Summary
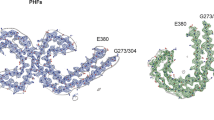
The antigenic profile of neurofibrillary tangles (NFT) in Alzheimer's disease (AD), senile dementia of Alzheimer type (SDAT), progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) and in non-demented aged humans was investigated by light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry using antisera and monoclonal antibodies to tubulin, microtubule-associated proteins (MAP1, MAP2 and tau), neurofilament proteins and determinants unique to Alzheimer paired helical filaments (PHF). Antibodies to tau proteins labeled NFT in all cases investigated (AD, SDAT, PSP and non-demented aged humans). However, one monoclonal antibody to PHF recognized numerous tangles in AD/SDAT, but only a small minority of the PSP tangles. Antibodies to tubulin, MAP1, MAP2 and neurofilament proteins did not selectively stain NFT. Whereas pretreatment of sections with phosphatase was required for the detection of tangles with Tau-1 monoclonal antibody, digestion of sections with either phosphatase or pronase had no significant effect on the staining pattern obtained with the other antibodies. Our studies show that, as previously described for AD/SDAT, phosphorylated tau polypeptides are also a major antigenic determinant of tangles in PSP, indicating that tangle formation may follow a common pathogenetic pathway in neurofibrillary degenerations. There is, however, at least one epitope in AD/SDAT tangles which seems to be absent on, or at least inaccessible in, the 15-nm straight fibrils of PSP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderton BH, Breinburg D, Downes MJ, Green PJ, Tomlinson BE, Ulrich J, Wood JN, Kahn J (1982) Monoclonal antibodies show that neurofibrillary tangles and neurofilaments share antigenic determinants. Nature 298:84–86
Anderton BH, Brion JP, Flament-Durand J, Haugh MC, Kahn J, Miller CCJ, Probst A, Ulrich J (1987) Neurofibrillary tangles and the neuronal cytoskeleton in Alzheimer's disease. In: Wurtman RJ, Corkin SH, Growdon JH (eds) Advances in basic research and therapies. Center for Brain Sciences and Metabolism Charitable Trust, Cambridge, MA,pp 179–187
Binder LI, Frankfurter A, Rebhun LI (1985) The distribution of Tau in the mammalian central nervous system. J Cell Biol 101:1371–1378
Brion JP, Couck AM, Passareiro E, Flament-Durand J (1985) Neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease: an immunohistochemical study. J Submicrosc Cytol 17:89–96
Bugiani L, Mancardi GL, Brusa A, Ederli E (1979) The fine structure of subcortical neurofibrillary tangles in progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 45:147–152
Cork LC, Sternberger NH, Sternberger LA, Casanova MF, Struble RG, Price DL (1986) Phosphorylated neurofilament antigens in neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 45:56–64
Delacourte A, Defossez A (1986) Alzheimer's disease: tau proteins, the promoting factors of microtubule assembly, are major components of paired helical filaments. J Neurol Sci 76:173–186
Dickson DW, Kress Y, Crowe A, Yen SH (1985) Monoclonal antibodies to Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. 2. Demostration of a common antigenic determinant between ANT and neurofibrillary degeneration in progressive supranuclear palsy. Am J Pathol 120:292–303
Gambetti P, Shecket G, Ghetti B, Hirano A, Dahl D (1983) Neurofibrillary changes in human brain. An immunocytochemical study with a neurofilament antiserum. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 42:69–79
Ghatak NR, Nochlin D, Hadfield MG(1980) Neurofibrillary pathology in progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 52:73–76
Gorevic PD, Goni F, Pons-Estel B, Alvarez F, Peress NF, Frangione B (1986) Isolation and partial characterization of neurofibrillary tangles and amyloid plaque core in Alzheimer's disease: immunohistochemical studies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 45:647–664
Grundke-Iqbal I, Johnson AB, Wisniewski HM, Terry RD, Iqbal K (1979) Evidence that Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles originate from neurotubules. Lancet i:578–580
Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Wisniewski HM (1982) Immunocytochemical studies on neurofibrillary changes. Exp Brain Res [Suppl] 5:20–25
Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Tung YC, Wisniewski HM (1984) Alzheimer paired helical filaments: immunochemical identification of polypeptides. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 62:259–267
Grundke-Iqbal I, Wang GP, Iqbal K, Tung YC, Wisniewski HM (1985) Alzheimer paired helical filaments:identification of polypeptides with monoclonal antibodies. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 68:279–283
Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Quinlan M, Tung YC, Zaidi MS, Wisniewski HM (1986a) Microtubule-associated protein tau. A component of Alzheimer paired helical filaments.J Biol Chem 261:6084–6089
Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Tung YC, Quinlan M, Wisniewski HM, Binder LI (1986b) Abnormal phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau in Alzheimer cytoskeletal pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:4913–4917
Haugh MC, Probst A, Ulrich J, Kahn J, Anderton BH (1986) Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles contain phosphorylated and hidden neurofilament epitopes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 49:1213–1220
Ihara Y, Abraham C, Selkoe DJ (1983) Antibodies to paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease do not recognize normal brain proteins. Nature 304:727–730
