Summary
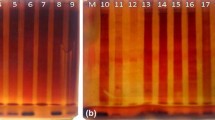
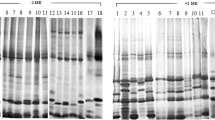
Methodology, based on starch and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, was developed for determining isozyme electrophoregrams (patterns) of 16 enzymes of cassava (Manihot esculenta Grantz) varieties as potential genotype markers. Extracts of five different tissues (root, stem, leaf, petiole and bud) were examined. In general, the nodal portions of the shoots gave isozyme patterns with the largest number of bands. Petiole extracts gave similar results but bud extracts gave poor patterns. The limited number of varieties that were examined could be distinguished by sequential classification on the basis of the isozyme patterns of acid phosphatase, esterase, glutamate oxaloacetase transaminase and phosphoglucoisomerase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BassiriA. & I.Rouhani, 1977. Identification of broad bean cultivars based on isozyme patterns. Euphytica 26: 279–286.
BoulterD., D. A.Thurmann & B. L.Turner, 1966. The use of disc electrophoresis of plant proteins in systematics. Taxon. 15: 135–142.
CardyB. J., C. W.Stuber & M. M.Goodman, 1981. Techniques for starch gel electrophoresis of enzymes from maize (Zea mays L.) in Institute of Statistics Monograph series No. 1317. North Carolina, State University, Raleigh, North Carolina.
ClaytonJ. W. & D. N.Tretiak, 1972. Amine citrate buffers for pH control in starch gel electrophoresis. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 29: 1169–1172.
FAO, 1984. Production Yearbook. Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations, Rome, p. 128–129.
GottliebL. D., 1973. Enzyme differentiation and phyllogeny inClarkia fransisciana, C. rubicunda andC. amoena. Evolution 27: 205–214.
HarrisH. & D. A.Hopkinson, 1976. Handbook of enzyme electrophoresis in human genetics. North Holland Publ. Co., Amsterdam.
Hussain, A., H. Ramirez, W. Roca & W. Bushuk, 1986. Identification of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) by electrophoretic patterns of esterase isozymes. Seed Sci. and Technol.
JohnsonB. L., 1967. Tetraploid wheats: seed protein electrophoretic patterns of the Emmer and Timopheevi groups. Science 158: 131–132.
National Academy of Sciences, 1974. Roots, tubers and plantains in African research capabilities. National Academy of Science, Washington, D.C. pp. 64–73.
PrzybylskaJ., S.Blixt, H.Parzysyz & Z.Zimniak-Przybylska, 1982. Isozyme variation in the genusPisum: I. Electrophoretic patterns of several enzyme systems. Genetica Polonica 23: 103–121.
QuirosF. C., 1981. Starch gel electrophoresis technique used with alfalfa and otherMedicago species. Can. J. Plant. Sci. 61: 745–749.
RobinsonP. J. & R. G.Megarrity, 1975. Characterization ofStylosanthes introductions by using seed protein patterns. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 26: 467–479.
ScandaliosJ. G., 1974. Isozymes in development and differentiation. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 25: 225–258.
Selander, R. K., M. H. Smith, S. Y. Yang, W. E. Johnson & J. B. Gentry, 1971. Biochemical polymorphism and systematics in the genusPeromycus. I. Variation in the old-field mouse (Peromyscus polionotus). Studies in Genetics VI. Univ. Texas Publ. 7103, p. 49–90.
ShawC. R. & R.Prasad, 1970. Starch gel electrophoresis of enzymes-a compilation of recipes. Biochem. Genet. 4: 297–320.
VaughanJ. G. & A.Waite, 1967. Comparative electrophoretic studies of the seed proteins of certain species ofBrassica andSinapis. J. Exp. Bot. 18: 100–109.
WeedenN. F., 1984. Distinguishing among white seeded bean cultivars by means of allozyme genotypes. Euphytica 33, 199–208.
WrigleyC. W., J. C.Autran & W.Bushuk, 1982. Identification of cereal varieties by gel electrophoresis of the grain proteins. In: Y.Pomeranz (Ed.), Advances in Cereal Science and Technology 5: 211–259. Am. Assoc. Cereal Chem. Inc. St. Paul, MN.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Joint publication of the Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical and the Department of Plant Science (No. 716), University of Manitoba. Presented in part at the 2nd International Symposium on Biochemical Approaches to Identification of Cultivars and Evaluation of Their Properties, 5–9 May, 1985, Braunschweig, West Germany.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramirez, H., Hussain, A., Roca, W. et al. Isozyme electrophoregrams of sixteen enzymes in five tissues of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) varieties. Euphytica 36, 39–48 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00730645
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00730645