Summary
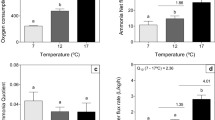
Frequencies of scaphognathite (ventilatory,f sc) and heart (f h) pumping, oxygen consumption (\(\dot M_{O_2 }\)), and hemolymph oxygen, carbon dioxide and pH levels were measured in adult Dungeness crabs (Cancer magister) during 7–10 day periods of exposure to 7, 12, and 17°C seawater. Ventilation volume (\(\dot V_w\)) was calculated for individual animals fromf sc and a previously determined relationship between stroke volume and animal mass.
\(\dot M_{O_2 }\) increases (Q10=2.3) with temperature were associated with larger increases inf sc (Q10=3.3) and\(\dot V_w\) (Q10=3.5) and smaller increases inf h (Q10=1.5). The incidence of unilateral scaphognathite pumping and pausing decreased as temperature rose.
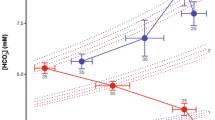
Postbranchial oxygen tension was maintained in vivo but hemolymph oxygen content decreased both in vivo and in vitro as temperature rose. Postbranchial carbon dioxide tension did not change significantly but relative alkalinity was maintained as temperature rose by loss of hemolymph bicarbonate. The effects of increased ventilation volume and potential mechanisms of bicarbonate regulation are discussed.
The responses of the essentially subtidalCancer magister are compared with those of subtidal, intertidal and terrestrial crabs demonstrating that the concepts of acid-base regulation developed for water and air breathing vertebrates are also applicable to water and air breathing crabs, and that intertidal crabs may exhibit transitional states.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albers, C.L.: Acid-base balance. In: Fish physiology, Vol. 4 (Hoar, W.S., Randall, D.J., eds.), pp. 173–208. New York: Academic Press 1970
Ansell, A.D.: Changes in oxygen consumption, heart rate and ventilation accompanying starvation in the decapod crustacean,Cancer pagurus. Neth. J. Sea Res.17, 455–475 (1973)
Austin, J.H., Sunderman, F.W., Camack, J.G.: The electrolyte composition and the pH of serum of a poikilothermous animal at different temperatures. J. Biol. Chem.72, 677–685 (1927)
Batterton, C.V., Cameron, J.N.: Characteristics of resting ventilation and response to hypoxia, hypercapnia, and emersion in the Blue CrabCallinectes sapidus (Rathbun). J. Exp. Zool.203, 403–418 (1978)
Cameron, J.N.: Rapid method for determination of total carbon dioxide in small blood samples. J. Appl. Physiol.31, 632–634 (1971)
Cameron, J.N.: Effects of hypercapnia in blood acid-base status, NaCl fluxes, and trans-gill potential in freshwater Blue CrabsCallinectes sapidus. J. comp. Physiol.123, 137–141 (1978a)
Cameron, J.N.: NaCl balance in Blue Crabs,Callinectes sapidus, in fresh water. J. comp. Physiol.123, 127–135 (1978b)
Cameron, J.N., Batterton, C.V.: Antennal gland function in the fresh-water blue crabCallinectus sapidus: Water, electrolyte, acid base and ammonia excretion. J. comp. Physiol.123, 143–148 (1978)
deFur, P.L., Mangum, C.P.: The effects of environmental variables on the heart rates of invertebrates. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. (in press)
Heisler, N., Weitz, A.M.: Extracellular and intracellular pH with changes of temperature in the dogfishScyliorhinus stellaris. Resp. Physiol.26, 249–263 (1976)
Howell, B.J., Baumgardner, F.W., Bondi, K., Rahn, H.: Acid-base balance in cold-blooded vertebrates as a function of body temperature. Am. J. Physiol.218, 600–606 (1970)
Howell, B.J., Rahn, H.: Regulation of acid-base balance in reptiles. In: Biology of the Reptilia, Vol. 5: Physiology A (Gans, C., Dawson, W.R., eds.), pp. 335–363. New York: Academic Press 1976
Howell, B.J., Rahn, H., Goodfellow, D., Herreid, C.: Acid-base regulation and temperature in selected invertebrates as a function of temperature. Am. Zool.13, 557–563 (1973)
Hughes, G.M., Knights, B., Scammel, C.A.: The distribution of PO2 and hydrostatic pressure changes within the branchial chambers in relation to gill ventilation of the shore crab,Carcinus maenas. J. Exp. Biol.51, 203–220 (1969)
Jackson, D.C.: The effect of temperature on ventilation in the turtle,Pseudemys scripta elegans. Resp. Physiol.12, 131–140 (1971)
