Summary
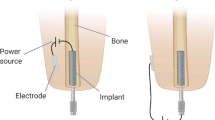
Electrical stimulation with 8 μA direct current was applied to the triradiate physeal cartilage of young rabbits for periods of 3, 4, and 5 weeks. The effect was evaluated by morphometric measurement and histological observation. We tried to improve some previously described technical problems (e.g., movement of electrode during experiment) in this model of the growing acetabulum. Statistically significant differences in acetabular depth were found between the experimental and the control side in the 3-week group, but no obvious differences were found among the other measurements. Characteristic thickening of the growing physeal cartilage, especially proliferating cells, was found in the stimulated sides. Electricity affects the cell behavior in the triradiate physeal cartilage as well as the growth plate of long bone, but further study is still necessary to find more appropriate conditions to gain actual growth.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong PF, Brighton CT (1986) Failure of the rabbit tibial growth plate to respond to the long-term application of a capacitively-coupled electrical field. J Orthop Res 4:446–451
Black J, Brighton CT (1979) Mechanisms of stimulation of osteogenesis by direct current. In: Brighton CT, Black J, Pollack SR (eds) Electrical properties of bone and cartilage: experimental effects and clinical applications. Grune & Stratton, New York, pp 215–224
Breur GJ, Van Enkevort BA, Farnum CE, Wilsman NJ (1991) Linear relationship between the volume of hypertrophyic chondrocytes and the rate of longitudinal bone growth in growth plates. J Orthop Res 9:348–359
Brighton CT, Cronkey JE, Osterman AL (1976) In vitro epiphyseal-plate growth in various constant electrical fields. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 58:971–978
Brighton CT, Pfeffer GB, Pollack SR (1983) In vivo growth plate stimulation in various capacitively coupled electrical fields. J Orthop Res 1:42–49
Brighton CT, Jensen L, Pollack SR, Tolin BS, Clark CC (1989) Proliferative and synthetic response of bovine growth plate chondrocytes to various capacitively coupled electrical fields. J. Orthop Res 7:759–765
Forgon M, Vámhidy V, Kellényi L (1985) Bone growth accelerated by stimulation of the epiphyseal plate with electric current. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 104:121–124
Hansson LI (1967) Daily growth in length of diaphysis measured by oxytetracycline in rabbit normally and after medullary plugging. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl 101:123–143
Harrison TJ (1958) The growth of the pelvis in the rat — a mensural and morphological study. J Anat 92:236–260
Kember NF (1973) Patterns of cell division in the growth plates of the rat pelvis. J Anat 116:445–452
Klems H (1981) Tierexperimentelle Studie zur Stimulation des Extremitätenwachstums durch elektrischen Gleichstrom. Z Orthop 119:315–319
Minkin C, Poulton BR, Hoover WH (1968) The effect of direct current on bone. Clin Orthop 57:303–309
Nogami H, Aoki H, Okagawa T, Mimatsu K (1982) Effects of electric current on chondrogenesis in vitro. Clin Orthop 163:243–247
Norton LA (1982) Effects of a pulsed electromagnetic field on a mixed chondroblastic tissue culture. Clin Orthop 167:280–289
Sato O, Akai M (1989) Effect of direct-current stimulation on the growth plate: in vivo study with rabbits. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 109:9–13
Seinsheimer F, Sledge CB (1981) Parameters of longitudinal growth rate in rabbit epiphyseal growth plates. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 63:627–630
Sissons HA, Hadfield GJ (1955) The influence of cortisone on the structure and growth of bone. J Anat 89:69–78
Smith RL, Nagel DA (1983) Effects of pulsing electromagnetic fields on both growth and articular cartilage. Clin Orthop 181:277–282
Watson J, de Haas WG, Hauser SS (1975) Effect of electric fields on growth rate of embryonic chick tibiae in vitro. Nature 254:331–332
Yabsley RH, Harris WR (1965) The effect of shaft fractures and periosteal stripping on the vascular supply to epiphyseal plates. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 47:551–566
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takei, N., Akai, M. Effect of direct current stimulation on triradiate physeal cartilage. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 112, 159–162 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00662280
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00662280