Summary
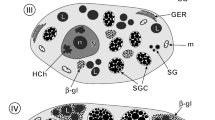
Vitellogenin (Vg) synthesis in cultured tissues was analysed biochemically in a soft tick,Ornithodoros moubata. Nine tissue fractions dissected from reproductive females were incubated in vitro in a specially designed Ringer containing35S-methionine. The synthesis of total protein and Vg was assayed by the radioactivity incorporated into precipitates with trichloroacetic acid and antivitellin (Vn)-serum, respectively. Fat body was the most active tissue in Vg synthesis, which comprised 46% of the Vg synthesis by all tissues and 42% of total protein synthesis by fat body. Protein synthesized by the fat body and precipitated with anti-Vn-serum was shown by electrophoresis and fluorography, to consist of six radioactive polypeptides corresponding to the components of Vg. Vg synthesized in cultured fat body was first accumulated in the tissue and secreted into the medium during incubation. Some tissues other than fat body showed low Vg synthesis (in each, less than 12% of total protein synthesis) which, however, may be due to contamination by fat body cells as seen with the scanning electron microscope (SEM). SEM also showed that fat body cells in the active stage of Vg synthesis expanded about 10-fold in length. Immunohistochemical analysis showed a very strong reaction with anti-Vn-IgG in the cytoplasm of fat body from reproductive females. Fat body from unfed females and other tissues including midgut, did not show any specific fluorescence. A positive reaction was obtained with developing oocytes. These results indicate that the fat body is the only site of Vg synthesis in this tick.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Vg :
-
vitellogenin
- Vn :
-
vitellin
- SDS :
-
sodium dodecyl sulfate
- PAGE :
-
polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- SEM :
-
scanning electron microscopy
- TCA :
-
trichloroacetic acid
References
Araman SF (1979) Protein digestion and synthesis in ixodid females. In: Rodriquez JG (ed) Recent advances in acarology, I. Academic Press, New York, London, pp 385–395
Boctor FN, Kamel MY (1976) Purification and characterization of two lipovitellins from eggs of the tick,Dermacentor andersoni. Insect Biochem 6:233–240
Bownes M, Hames BD (1977) Accumulation and degradation of three major yolk proteins inDrosophila melanogaster. J Exp Zool 200:149–156
Chamberlain JP (1979) Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem 98:132–135
Chinzei Y (1983) Quantitative changes of vitellogenin and vitellin in adult female ticks,Ornithodoros moubata, during vitellogenesis. Mie Med J (Jpn) 27:117–127
Chinzei Y, Chino H, Takahashi K (1983) Purification and properties of vitellogenin and vitellin from a tick,Ornithodoros moubata. J Comp Physiol 152:13–21
Coons LB, Tarnowski B, Ourth DD (1982)Rhipicephalus sanguinius: Localization of vitellogenin synthesis by immunological methods and electron microscopy. Exp Parasitol 54:331–339
Diehl PA (1970) Zur Oogenese beiOrnithodoros moubata (Murray (Ixodoidea, Argasidae) unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Vitellogenese. Acta Trop 27:302–355
Diehl PA, Aeschlimann A, Obenchain FD (1982) Tick reproduction: oogenesis and oviposition. In: Obenchain FD, Galun R (eds) Physiology of ticks. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 277–350
Hagedorn HH, Kunkel JG (1979) Vitellogenin and vitellin in insects. Annu Rev Entomol 24:475–505
Hecker H, Aeschlimann A (1970) Ultrastrukturelle Aspekte der Eibildung beiRhicephalus bursa (Canestrini and Fanzago) (Ixodoidea, Ixodidae). Z Tropenmed Parasit 21:31–45
Jenni L (1971) Synthese und Aufnahme von Proteinen während der Vitellogenese in Ovocyten vonOrnithodoros moubata Murray (Ixodoidea: Argasidae). Acta Trop 28:105–163
Kirby BA (1963) The biochemistry of the insect fat body. Adv Insect Physiol 1:112–174
Obenchain FD, Oliver JH Jr (1973) A qualitative analysis of the form, function and interrelationships of fat-body and associated tissues in adult ticks (Acari-Ixodoidea). J Exp Zool 186:217–236
Obenchain FD, Dhadialla TS, Ahmad Z, Ojowa R (1978) The processing of lipovitellins in the brown ear tickRhipicephalus appendiculatus. Annu Rep ICIPE (Nairobi) 1978:42–44
Pound JM, Oliver JH (1979) Juvenile hormone: evidence of its role in the reproduction of ticks. Science 206:355–357
Shigematsu H (1960) Protein metabolism in the fat body of the silkworm,Bombyx mori L. Bull Sericul Exp St (Tokyo) 16:141–170 (in Japanese and English Summary)
Tata JR (1978) Induction and regulation of vitellogenin synthesis by estrogen. In: Litwack G (ed) Biochemical actions of hormones, vol 5. Academic Press, New York, pp 397–431
Tatchell RJ (1969) The ionic regulatory role of the salivary secretion of the cattle tickBoophilus microplus. J Insect Physiol 15:1421–1430
Tatchell RJ (1971) Electrophoretic studies on the proteins of the haemolymph, saliva and eggs of the cattle tickBoophilus microplus. Insect Biochem 1:47–55
Wyatt GR (1975) Hemolymph in insects and arachnids — some biochemical features. In: Maramorosch K, Shope RE (eds) Invertebrate immunity. Academic Press, New York, pp 225–240
Wyatt GR, Pan ML (1978) Insect plasma proteins. Annu Rev Biochem 47:779–817
Yano I (1981) Scanning electronmicroscope study on the comblike teath ofPlecoglossus alitivelis Temminck et Schlegel. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fisheries 47:437–442
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chinzei, Y., Yano, I. Fat body is the site of vitellogenin synthesis in the soft tick,Ornithodoros moubata . J Comp Physiol B 155, 671–678 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00694580
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00694580