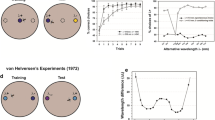
Summary
Using a fully automatized procedure and a training scheme symmetrical with respect to the visual stimuli as well as to the aversive stimulus,Drosophila could be conditioned to blue and yellow lights. With constant test conditions and variation of the light intensities during the training procedure, it could be shown that the flies respond primarily to the colour of the light.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benzer, S.: Behavioral mutants ofDrosophila isolated by countercurrent distribution. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.)58, 1112 (1967)
Bicker, G., Spatz, H.-C.: Maze learning ability ofDrosophila melanogaster. Nature (Lond.)260, 371 (1976)
Burkhardt, D.: Colour discrimination in insects. Adv. Insect Physiol.2, 131–173 (1964)
Cosens, D., Wright, R.: Light elicited isolation of the complementary visual input systems in white-eyedDrosophila. J. Insect Physiol.81, 309 (1975)
Fischbach, K.F.: Funktionelle Differenzierung und Wechselwirkungen der Rezeptorsysteme im Komplexauge vonDrosophila melanogaster. (Thesis, Freiburg 1976)
Franceschini, N.: Sampling of the visual environment by the compound eye of the fly: Fundamentals and applications. In: Photoreceptor optics (ed. A.W. Snyder, R. Menzel). Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1975
Frisch, K. von: Der Farbensinn und Formensinn der Biene. Zool. Jb., Abt. allg. Zool. Physiol.35, 1 (1914)
Fukushi, T.: Olfactory conditioning in the housefly,Musca domestica. Annot. Zool. Jap.46, 135 (1973)
Fukushi, T.: Classical conditioning to visual stimuli in the housefly,Musca domestica. J. Insect Physiol.22, 361 (1976)
Hamilton, W.F.: A direct method of testing color vision in lower animals. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.)8, 350 (1922)
Harris, W.A., Stark, W.S., Walker, J.A.: Genetic dissection of the photoreceptor system in the compound eye ofDrosophila melanogaster. J. Physiol. (Lond.)256, 415 (1976)
Hay, D.A.: Strain differences in maze-learning ability ofDrosophila melanogaster. Nature (Lond.)257, 45 (1975)
Heisenberg, M., Götz, K.G.: The use of mutations for the partial degradation of vision inDrosophila melanogaster. J. comp. Physiol.98, 217 (1975)
Jacob, K.G., Willmund, R., Folkers, E., Fischbach, K.-F., Spatz, H.-Ch.: T-maze phototaxis ofDrosophila melanogaster and several mutants in the visual systems. J. comp. Physiol., in press (1977)
McEwen, R.S.: The reaction to light and gravity inDrosophila and its mutants. J. exp. Zool.25, 49 (1918)
Menne, D.: Farbensehen beiDrosophila melanogaster. (Thesis, Freiburg 1976)
Minke, B., Wu, C.F., Pak, W.L.: Isolation of light induced response of the central retinula cells from the electroretinogram ofDrosophila. J. comp. Physiol.98, 345 (1975)
Murphey, R.M.: Instrumental conditioning of the fruit fly,Drosophila melanogaster. Anim. Behav.15, 153 (1967)
Murphey, R.M.: Spatial discrimination performance ofDrosophila melanogaster: Some controlled and uncontrolled correlates. Anim. Behav.17, 43 (1969)
Murphey, R.M.: Spatial discrimination performance ofDrosophila melanogaster: Test-retest assessements and a reinterpretation. Anim. Behav.21, 687 (1973)
Nelson, M.C.: Classical conditioning in the blowfly (Phormia regina): associative and excitatory factors. J. comp. physiol. Psychol.77, 353 (1971)
Purdy, D. McL.: Spectral hue as a function of intensity. Amer. J. Psychol.43, 541 (1931)
Quinn, W.G., Harris, W.A., Benzer, S.: Conditioned behavior inDrosophila melanogaster. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.)71, 708 (1974)
Schümperli, R.: Evidence for colour vision inDrosophila melanogaster through spontaneous phototactic choice behaviour. J. comp. Physiol.86, 77 (1973)
Snedecor, G.W., Cochran, W.G.: Statistical methods (6th ed.). Ames, Iowa: Iowa State University Press 1967
Spatz, H.-Ch., Emanns, A., Reichert, H.: Associative learning ofDrosophila melanogaster. Nature (Lond.)248, 359 (1974)
SPSS, Statistical package for the social sciences (ed. N. Nie). New York: McGraw Hill (1975)
Stark, W.S.: Spectral sensitivity of visual response alternations mediated by interconversions of native and intermediate photopigments inDrosophila. J. comp. Physiol.105, 15 (1975)
Yeatman, F.R., Hirsch, J.: Attempted replication of, and selective breeding for, instrumental conditioning ofDrosophila melanogaster. Anim. Behav.19, 454 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
We are grateful to Dr. W. Edrich and K.-F. Fischbach for exchange of ideas. Dr. J. Bammert gave advice for the statistical treatment.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Menne, D., Spatz, H.C. Colour vision inDrosophila melanogaster . J. Comp. Physiol. 114, 301–312 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00657325
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00657325