Ihara Y, Nukina N, Miura R, Ogawara M (1986) Phosphorylated tau protein is integrated into paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease. J Biochem 99:1807–1810
Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I, Zaidi T, Merz PA, Wen GY, Shaikh SS, Wisniewski HM (1986) Defective brain microtubule assembly in Alzheimer's disease. Lancet ii:421–426
Jellinger K (1971) Progressive supranuclear palsy(subcortical argyrophilic dystrophy). Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 19:347–352
Jellinger K, Riederer P, Tomonaga M (1980) Progressive supranuclear palsy: clinicopathological and biochemical studies. J Neural Transm [Suppl] 16:114–128
Kosik KS, Duffy LK, Dowling MM, Abraham C, McCluskey A, Selkoe DJ (1984) Microtubule-associated protein 2:monoclonal antibodies demonstrate the selective incorporation of certain epitopes into Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:7941–7945
Kosik KS, Joachim CL, Selkoe DJ (1986) Microtubule-associated protein tau is a major antigenic component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:4044–4048
Miller CCJ, Brion JP, Calvert R, Chin TK, Eagles PAM, Downes MJ, Flament-Durand J, Haugh M, Kahn J, Probst A, Ulrich J, Anderton BH (1986) Alzheimer's paired helical filaments share epitopes with neurofilament side arms. EMBO J 5:269–276
Montpetit V, Clapin DF, Gubermann A (1985) Substructure of 20 nm filaments of progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 68:311–318
Perry G, Rizzulo N, Autilio-Gambetti L, Gambetti P (1985) Paired helical filaments from Alzheimer disease patients contain cytoskeletal components. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:3916–3920
Perry G, Dennis DJ, Block BR, Stuart D, Autilio-Gambetti L, Gambetti P (1986) Electron microscopic localization of Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangle components recognized by an antiserum to paired helical filaments. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 45:161–168
Powell H, London G, Lampert P (1974) Neurofibrillary tangles in progressive supranuclear palsy. Electron microscopic observations. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 26:637–653
Rasool CG, Abraham C, Anderton BH, Haugh M, Kahn J, Selkoe DJ (1984) Alzheimers disease: immunoreactivity of neurofibrillary tangles with anti-neurofilament and antipaired helical filament antibodies. Brain Res 310:249–260
Reese TS, Karnovsky MJ (1967) Fine structural localisation of a blood-brain barrier to exogenous peroxidase. J Cell Biol 34:207–217
Roy S, Hirano A, Ghatak NR, Zimmermann HM (1974) Electron microscopic study of neurofibrillary tangles in Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 29:175–179
Shibayama H, Kitoh J (1978) Electron microscopic structure of the Alzheimer's neurofibrillary changes in case of atypical senile dementia. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 41:229–234
Sternberger NH, Sternberger LA, Ulrich J (1985) Aberrant neurofilament phosphorylation in Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:4274–4276
Takauchi S, Mizuhara T, Miyoshi K (1983) Unusual paired helical filaments in progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 59:225–228
Tellez-Nagel I, Wisniewski HM (1973) Ultrastructure of neurofibrillary tangles in Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome. Arch Neurol 29:324–327
Tomonaga M (1977) Ultrastructure of neurofibrillary tangles in progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 37:177–181
Wang GP, Grundke-Iqbal I, Kascsak RJ, Iqbal K, Wisniewski HM (1984) Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles: monoclonal antibodies to inherent antigen(s). Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 62:268–275
Wiche G, Briones E, Hirt H, Krepler R, Artlieb U, Denk H (1983) Differential distribition of microtubule-associated proteins MAP-1 and MAP-2 in neurons of rat brain and association of MAP-1 with microtubules of neuroblastoma cells (clone N2A). EMBO J 2:1915–1920
Wood JG, Mirra SS, Pollock NJ, Binder LI (1986) Neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer disease share antigenic determinants with the axonal microtubule-associated protein tau. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:4040–4043
Yagishita S, Itoh Y, Amano N, Nakano T, Saitoh A (1979) Ultrastructure of neurofibrillary tangles in progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 48:27–30
Yagishita S, Itoh Y, Wang N, Amano N (1981) Reappraisal of the fine structure of Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangles. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 54:239–246
Yen SH, Horoupian DS, Terry RD (1983) Immunocytochemical comparison of neurofibrillary tangles in senile dementia of Alzheimer type, progressive supranuclear palsy, and postencephalitic parkinsonism. Ann Neurol 13:172–175
Yen SH, Crowe A, Dickson DW (1985) Monoclonal antibodies to Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. 1. Identification of polypeptides. Am J Pathol 120:282–291
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by a project of the Austrian Ministery of Science and Research
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bancher, C., Lassmann, H., Budka, H. et al. Neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease and progressive supranuclear palsy: antigenic similarities and differences. Acta Neuropathol 74, 39–46 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00688336
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00688336