Abstract
Flux parameters, zero-plane displancement height and roughness length of a forest canopy are determined taking into consideration a transition layer and atmospheric diabatic influences. The present study, unlike previous studies by DeBruin and Moore (1985) and Lo (1990) that accounted for the velocity profile alone, make use of information from both wind and temperature profiles in formulating the governing equations. However, only the top level measurement is assumed to be within the logarithmic regime. In addition to the mass conservation principle (e.g., Lo, 1990; DeBruin and Moore, 1985), an analytic relationship between the Monin-Obukhov length and the bulk Richardson number is employed as the closure equation for the governing system.
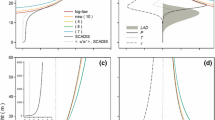
The present method is applied to profile measurements taken at Camp Borden (den Hartog and Neumann, 1984) in and above a forest canopy with mean crown height of about 18.5 m. Profile data under neutral or near-neutral conditions yieldedd=12.69 m andz 0=0.97 m, which are realistic values. In general,z 0 increases slightly with increasing wind yet remains relatively constant with respect to small variation of stabilities. On the other hand, increases of wind speed reduced values of displacement height,d, by as much as 50%. The influence, if any, of stability ond, however, is not clear from the results of the present study. The validity of using profile data of limited height is also carefully examined. At least for neutral or near-neutral stabilities, the present method can yield realistic results even though the profile heights are substantially below the ‘transition layer height’ suggested by Garratt (1978).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Byun, D. W.: 1990, ‘On the Analytical Solutions of Flux-Profile Relationships for the Atmospheric Surface Layer’,J. Appl. Meteorol. 29, 652–657.
DeBruin, H. A. R. and Moore, C. J.: 1985, ‘Zero-Plane Displacement and Roughness Length for Tall Vegetation, Derived from a Simple Mass Conservation Hypothesis’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 31, 39–49.
Charnock, H.: 1955, ‘Wind Stress on the Water Surface’,Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 81, 639–640.
Chen, F. and P. Schwerdtfeger: 1989, ‘Flux-Gradient Relationships for Momentum and Heat over a Rough Natural Surface’,Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 115, 335–352.
Garratt, J. R.: 1978, ‘Transfer Characteristics for a Heterogeneous Surface of Large Aerodynamic Roughness’,Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 104, 491–502.
Garratt, J. R.: 1980, ‘Surface Influence upon Vertical Profiles in the Atmospheric Near-Surface Layer’,Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 106, 803–819.
den Hartog, G. and Neumann, H. H.: 1984, ‘An Empirical Study on Dry Deposition of Air Pollutants to Forest-Project Description’, Report AQRB-84-Q11-L., Atmospheric Environment Service, Canada.
Lesnik, G. E.: 1973, ‘Estimation of Displacement-Layer Thickness and Roughness Parameter from Measurements above a Forest’,Izv., Atmos. and Oceanic Physics 9(1), 88–90.
Lo, A. K.: 1977, ‘An Analytical-Empirical Method for Determining the Roughness Length and Zero-Plane Displacement’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 12, 141–151.
Lo, A. K.: 1990, ‘On the Determination of Zero-Plane Displacement and Roughness Length for Flow over Forest Canopy’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 51, 255–268.
Lo, A. K.: 1993, ‘The Direct Calculation of Fluxes and Profiles in the Marine Surface Layer using Measurements from a Single Atmospheric Level’,J. Appl. Meteorol. 32, 1894–1900.
Marunich, S. V.: 1971, ‘Kharakteristiki turbulentonosti v usloviyakh lesa po gradientnyum i strukturnyn wablyudeniyam’,Trudy, G.G.I. 198, 154–165.
Molion, L. C. B. and Moore, C. J.: 1983, ‘Estimating the Zero-Plane Displacement for Tall Vegetation using a Mass Conservative Method’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 25, 115–125.
Monin, A. S. and Yaglom, A. M.: 1971,Statistical Fluid Mechanics of Turbulence, Vol. 1, The MIT Press, Cambridge, 769 pp.
Neumann, H. H., den Hartog, G., and Shaw, R. H.: 1988, ‘Leave Area Measurements during Autumn Leaf Fall for a Deciduous Forest Based on Hemispheric Photographs and Leaf-Litter Collection’,Agric. Forest Meteorol. 45, 325–345.
Raupach, M. R.: 1979, ‘Anomalies in Flux-Gradient Relationships over Forest’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 16, 467–486.
Raupach, M. R., Thom, A. S., and Edwards, I.: 1980, ‘Wind-Tunnel Study of Turbulent Flow Close to Regularly Arrayed Rough Surfaces’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 18(4), 373–397.
Raupach, M. R.: 1994, ‘Simplified Expressions for Vegetation Roughness Length and Zero-Plane Displacement as Functions of Canopy Height and Area Index’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 71, 211–216.
Tajchman, S. J.: 1981, ‘Comments on Measuring Turbulent Exchange within and above Forest Canopy’,Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 62, 1550–1559.
Tennekes, H.: 1982, ‘Similarity Relations, Scaling Laws, and Spectral Dynamics’, in F. T. M. Nieuwstadt and H. van Dop (eds.),Atmospheric Turbulence and Air Pollution Modelling, D. Reidel Publ. Co., Dordrecht, Holland, pp. 37–64.
Zoumakis, N. M.: 1994, ‘Determination of the Mean Wind Speed and Momentum Diffusivity Profiles above Tall Vegetation and Forest Canopies using a Mass Conservation Assumption’,J. Appl. Meteorol. 33, 295–302.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kou-Fang Lo, A. Determination of zero-plane displacement and roughness length of a forest canopy using profiles of limited height. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 75, 381–402 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00712270
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00712270