Summary
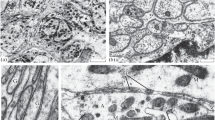
InLumbricus terrestris the wall of the pharynx is built up from obliquely striated longitudinal and circular muscle layers. The occurrence of perikarya and nerve bundles showing green fluorescence suggests the presence of aminergic innervation in the pharynx. A significant number of chemical synapses were detected in the neuropil among axon terminals. The junctional gap is generally 100–300 nm wide in type I junctions which resemble the cholinergic motor endplates of vertebrate skeletal muscle. A narrow junctional gap of about 25 nm is characteristic of the “close contacts” in the type II neuromuscular junction. Agranular spherical vesicles, together with small and large dense-cored granules, fill in these axon terminals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambache N, Dixon AStJ, Wright EA (1945) Some observations on the physiology and pharmacology of the nerve endings in the crop and gizzard of the earthworm, with special reference to the effects of cooling. J Exp Biol 21:46–57
Benedeczky I, Halasy K, Csoknya M (1987) Fine structure of the neuromuscular junctions in the alimentary tract of phylogenetically different animal species. Acta Biol Hung 38:363–382
Clark JL (1956) On the nervous system ofLumbricus terrestris. Proc R Soc 8:343–356
Couteaux R (1973) Motor end-plate structure. In: Bourne GH (ed) The structure and function of muscle. Academic Press, New York, London
Csoknya M, Benedeczky I (1987) Structure and innervation of the oesophagus of the earthworm (Lumbricus terrestris L.). Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch 101:1052–1067
Dechant E (1906) Beitrag zur Kenntnis des peripheren Nervensystems des Regenwurms. Arb Zool Inst Univ Wien 16:361–382
de la Torre JC, Surgeon JW (1976) A methodological approach to rapid and sensitive monoamine histofluorescence using a modified glyoxilic acid technique: the SPG method. Histochemistry 49:81–93
Farnesi RM, Vagnetti D (1975) The fine structure of the myoneural junctions in the body wall muscles inBranchiobdela pentodonta Whit. (Annelida, Oligochaeta), Anat Rec 182:91–102
Gabella G (1979) Innervation of the gastrointestinal tract. Int Rev Cytol 59:129–193
Gábriel R, Halasy K, Csoknya M (1988) Visualization of neurons by NADH-diaphorase staining in myenteric plexus of some invertebrate and vertebrate species. Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch 102:760–769
Gardy M (1957) Studies on the digestive tract ofLumbricus terrestris. Biol Rev City Coll New York 19:2–7
Geffen LB, Livett BG (1971) Synaptic vesicles in sympathetic neurons. Physiol Rev 51:98–157
Halasy K, Benedeczky I, Csoknya M (1988) Ultrastructural comparison of enteric neuromuscular junctions in some invertebrates. Symp Biol Hung 36:199–211
Hess WN (1925) Nervous system of the earthworm,Lumbricus terrestris L. J Morphol 40:235–259
Hickman CP, Hickman CP, Hickman F (1979) The segmented worms. In: Integrated principles of zoology. CV Mosby, St Louis, Toronto, London, pp 300–326
Hidaka T, Ito Y, Kuriyama H (1969) Membrane properties of the somatic muscle (obliquely striated muscle) of earthworm. J Exp Biol 50:387–403
Komuro T, Baluk P, Burnstock G (1982) An ultrastructural study of nerve profiles in the myenteric plexus of the rabbit colon. Neurosci 7:295–305
Lankester ER (1865) The anatomy of the earthworm. Q J Microsc Sci NS 3:99–104
Mill PJ, Knapp MF (1970) Neuromuscular junctions in the body wall muscles of the earthworm,Lumbricus terrestris (L.). J Cell Sci 7:263–271
Millott N (1943a) The visceral nervous system of the earthworm. I. Nerves controlling the tone of the alimentary canal. Proc R Soc Lond B 131:271–295
Millott N (1943b) The visceral nervous system of the earthworm. II. Evidence of chemical transmission and the action of sympatheticomimetic and para-sympatheticomimetic drugs on the tone of the alimentary canal. Proc R Soc Lond B 131:362–373
Millott N (1944) The visceral nervous system of the earthworm. III. Nerves controlling secretion of protease in the anterior intestine. Proc R Soc Lond B 132:200–212
Quatrèfages MA (1847) Note sur L'anatomie des sangsues et des lombrics. Ann Sci Nat 7:36–41
Retzius G (1892) Das Nervensystem der Lumbricinen. Biol Unters NF Bd 3:1–16
Reynolds ES (1963) The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 17:208–212
Rosenbluth J (1972) Myoneural junctions of two ultrastructurally distinct types in earthworm body muscle. J Cell Biol 54:566–579
Smallwood WM (1923) The nerve net in the earthworm: Preliminary report. Proc Nat Acad Sci Washington 9:95–100
Wu KS (1939) On the physiology and pharmacology of the earthworm gut. J Exp Biol 16:184
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benedeczky, I., Csoknya, M., Fekete, É. et al. Ultrastructure of the nerve-muscle junction in the pharynx of the earthworm,Lumbricus terrestris . Zoomorphology 109, 337–341 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00803574
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00803574