Summary
A strain ofFusarium moniliforme, previously used for microbial protein production, excreted lactase (β-D-galactosidase, EC.3.2.1 23) when cultivated either in a whey liquid medium or on a wheat bran solid medium. The enzyme produced in both media had pH and temperature optima of 4–5 and 50–60°C respectively and was particularly suitable for processing acid whey.
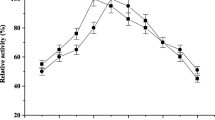
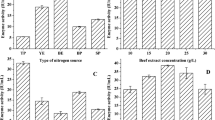
In the whey culture, maximum lactase yield was observed after 95 h of growth at 30°C and whey lactose concentration of 9%. The addition of ammonium, potassium and sodium ions to the growth medium considerably enhanced lactase production. A maximum enzyme yield corresponding to hydrolysis of 3 nmoles o-nitrophenyl-β-D-galactopyranoside sec−1 ml−1 of growth medium, at pH 5 and 60°C, was obtained.
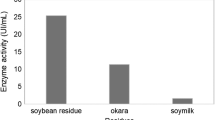
In the wheat bran culture, the maximum enzyme yield was obtained after 140 h of growth at 28–30°C. A marked increase in the enzyme production was observed when nitrate or phosphate was added to the growth medium. Also, the addition of certain agricultural by-products (molasses, whey) enhanced lactase production. The observed maximum yield corresponding to the hydrolysis of 182 nmoles of ONPG sec−1 g−1 of wheat bran, at pH 5 and 60°C, is comparable to that reported for certain microorganisms used commercially for lactase production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blankenship LC, Wells PA (1974) Microbial beta-galactosidase: a survey for neutral pH optimum enzymes. J Milk Food Technol 37:199–202
Davies R (1964) Lactose utilization and hydrolysis inSaccharomyces fragilis. J Gener Microbiol 37:81–89
Drouliscos NJ, Macris BJ, Kokke R (1976) Growth ofFusarium moniliforme on carob aqueous extract and nutritional evaluation of its biomass. Appl Environ Microbiol 31 (5):691–694
Holsinger VH (1978) Application of lactose-modified milk and whey. Food Technol 32 (3):35–40
Macris BJ, Kokke R (1977) Kinetics of growth and chemical composition ofFusarium moniliforme cultivated on carob aqueous extract for microbial protein production. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 4:93–99
Mustranta A, Karvonen E, Linko M (1980). Production of mold lactases. VI Intern Ferm Symp Abstracts, London Ontario Canada
Newmark P (1980) Fungal food Nature 287:6
Nickerson TA, Vujicic JF, Lin AY (1976) Colorimetric estimation of lactose and its hydrolytic products. J Dairy Sci 59:386–390
Park YK, De Santi MSS, Pastore GM (1979) Production and characterization of β-galactosidase fromAspergillus oryzae. J Food Sci 44:100–103
Pastore GM, Park YK (1979) Screening of high β-galactosidase-producing fungi and characterizing the hydrolysis properties of a selected strain. J Food Sci 44:1577–1580
Rao-Ramana MV, Dutta SM (1977) Production of beta-galactosidase fromStreptococcus thermophilus grown in whey. Appl Environ Microbiol 34 (2):185–188
Rosensweig N (1969) Adult human milk intolerance and intestinal lactase deficiency. A review J Dairy Sci 52:585–587
Sorrensen SG, Crisan EV (1974) Thermostable lactase from thermophilic fungi. J Food Sci 39:1184–1187
Wendorff WL, Amudson CH, Olson NF (1970) Nutrient requirements and growth conditions for production of lactase enzyme bySaccharomyces fragilis. J Milk Food Technol 33:451–455
Wierzbicki LE, Kosikowski FV (1973) Lactase potential of various microorganisms grown in whey. J Dairy Sci 56:26–32
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Macris, B.J. Production of extracellular lactase fromFusarium moniliforme . European J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 13, 161–164 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00703046
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00703046