Summary
Anterior tibial muscle biopsies of the hemiplegic side of 16 patients with a cerebrovascular accident in the middle cerebral artery region were analyzed qualitatively and quantitatively by enzyme histochemistry and electron microscopy.
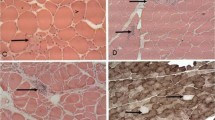
Patients grouped according to the time lapsed as from the occurrence of the accident (1–17 months) demonstrated a progressive decrease in the fiber diameter and changes in fiber type distribution with predominant type II atrophy and type I predominance. Nuclear internalization, myopathic alterations, and perifascicular fatty infiltrations were observed constantly.
In the affected fibers the ultrastructural findings were myofibrillar alterations with the formation of rods and cytoplasmic bodies. There was accumulation of lipofuscin, glycogen, and lipid droplets. Microvascular changes were observed frequently.
Biopsies from the asymptomatic legs were either normal or showed age-related muscle alterations.
Correlation was noted between the clinical and functional status of the patients and the morphological aspects seen in muscle biopsies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brooke MH, Engel WK (1969) the histographic analysis of human muscle biopsies with regard to fiber types. Part 2: Diseases of the upper and lower motor neuron. Neurology (Minneap) 19:378–393
Dubowitz V, Brooke MH, (1973) Muscle biopsy. A modern approach. Saunders, London
Edström L (1969) Selective changes in the size of red and white muscle fibers in upper motor neuron lesions and parkinsonism. J Neurol Sci 11:537–550
Edwars R, Young A, Wiles M (1980) Needle biopsy of skeletal muscle in the diagnosis of myopathy and the clinical study of muscle function and repair. New Engl J Med 302:261–271
Engel WK (1962) The essentiality of histo- and cytochemical studies of skeletal muscle in the investigation of neuromuscular disease. Neurology (Minneap) 12:778–794
Essen B (1977) Intramuscular substrate utilization during prolonged exercise. Ann NY Acad Sci 201:30–43
Fenichel GM, Daroff RB, Glaser GH (1964) Hemiplegic atrophy: histological and etiologic considerations. Neurology (Minneap) 14:883–890
Feudell P, Fischer W (1956) Tropische und vasomotorische Störungen bei kapsularen Hemiplegien. Dtsch Arch Klin Med 203:117–134
Jennekens FGI, Tomlinson BE, Walton JN (1971) Histochemical aspects of five limb muscles in old age. An autopsy study. J Neurol Sci 14:259–276
Kennard MA, Viets HR, Fulton JF (1934) The syndrome of the premotor cortex in man: impairment of skilled movements, forced grasping spasticity and vasomotor disturbances. Brain 57:69–84
Lithell H, Orlander J, Schele R, Sjodin B, Karlsson J (1979) Changes in lipoprotein-lipase activity and lipid stores in human skeletal muscle with prolonged heavy exercise. Acta Physiol Scand 107:257–261
Patel AN, Razzak ZA, Dastur DK (1969) Disuse atrophy of human skeletal muscles. Arch Neurol (Chic) 20:413–421
Poloni M, Scelsi R, Marchetti C, Nappi G (1979) Un caso di miopatia acuta ipokaliemica: studio clinico e morfologico. In: Aloisi M, Terzian H, Fiaschi A (eds) Malattie neuromuscolari. Cortina, Verona, pp 447–457
Prince FP, Hikida RS, Hagerman FG, Staron RS, Allen WH (1981) A morphometric analysis of human muscle fibres with relation to fibre types and adaptations to exercise. J Neurol Sci 49:165–179
Scelsi R, Marchetti C, Poggi P (1980) Histochemical and ultrastructural aspects of M. vastus lateralis in sedentary old people (age 65–89 years). Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 51:99–105
Scelsi R, Marchetti C, Poggi P, Lotta S, Lommi G (1982) Muscle fiber morphology and distribution in paraplegic patients with traumatic cord lesions. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 57:243–248
Schmitt HP (1976) Measurements of voluntary muscle fibre cross sections: A comparative study of different possible methods Microsc Acta 77:427–440
Silverstein A (1955) Diagnostic localizing value of muscle atrophy in parietal lobe lesions. Neurology (Minneap) 5:30–55
Siperstein MD, Raskin PR, Burns H (1973) Electron-microscopic quantification of diabetic microangiopathy. Diabetes 22:514–524
Sjöström M, Ängquist KA, Rais O (1980) Intermittent claudication and muscle fibre fine structure: Correlation between clinical and morphological data. Ultrastruct Pathol 1:309–326
Sturup G, Boltan B, Williams DJ, Carmichael SA (1935) Vasomotor responses in hemiplegic patients. Brain 58:456–469
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scelsi, R., Lotta, S., Lommi, G. et al. Hemiplegic atrophy. Acta Neuropathol 62, 324–331 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00687615
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00687615