Summary
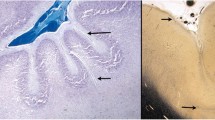
The cytoarchitectonics of the cerebral unlayered polymicrogyria located at the borders of a bilateral porencephalic defect is characterized by minute convolutions not exteriorized by sulci, in which blood vessels and increased numbers of fibrillary astrocytes are present in the fused molecular layers. The cellular organization, based on the analysis of Golgi sections, differs among gyral, intermediate, and sulcal regions and represents variable degree of cellular damage and structural organization of the cerebral mantle injured approximately in gestational month 5. Polymicrogyria may be produced by incomplete ischemia of radial territories vascularized by cortical blood vessels penetrating at right angles from the surface which is the result of the imbalance between the impaired cerebral blood flow of occluded large prerolandic arteries, responsible for the porencephalic defect, and the arterial meningeal anastomoses.
Abnormal folding in polymicrogyria may be generated by lateral differences in the cortical thickness of adjoining areas, and by the imbalance in growth rates of laterally contiguous cortical regions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barron DH (1950) An experimental analysis of some factors involved in the development of the fissure pattern of the cerebral cortex. J Exp Zool 113:553–573
Bertrand I, Gruner J (1955) The status verrucosus of the cerebral cortex. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 14:331–347
Biclchowski M (1915) Uber Microgyrie. J Psychol Neurol (Lpz) 22:1–47
Caviness VS, Jr (1976) Reeler mutant mice and laminar distribution of afferents in the neocortex. Exp Brain Res [Suppl] 1:267–273
Caviness VS, Frost DD, Hayes NL (1976) Barrels in somatosensory cortex of normal and reeler mutant mice. Neursci Lett 3:7–14
Caviness VS, Williams RS (1979) Cellular pathology of developing human cortex. In: Katzman R (ed) Congenital and acquired cognitive disorders. Raven Press, New York, pp 69–89
Caviness VS, Yorke CH (1976) Interhemispheric neocortical connections of the corpus callosum in the reeler mutant mouse: A study based on anterograde and retrograde methods. J Comp Neurol 170:449–460
Colwell SA (1976) Combined anterograde-retrograde tracing of the connections of the reeler mutant cortex. Anat Rec 184:380
Crome L (1952) Microgyria. J Pathol Bacteriol 64:479–495
Dekaban A (1965) Large defects in cerebral hemispheres associated with cortical dysgenesis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 24:512–530
De Leon GA (1972) Observations on cerebral and cerebellar microgyria. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 20:278–287
Dobbing J, Sands J (1970) Timing of neuroblast multiplication in developing human brain. Nature 226:639–640
Duckett S (1971) The establishment of internal vascularization in the human telencephalon. Acta Anat 80:107–113
Dvorak K, Feit J, Jurankova Z (1978) Experimentally induced focal microgyria and status verrucosus deformis in rats. Pathogenesis and interrelations, histological and autoradiographic study. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 44:121–129
Ferrer I, Fernandez-Alvarez E (1977) Lisencefalia: Agiria. Un estudio con el método de Golgi. J Neurol Sci 34:109–120
Ferrer I, Fabregues I, Coll J, Riblasta T, Rives A (1984a) Tuberous sclerosis: A Golgi study of cortical tuber. Clin Neuropathol 3:47–51
Ferrer I, Xumetra A, Santamaria J (1984b) Cerebral malformation induced by prenatal X-irradiation: an autoradiographic and Golgi study. J Anat (Lond) 138:81–93
Friede RL (1975) Development neuropathology. Springer, Wien, pp 303–307
Hallervorden J, Meyer JE (1956) Cerebrale Kinderlähmung. In: Henke F, Lubarsch O, Rössle R (Hrsg) Handbuch der speziellen pathologischen Anatomie und Histologie, vol 13/14. Springer, Berlin, pp 194–282
Hanaway J, Lee SI, Netsky MG (1968) Pachygyria: relation of findings to modern embryologic concepts. Neurology 18:791–799
Huttenlocher PR, Wollmann RL (1980) The fine structure of cerebral cortex in tuberous sclerosis. A Golgi study. Ann Neurol 8:223
Jacob H (1940) Die feinere Oberflächengestaltung der Hirnwindungen; die Hirnwarzenbildung und die Mikropolygyrie. Z Gesamte Neurol Psychiatrie 170:64–84
Jellinger K, Rett A (1976) Agyria: Pachygyria (lissencephaly syndrome). Neuropadiatrie 7:66–91
Jones EG, Valentino KL, Fleshman JW, Jr (1982) Adjustment of connectivity in rat neocortex after prenatal destruction of precursor cells of layers II–IV. Dev Brain Res 2:425–431
Kier EL (1974) Fetal cerebral arteries: a phylogenic and ontogenic study. In: Newton TH, Potts DG (eds) Radiology of the skull and brain, vol 2, book 1. Mosby, St. Louis, pp 1089–1130