Johansen, K., Lenfant, C., Mecklenburg, T.A.: Respiration in the crab,Cancer magister. Z. vergl. Physiol.70, 1–19 (1970)
Lenfant, C., Johansen, K.: Gas transport by hemocyanin containing blood of the CephalopodOctopus dofleini. Am. J. Physiol.209, 991–998 (1965)
Mangum, C.P.: Evaluation of the functional properties of invertebrate hemoglobins. Neth. J. Sea Res.7, 303–315 (1973)
Mangum, C.P., Shick, J.M.: The pH of body fluids of marine invertebrates. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.42A, 693–697 (1972)
Mangum, C.P., Towle, D.W.: Physiological adaptation to unstable environments. Am. Sci.65, 67–75 (1977)
McDonald, D.G.: Respiratory physiology of the crabCancer magister. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Biology, University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta, Canada (1977)
McDonald, D.G., McMahon, B.R., Wood, C.M.: Patterns of heart and scaphognathite activity in the crabCancer magister. J. Exp. Zool.202, 33–44 (1977)
McMahon, B.R., Wilkens, J.L.: Simultaneous apnoea and bradycardia in the lobsterHomarus americanus. Can. J. Zool.50, 165–170 (1972)
McMahon, B.R., Wilkens, J.L.: Periodic respiratory and circulatory performance in the red rock crab,Cancer productus. J. Exp. Zool.202, 363–374 (1977)
Newell, R.C., Ahsanullah, M., Pye, V.I.: Aerial and aquatic respiration in the shore crab,Carcinus maenas (L.). Comp. Biochem. Physiol.43A, 239–252 (1972)
Rahn, H.: Gas transport from the external environment to the cell. Ciba Foundation Symposium: Development of the lung. London: Churchill 1967
Rahn, H., Baumgardner, F.W.: Temperature and acid-base regulation in fish. Resp. Physiol.14, 171–182 (1972)
Randall, D.J., Cameron, J.N.: Respiration and control of arterial pH as temperature changes in rainbow trout,Salmo gairdneri. Am. J. Physiol.225, 997–1002 (1973)
Reeves, R.B.: An imidazole alphastat hypothesis for vertebrate acid-base regulation: Tissue carbon dioxide content and body temperature in bullforgs. Resp. Physiol.14, 219–236 (1972)
Reeves, R.B.: The interaction of body temperature and acid-base balance in ectothermic vertebrates. Ann. Rev. Physiol.39, 559–586 (1977)
Taylor, E.W., Butler, P.J.: Aquatic and aerial respiration in the shore crab,Carcinus maenas (L.), acclimated to 15°C. J. comp. Physiol.127, 315–323 (1978)
Taylor, E.W., Butler, P.J., Sherlock, P.J.: The respiratory and cardiovascular changes associated with the emersion response ofCarcinus maenas (L.) during environmental hypoxia at three different temperatures. J. comp. Physiol.86, 95–115 (1973)
Taylor, E.W., Butler, P.J., Al-Wassia, A.: The effect of a decrease in salinity on respiration, osmoregulation and activity in the shore crab,Carcinus maenas (L.) at different acclimation temperatures. J. comp. Physiol.119, 155–170 (1977)
Toulmond, A.: Temperature-induced variations of blood acid-base status in the lugworm,Arenicola marina I: In vitro study. Resp. Physiol.31, 139–149 (1977a)
Toulmond, A.: Temperature-induced variations of blood acid-base status in the lugworm,Arenicola marina II: In vivo study. Resp. Physiol.31, 151–160 (1977b)
Truchot, J.P.: Temperature and acid-base regulation in the shore crabCarcinus maenas (L.), Resp. Physiol.17, 11–20 (1973)
Truchot, J.P.: Factors controlling in vitro and in vivo oxygen affinity of the hemocyanin in the crabCarcinus maenas (L.). Resp. Physiol.24, 173–189 (1975)
Truchot, J.P.: Carbon dioxide combining properties of the blood of the shore crabCarcinus maenas (L.): Carbon dioxide solubility coefficients and carbonic acid dissociation constants. J. Exp. Biol.64, 45–57 (1976)
Wajcman, H., McMahill, P., Mason, H.S.: Automatic measurement of the oxygen affinity ofCancer magister hemocyanin. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.57B, 139–141 (1977)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by Grant No. A.5762 National Research Council of Canada
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McMahon, B., Sinclair, F., Hassall, C.D. et al. Ventilation and control of acid-base status during temperature acclimation in the crab,Cancer magister . J Comp Physiol B 128, 109–116 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689474
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689474