Summary
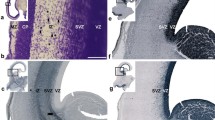
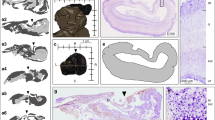
Reduced size of convolutions and midcortical laminar necrosis are approximately co-extensive in the cerebral hemispheres of a child, one of twins, dying at 18 months. Because the underlying laminar arrangement of neurons and the basic gyral pattern are normal, the cortical damage probably occurred not earlier than the third trimester of gestation. Neurons surviving above and below the zone of tissue necrosis, like their homologs in normal cortex, are entrained in multineuronal radial assemblies. Below the zone of necrosis the relative positions of radially adjacent neurons are unaltered. Above, however, in places where the molecular layer is reduced in width, neurons are displaced radially outward toward the pial surface. In places the pia is breached and bridged by a mesenchymal-glial cicatrix. Where this has happened neurons have migrated beyond the cerebral boundary and have established an ectopia in the subarachnoid compartment. These observations suggest that relatively undifferentiated intracortical neurons are held in radial assemblies by bonds which prevent their tangential displacement. The molecular layer appears to serve as a barrier to their radial displacement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astrom, K. E.: On the early development of the isocortex in fetal sheep. In: Developmental Neurology. Progress in Brain Research, Vol. 26 (eds. C. G. Bernhard and J. P. Schadé), pp. 1–59 New York: Elsevier 1967
Brodmann, K.: Vergleichende Lokalisationslehre der Großhirnrinde in ihren Prinzipien dargestellt auf Grund des Zellenbaues. Leipzig: J. A. Barth 1909
Caviness, V. S., Jr., Rakic, P.: Mechanisms of cortical development: a view from mutations in mice. In: Annual Review of Neuroscience (eds. W. M. Cowan, Z. W. Hall, and E. R. Kandel). Palo Alto: Annual Reviews, Inc. 1978 (in press)
Chi, J. G., Dooling, E. C., Gilles, F. H.: Gyral development of the human brain. Ann. Neurol.1, 86–93 (1977)
Crome, L., Stern, J.: Pathology of Mental Retardation. London: Churchill Livingston 1972
del Cerro, M., Walker, J. R., Stoughton, R. L., Cosgrove, J. W.: Displaced neural elements within the cerebellar fissures of normal and experimental albino rats. Anat. Rec.184, 389 (1976)
Hatten, M. E., Trenkner, E., Sidman, R. L.: Cell migration and cell-cell interactions in primary cultures of embryonic mouse cerebellum. Neurosci. Abs.2, 1023 (1976)
Jones, K. L., Smith, D. W.: The fetal alcohol syndrome. Teratology12, 1–10 (1975)
Kölliker, A. von: Handbuch der Gewebelehre des Menschen. Leipzig: Engelmann 1896
Levine, D. N., Fisher, M. A., Caviness, V. S., Jr.: Porencephaly with microgyria: a pathologic study. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)29, 99–113 (1974)
Morest, D. K.: A study of neurogenesis in the forebrain of opossum pouch young. Z. Anat. Entwickl.-Gesch.130, 265–305 (1970)
Rabinowicz, T.: The cerebral cortex of the premature infant of the 8th month. Prog. Brain Res.4, 39–86 (1964)
Rakic, P.: Mode of cell migration to the superficial layers of fetal monkey neocortex. J. Comp. Neurol.145, 61–84 (1972)
Rakic, P.: Timing of major ontogenetic events in the visual cortex of the rhesus monkey. In: Brain Mechanisms in Mental Retardation (eds. N. A. Buchwald and M. A. B. Brazier), pp. 3–40 New York: Academic Press 1975
Richman, D. P., Stewart, R. M., Caviness, V. S., Jr.: Cerebral microgyria in a 27 week fetus: an architectonic and topographic analysis. J. Neuropath. Exp. Neurol.33, 374–384 (1974)
Richman, D. P., Stewart, R. M., Hutchinson, J. W., Caviness, V. S., Jr.: Mechanical model of brain convolutional development. Science189, 18–21 (1975)
Robain, O., Lyon, G.: Les micrencéphalies familiales par malformation cérébrale. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)20, 96–109 (1972)
Sidman, R. L., Rakic, P.: Neuronal migration with special reference to developing human brain: a review. Brain Res.62, 1–35 (1973)
Stoughton, R. L., del Cerro, M., Walker, J. R., Swarz, J. R.: Presence of displaced neuronal elements within rat cerebellar fissures. Brain Res. (1977) (in press)
Varon, S. S.: In vitro study of developing neural tissue and cells: past and prospective contributions. In: The Neurosciences Second Study Program (ed. F. O. Schmitt), pp. 83–99. New York: The Rockefeller University Press 1970
Walker, J. R., Stoughton, R. L., Palter, M. D., Swarz, J. R., del Cerro, M.: Displaced neural elements within rat cerebellar fissures. Neurosci. Abs.2, 632 (1976)
Willis, R. A.: The Borderland of Embryology and Pathology. London: Butterworth and Co., Ltd. 1958
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported in part by USPHS Grant 1 R01 NS12005-02, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, U.S.A.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caviness, V.S., Evrard, P. & Lyon, G. Radial neuronal assemblies, ectopia and necrosis of developing cortex: A case analysis. Acta Neuropathol 41, 67–72 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689559
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689559