Landrieu P, Goffinet A (1981) Inverte pyramidal neurons and their axons in the neocortex of reeler mutant mice. Cell Tissu Res 218:293–301
Larroche JC (1977) Cytoarchitectonic abnormalities (abnormalities of cell migration) In: Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW (eds) Handbook of clinical neurology, vol 30. North Holland, Amsterdam, pp 479–506
Lyon G, Robain O (1967) Etude comparative des encéphalopathies circulatoires prénatales et para-natales (hydranencéphalies, porencephalies et encephalomalacies cystiques de la substance blanche). Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 9:79–98
Marburg O, Rezek PHR, Marks MB (1945) Porencephaly. II. Studies in phlebothromobosis and phlebostasis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 4:43–58
Marin-Padilla M (1970) Prenatal and early postnatal ontogenesis of the human motor cortex. A Golgi study. I The sequential development of the cortical layers. Brain Res 23:167–183
Marques Dias MJ, Harmant-van Rijckervorsel G, Landrieu P, Lyon G (1984) Prenatal cytomegalovirus disease and cerebral microgyria: Evidence for perfusion failure, not disturbance in histogenesis, as major cause of fetal cytomegalovirus encephalopathy. Neuropediatrics 15:18–24
Pape KE, Wigglesworth JS (1979) Haemorrhage, ischaemia and the perinatal brain. In: Clinics in Developmental Medicine, nos 69/70. Heineman, London, pp 11–38
Pinto-Lord MC, Evrard P, Caviness VS, Jr (1979) Determination of cell shape and orientation. A comparative Golgi analysis of cell-axon interelationships in the developing neocortex of normal and reeler mice. J Comp Neurol 187:49–70
Poliakov GI (1967) Embryonal and postembryonal development of neurons of the human cerebral cortex. In: Hassler R, Stephen H (eds) Evolution of the forebrain, phylogenesis and ontogenesis of the forebrain. Plenum Press, New York, pp 249–258
Ranke O (1910) Beiträge zur Kenntnis der normalen und pathologischen Hirnrindenbildung. Beitr Pathol Anat 47:51–125
Richman DP, Stewart RM, Caviness VS, Jr (1974) Cerebral microgyria in a 27-week fetus. An architectonic and topographic analysis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 33:374–384
Richman DP, Stewart RM, Hutchinson HW, Caviness VS, Jr (1975) Mechanical model of brain convolutional development. Science 189:18–21
Shimada A, Abe Y, Yamato T, Ohta S, Yamazaki S, Okya N (1982) The pathogenesis of abnormal cytoarchitecture in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus of the mouse treated transplacentally with cytosine arabinoside. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 58:159–167
Sidman RL, Rakic P (1973) Neuronal migration with special reference to developing human brain. A review. Brain Res 62:1–35
Solcher H (1968) Zur Neuroanatomie und Neuropathologie der Frühfetalzeit. Monogr Gesamt geb Neurol Psychiatr (Berl) 127:1–78
Steindler DA (1976) Combined anterograde-retrograde tracing of the connections of reeler mouse cortex. Anat Res 184:540
Steindler DA (1977) Cortical barrels, thalamic barreloids and trigemino-cerebellar projections in normal and reeler mutant mice. Anat Res 187:722–723
Stewart RM, Richman DP, Caviness VS, Jr (1975) Lissencephaly and pachygyria. An architectonic and topographical analysis. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 31:1–12
Thalhammer O (1952) Mißbildung: Vorschlag zu einer neuen Nomenklatur angeborener Störungen. Arch Kinderheilkd 145:100–115
Urich H (1976) Malformations of the nervous system, perinatal damage and related conditions in early life. In: Blackwood W, Corsellis JAN (eds) Greenfield's neuropathology. Edward Arnold, Edinburgh, pp 361–469
Van der Eeken H (1968) Anatomy and embryology of cerebral circulation. Prog Brain Res 30:1–25
Van der Eeken H, Adams RD (1953) The anatomy and functional significance of the meningeal arterial anastomoses of the human brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 12:132–157
Williams RS, Ferrante RJ, Caviness VS, Jr (1975) Neocortical organization in human cerebral malformations. A Golgi study. Neurosci Abstr 1:776
Williams RS, Ferrante RJ, Caviness VS, Jr (1976) The cellular pathology of microgyria. A Golgi analysis. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 36:269–283
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to A. Gonzalez
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferrer, I. A golgi analysis of unlayered polymicrogyria. Acta Neuropathol 65, 69–76 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689830
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689830