Summary
-
1.
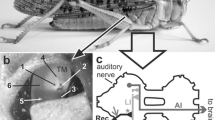
The reactions of tympanic nerve fibers ofLocusta migratoria were recorded by glass microelectrodes in the metathoracic ganglion.
-
2.
The units were classified by frequency-, intensity-, and directional characteristics as well as by their response pattern. The response to speciesspecific song is compared with the response to song ofEphippiger ephippiger.
-
3.
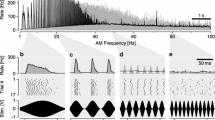
The physiological properties lead to a classification into three types of low-frequency neurons (characteristic frequency 3.5–4 kHz; 4kHz; 5.5–6 kHz) and one type of high-frequency neuron (12–20 kHz). This is similar to other species (Gray, 1960, Michelsen, 1971).
-
4.
Intensity-coding is done by sharp rising intensity characteristics and by different absolute thresholds of the units.
-
5.
There is a marked directional sensitivity with some differences between LF and HF units. In the low frequency range the tympanal organ seems to react as a pressure gradient receiver; for high frequencies another mechanism is discussed.
-
6.
No filtering of species-specific song takes place at the level of the receptor cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Adam, L.J.: Neurophysiologie des Hörens und Bioakustik einer Feldheuschrecke (Locusta migratoria). Z. vergl. Physiol.63, 227–289 (1969)
Adam, L.J., Schwartzkopff, J.: Getrennte nervöse Repräsentation für verschiedene Tonbereiche im Protocerebrum vonLocusta migratoria. Z. vergl. Physiol.54, 246–255 (1967)
Autrum, H.: Über Gehör- und Erschütterungssinn bei Loeustiden. Z. vergl. Physiol.28, 580–637 (1941)
Autrum, H., Schwartzkopff, J., Swoboda, H.: Der Einfluß der Schallrichtung auf die Tympanalpotentiale vonLocusta migratoria. Biol. Zbl.80, 385–402 (1961)
Dörrscheidt, G. J.: Statistical modulation analysis of animal sounds as a basis for computer synthesised quasi —natural stimuli in bioacoustical research. Proc. 2nd. Seminar on Experimental Simulating and Solving of Probality Problems. Prag 1973 (in press)
Gray, E.G.: The fine structure of the insect ear. Phil. Trans. B243, 75–94 (1960)
Haskell, P.T.: Hearing in certain Orthoptera. I. Physiology of sound receptors. II. The nature of the response of certain receptors to natural and imitation stridulation. J. exp. Biol.33, 756–776 (1956)
Haskell, P.T.: Stridulation and associated behaviour in certain Orthoptera. I. Analysis of the stridulation of, and the behaviour between males. Brit. J. Anim. Behav.5, 139–148 (1957)
Helversen, D. von: Gesang des Männchens und Lautschema des Weibchens bei der FeldheuschreckeChortippus biguttulus (Orthoptera, Acrididae). J. comp. Physiol.81, 381–422 (1972)
Horridge, G.A.: Pitch discrimination in Orthoptera (Insecta) demonstrated by responses of central auditory neurons. Nature (Lond.)185, 623–624 (1960)
Horridge, G.A.: Pitch discrimination in locusts. Proc. roy. Soc. B155, 218–231 (1961)
Kalmring, K.: Akustische Neuronen im Unterschlundganglion der WanderheuschreckeLocusta migratoria. Z. vergl. Physiol.72, 95–110 (1971)
Kalmring, K., Rheinländer, J., Römer, H.: Akustische Neuronen im Bauchmark vonLocusta migratoria. Der Einfluß der Schallrichtung auf die Antwortmuster. J. comp. Physiol.80, 325–352 (1972)
Katsuki, Y.: Neural mechanisms of hearing in cats and insects. In: Electrical activity of single cells (ed. Y. Katsuki) pp. 53–75. Tokyo: Iga Kushuin 1960
Michelsen, A.: Pitch discrimination in the locust ear: Observations on single cells. J. Insect Physiol.12, 1119–1131 (1966)
Michelsen, A.: The physiology of the locust ear. I. Frequency sensitivity of single cells in the isolated ear. II. Frequency discrimination based upon resonances in the tympanum. III. Acoustical properties of the intact ear. Z. vergl. Physiol.71, 49–128 (1971)
Murray, M.J.: Fibre groups in the auditory nerve of the locust. Nature (Lond.)218, 95–96 (1968)
Popov, A.V.: Electrophysiological studies on the peripheral auditory neurons in the locust (in Russian). J. evol. biochem. Physiol.1, 239–250 (1965)
Popov, A.V.: Synaptic transmission at the level of the first synapses of the auditory system inLocusta migratoria [in Russian]. In: Evolutionary neurophysiology and neurochemistry (ed. E.M. Krebs). Leningrad: Nauka 1967
Rehbein, H.G.: Experimentell-anatomische Untersuchungen über den Verlauf der Tympanalnervenfasern im Bauchmark von Feldheuschrecken, Laubheuschrecken und Grillen. Verh. dtsch. Zool. Ges.66, 184–189 (1973)
Rehbein, H.G., Kalmring, K., Römer, H.: Structure and function of acoustic neurons in the thoracic ventral nerve cord ofLocusta migratoria (Acrididae). J. comp. Physiol.95, 263–280 (1974)
Rheinländer, J.: Transmission of acoustic information at three neuronal levels in the auditory system ofDecticus verrucivorus (Tettigoniidae, Orthoptera). J. comp. Physiol.97, 1–53 (1975)
Rheinländer, J., Kalmring, K.: Die afferente Hörbahn im Bereich des Zentralnervensystems vonDecticus verrucivorus (Tettigoniidae). J. comp. Physiol.85, 361–410 (1973)
Suga, N.: Peripheral mechanism of hearing in locust. Jap. J. Physiol.10, 533–546 (1960)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mit Unterstützung der Deutschen Forschungsgemeinschaft und im Rahmen des Programms des SFB 114 und zusätzlichen Leihgaben an Prof. Schwartzkopff
Herrn Prof. Dr. J. Schwartzkopff danke ich für die Unterstützung der Arbeit und die intensive Diskussion der Ergebnisse. Den Herren Dr. J. Rheinländer, Dr. K. Kalmring und H.G. Rehbein bin ich für die eingehende Diskussion im Verlauf der Arbeit dankbar, ebenso wie den Herren Dr. Leppelsack und Dr. Dörrscheidt für die Überlassung der Computerprogramme.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Römer, H. Die Informationsverarbeitung tympanaler Rezeptorelemente vonLocusta migratoria (Acrididae, Orthoptera). J. Comp. Physiol. 109, 101–122 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00663438
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00663438