligodendrocyte glycoprotein is a member of a subset of the immunoglobulin superfamily encoded within the major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:7990–7994
Piddlesden S, Lassmann H, Zimprich F, et al (1993) The demyelinating potential of antibodies to myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein is related to their ability to fix complement. Am J Pathol 143:555–564
Raine C (1984) Biology of disease. The analysis of autoimmune demyelination: its impact upon multiple sclerosis. Lab Invest 50:608–635
Richert J (1992) Human T cell recognition of myelin basic protein peptides. In: Martenson RE (ed) Myelin: biology and chemistry. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Fla, pp 833–847
Satoh J, Sakai K, Endoh M, et al (1987) Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis mediated by murine encephalitogenic T cell lines specific for myelin proteolipid apoprotein. J Immunol 138:179–184
Schluesener HJ, Sobel RA, Linington C, et al (1987) A monoclonal antibody against a myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein induces relapses and demyelination in central nervous system autoimmune disease. J Immunol 139:4016–4021
Schwerer B, Kitz K, Lassmann H, et al (1984) Serum antibodies against glycosphingolipids in chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Demonstration by ELISA and relation to serum in vivo demyelinating activity. J Neuroimmunol 7:107–119
Scolding NJ, Frith S, Linington C, et al (1989) Myelin-oligodendrocyte glycoprotein is a surface marker of oligodendrocyte maturation. J Neuroimmunol 22:169–176
Sela M, Arnon R, Teitelbaum D (1990) Suppressive activity of Cop-1 in EAE and its relevance to multiple sclerosis. Bull Inst Pasteur 88:303–314
Sun J, Link H, Olsson T, et al (1991) T and B cell responses to myelinoligodendrocyte glycoprotein in multiple sclerosis. J Immunol 146:1490–1495
Teitelbaum D, Meshorer A, Hirshfeld T, et al (1971) Suppression of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by a synthetic polypeptide. Eur J Immunol 1:242–248
Veen RC van der, Trotter JL, Clark HB, et al (1989) The adoptive transfer of chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis with lymph node cells sensitized to myelin proteolipid protein. J Neuroimmunol 21:183–191
Xiao BG, Linington C, Link H (1991) Antibodies to myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with multiple sclerosis and controls. J Neuroimmunol 31:91–96
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported in part by the Israel Academy of Science and Humanities, the National Multiple Sclerosis Society, the French-Israeli Cooperative Research Program, and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben-Nun, A., Mendel, I., Bakimer, R. et al. The autoimmune reactivity to myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) in multiple sclerosis is potentially pathogenic: Effect of copolymer 1 on MOG-induced disease. J Neurol 243 (Suppl 1), S14–S22 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00873697
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00873697