Abstract
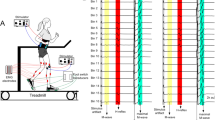
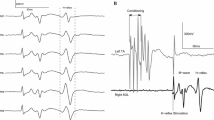
In the present study, we investigated whether weak (10% of maximal voluntary contraction) tonic dorsiflexion (DF) and plantarflexion (PF) affects the two conventional parameters used for evaluating the excitability of the soleus motoneuron (MN) pool, i.e. the ratio of the threshold of H-reflex to that of M-response (Hth:Mth) and the ratio of the maximal amplitude of H-reflex to that of M-response (Hmax:Mmax) in human subjects. The results showed that the Hmax:Mmax decreased during DF and increased during PF compared with that during rest, whereas no clear alteration was observed in Hth:Mth. These results are consistent with the scheme proposed by earlier workers, who have argued that neither inhibitory nor facilitatory effects of the conditioning stimulus apply to specific spinal reflex circuits occurring around the threshold of the test H-reflex. It is suggested, therefore, that the conventional use of the Hth:Mth ratio as a parameter reflecting the excitability of the MN pool should be reconsidered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boorman G, Hullinger M, Lee RG, Tako T, Tanaka R (1991) Reciprocal Ia inhibition in patients with spinal spasticity. Neurosci Lett 127:57–60
Casabona A, Polizzi M, Perciavalle V (1990) Difference in Hreflex between athletes trained for explosive contractions and non-trained subjects. Eur J Appl Physiol 61:26–32
Crone C, Hultborn H, Maziéres L, Nielsen J, Pierrot-Deseilligny E (1990) Sensitivity of monosynaptic test reflex to facilitation and inhibition as a function of the test reflex size: a study in man and the cat. Exp Brain Res 81:35–44
Davies TW, Lader MH (1985) Determination of excitability in human proprioceptive reflexes: analysis and characteristics of EMG threshold of postural muscle. Brain Res 60:375–380
Davies TW (1985) Reciprocal inhibition of proprioceptive reflexes in man revealed by a threshold shift technique. Neurosci Lett 60:375–380
Funase K, Imanaka K, Nishihira Y Excitability of the soleus motoneuron pool revealed by the developmental slope of the H-reflex as reflex gain. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol (in press)
Henneman E (1981) Recruitment of motoneurons: the size principle. In: Desmedt JE (ed) Progress in neurophysiology. Karger, Basel, pp 27–60
Henneman E, Somjen G, Carpenter DO (1965) Functional significance of cell size in spinal neurons. J Neurophysiol 28:560–580
Kagamihara Y, Komiyama T, Ohi K, Tanaka R (1992) Facilitation of agonist motoneuron upon initiation of rapid and slow voluntary movements in man. Neurosci Res 14:1–11
Kayser B, Bökenkamp R, Binzoni T (1993) Alpha-motoneuron excitability at high altitude. Eur J Appl Physiol 66:1–4
Meinck H (1980) Facilitation and inhibition of the human H reflex as a function of the amplitude of the control reflex. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 48:203–211
Nielsen J, Kagamihara Y, Crone C, Hultborn H (1992) Central facilitation of Ia inhibition during tonic ankle dorsiflexion revealed after blockade of peripheral feedback. Exp Brain Res 88:651–656
Nielsen J, Crone C, Hultborn H (1993) H-reflex are smaller in dancers from The Royal Danish Ballet than well-trained athletes. Eur J Appl Physiol 66:116–121
Rothwell JC, Day BL, Berardelli A, Marsden C (1984) Effects of motor cortex stimulation on spinal interneurones in intact man. Exp Brain Res 54:382–384
Schieppati M (1987) The Hoffmann reflex: a means of assessing spinal reflex excitability and its descending control in man. Prog Neurobiol 28:345–376
Schomburg ED (1990) Spinal sensorimotor systems and their supraspinal control. Neurosci Res 7:265–340
Shindo M (1990) Segmental function and their central control. Jpn-Dtsche Med Ber 35:180–192
Sindo M, Harayama H, Kondo K, Yanagisawa N, Tanaka R (1984) Changes in reciprocal Ia inhibition during voluntary contraction in man. Exp Brain Res 53:400–408
Tanaka R (1976) Reciprocal Ia inhibition and voluntary movements in man. In: Homma S (ed) Progress in brain research. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 291–302
Tanaka R (1986) The Hoffmann-reflex. J Physiol Soc Jpn 48:719–734
Vallbo AB (1970) Discharge patterns in human muscle spindle afferents during isometric voluntary contractions. Acta Physiol Scand 80:552–566
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Funase, K., Imanaka, K., Nishihira, Y. et al. Threshold of the soleus muscle H-reflex is less sensitive to the change in excitability of the motoneuron pool during plantarflexion or dorsiflexion in humans. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 69, 21–25 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00867922
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00867922