Summary
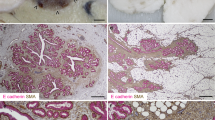
In this study the proliferative and secretory activity of human pregnant and lactating breast has been examined. 17 cases of pregnant tissue were obtained, comprising 9 from first trimester, 6 from the second and 2 from the third, together with 3 cases of lactating breast. Proliferation, measured by 3H thymidine autoradiography, gave a constant Thymidine labelling index of approximately 6% during the first 20 weeks, with a reduction by 50% thereafter. Levels of 0.2% were seen during lactation. Morphological assessment showed a high frequency of both mitosis and apoptosis throughout gestation. Although mitotic frequency did reduce with time, values were more variable than thymidine labelling. The reduction in thymidine uptake halfway through pregnancy coincided with generalised morphological lactational differentiation and the major immunocytochemical expression of alpha-lactalbumin. However, cytoplasmic expression of the secretory component of IgA was generalised and marked even during the first trimester and was closely related to increased proliferation and general synthetic cellular activity. These and other observations support a complex relationship of autocrine and paracrine factors in addition to the customary endocrine ones for breast regulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ances IG (1972) Serum concentrations of epidermal growth factor in human pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 115:357–362
Anderson TJ, Ferguson DJP, Raab GM (1982) Cell turnover in the ‘resting’ human breast: the influence of parity, contraceptive pill, age and laterality. Br J Cancer 46:376–382
Bailey AJ, Sloane JP, Trickey BS, Ormerod MG (1982) An immunocytochemical study of alphalactalbumin in human breast tissue. J Pathol 137:12–23
Brantzaeg P (1974) Mucosal and glandular distribution of immunoglobulin components: Differential localization of free and bound SC in secretory epithelial cells. J Immunol 112:1553–1559
Brew K, Vanaman TC, Hill RL (1968) The role of alpha-lactalbumin and the A protein in lactose synthetase: a unique mechanism for the control of a biological reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 59:491–497
Calaf G, Russo IH, Roi LD, Russo J (1986) Effects of peptides and steriod hormones on cell kinetic parameters of normal human breast tissue in organ culture. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 3:135–140
Carson FL, Martin JH, Lynn JA (1973) Formalin fixation for electron microscopy. A re-evaluation. Am J Clin Pathol 59:365–373
Clayton F, Ordonez NG, Hanssen GM, Hanssen H (1982) Immunoperoxidase localization of lactalbumin in malignant breast neoplasms. Arch Pathol Lab Med 106:268–270
Ferguson DJP, Anderson TJ (1981) Morphological evaluation of cell turnover in relation to the menstrual cycle in the ‘resting’ human breast. Br J Cancer 44:177–181
Ferguson DJP, Anderson TJ (1983) A morphological study of the changes which occur during pregnancy in the human breast. Virchows Arch (Pathol Anat) 401:163–175
Going JJ, Anderson TJ, Battersby S, MacIntyre C (1988) Proliferation and secretory activity in human breast during natural and artificial menstrual cycles. Am J Pathol 130:193–204
Hirata Y, Moore GW, Bertagna C, Orth DN (1980) Plasma concentrations of immunoreactive human epidermal growth factor (Urogastrone) in man. J Clin Endoc Metab 50:440–444
Imagawa W, Tomooka Y, Hamamoto S, Nandi S (1985) Stimulation of mammary epithelial cell growth in vitro: interaction of epidermal growth factor and mammogenic hormones. Endocrinology 116:1514–1524
Kuhn LC, Kraehenbuhl J-P (1979) Role of secretory component, a secreted glycoprotein, in the specific uptake of IgA dimer by epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 254:11072–11081
McManus MJ, Welsch CW (1984) The effect of estrogen, progesterone, thyroxine and human placental lactogen on DNA synthesis of human breast ductal epithelium maintained in athymic nude mice. Cancer 54:1920–1927
Meyer JS (1977) Cell proliferation in normal human breast ducts, fibroadenomas and other ductal hyperplasias measured by nuclear labelling with tritiated thymidine. Hum Pathol 8:67–81
Meyer JS (1984) Practical breast carcinoma cell kinetics: review and update. Breast Cancer Res Treatment 4:79–88
Meyer JS, Connor RE (1982) Cell proliferation in fibrocystic disease and postmenopausal breast ducts measured by thymidine labeling. Cancer 50:746–751
Mukherji MJ (1983) The relationship between mitosis and apoptosis in the normal ‘resting’ human breast. B.Sc. Hons Thesis. University of Edinburgh
Oka T, Yoshimura M (1986) Paracrine regulation of mammary gland growth. Clin Endoc Metab 15:79–97
Pardee A, Campisi J, Gray HE, Dean M, Sonenshein G (1985) Cellular oncogenes, growth factors and cellular growth control. In: Ford RJ, Maizel AL (eds) Mediators in cell growth and differentiation. Raven Press, New York pp 21–29
Rigg LA, Lein A, Yen SSC (1977) Pattern of increase in circulating prolactin levels during human lactation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 129:454–456
Salazar H, Tobon H, Josimovich JB (1975) Developmental gestational and postgestational modifications of the human breast. Clinical Obstet Gynecol 18:113–137
Short RV, Drife JO (1977) The aetiology of mammary cancer in man and animals. Symp Zool Soc Lond 41:211–230
Sternberger LA (1986) Immunocytochemistry. John Wiley & Sons, New York, 3rd Ed, p 90
Stewart HJ, Edwards PE, Foster V, Perusinghe N, O'Hara MJ, Gusterson BA (1987) Maintenance of normal human breast organoids within rat mammary fat pads in organ culture. Virchows Arch A (Pathol Anat) 410:495–500
Tonelli QJ, Sorof S (1980) Epidermal growth factor requirement for development of cultured mammary gland. Nature 285:250–252
Tulchinsky D, Hobel CJ, Yeager E, Marshall JR (1972) Plasma estrone, estradiol, estriol, progesterone and 17-hydroxyprogesterone in human pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 122:1095–1100
Tyson JE, Hwang P, Guyda H, Friesen HG (1972) Studies of prolactin secretion in human pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 113:14–20
Tyson JE, Khojandi M, Huth J, Andreassen B (1975) The influence of prolactin secretion on human lactation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 40:764–773
Wilson GD, Woods KL, Walker RA, Howell A (1980) Effect of prolactin on lactalbumin production by normal and malignant human breast tissue in organ culture. Cancer Res 40:486–489
Wyllie AH, Kerr JFR, Currie AR (1980) Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol 68:251–306
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Battersby, S., Anderson, T.J. Proliferative and secretory activity in the pregnant and lactating human breast. Vichows Archiv A Pathol Anat 413, 189–196 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00718610
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00718610