Abstract
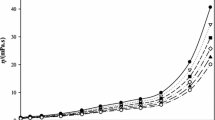
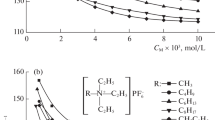
Ethylammonium nitrate (ETAN), a low melting fused salt which is completely miscile in water and in many non-aqueous solvents, was used as a model system for the study of concentrated non-aqueous electrolyte solutions. Acetonitrile (AN) was chosen as a representative aprotic solvent. Some data were also obtained for water as solvent. The properties investigated over the whole mole fraction range, many as a function of temperature, were solid-liquid phase diagram, volume, heat capacity, conductivity and viscosity. Most properties in both solvents vary in a regular fashion over the whole mole fraction range and the properties at high concentration rapidly tend to those of the molten salt. The apparent volumes and heat capacities vary linearly with lnX2 over a large mole fraction range. There is evidence of significant association in AN (K A =1094 l-mol−) but not in water. The low concentration thermodynamic data were fitted with an association model using the above K A to obtain the partial molar quantities of ETAN at infinite dilution and in the associated state. These latter values are of the same magnitude as the molar quantities of the molten electrolyte.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Barthel, H.-J. Gores, G. Schmeer, and R. Wachter, inTopics in Current Chemistry, Vol. III (Springer Verlag, Heidelberg, 1983) p. 33.
G. J. Janz and R. P. T. Tomkins,Nonaqueous Electrolytes Handbook, Vol. 1 (Academic Press, New York, 1972).
J. E. Desnoyers and C. Jolicoeur, inComprehensive Treatise of Electrochemistry, Vol 5, B. E. Conway, J. O. M. Bockris, and E. Yeager, eds., (Plenum, New York, 1983) p. 1.
J. I. Lankford and C. M. Criss,J. Solution Chem. 16, 753 and 885 (1987).
J. Barthel, L. Iberl, J. Rossmaier, H. J. Gores, and B. Kaukal,J. Solution Chem. 19, 321 (1990).
J. Barthel and W. Kunz,J. Solution Chem. 17, 399 (1988).
D. Inman and D. G. Lovering,Ionic Liquids (Plenum, New York, 1981).
D. F. Evans, A. Yamauchi, R. Roman, and E. Z. Casassa,J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 86, 89 (1982).
M. Allen, D. F. Evans, and R. Lumry,J. Solution Chem. 14, 549 (1985).
M. Hadded, M. Biquard, P. Letellier, and R. Schaal,Can. J. Chem. 63, 565 (1985).
M. Biquard, P. Letellier, and M. Fromon,Can. J. Chem. 63, 3587 (1985).
M. Hadded, H. Bahri, and P. Letellier,J. Chim. Phys. 83, 419 (1986).
R. G. Horn, D. F. Evans, and B. W. Ninham,J. Phys. Chem. 92, 3531 (1988).
M. Hadded, A. Mayaffre, and P. Letellier,J. Chim. Phys. 86, 525 (1989).
R. Zana, G. Perron, and J. E. Desnoyers,J. Solution Chem. 8, 729 (1979).
F. Quirion, D. Lambert, and G. Perron,Can. J. Chem. 70, 2745 (1992).
P. Picker, E. Tremblay, and C. Jolicoeur,J. Solution Chem. 3, 377 (1974).
P. Picker, P.-A. Leduc, P. R. Philip, and J. E. Desnoyers,J. Chem. Thermodyn. 3, 631 (1971).
J. E. Desnoyers, C. de Visser, G. Perron, and P. Picker,J. Solution Chem. 5, 605 (1976).
R. DeLisi, S. Milioto, and R. E. Verrall,J. Solution Chem. 19, 639 (1990).
A. H. Roux, unpublished results.
Depository of unpublished Data, CISTI, NRC, Ottawa, ON, Canada K1A 0S2.
G. Perron, L. Couture, and J. E. Desnoyers,J. Solution Chem. 21, 433 (1992).
C. Treiner and R. M. Fuoss,Z. Phys. Chem. 228, 343 (1965).
G. Perron, L. Couture, D. Lambert, and J. E. Desnoyers,J. Electroanal. Chem. 355, 277 (1993).
J.-C. Justice, inComprehensive Treatise of Electrochemistry, Vol. 5, B. E. Conway, J O'M. Bockris, and E. Yeager, eds., (Plenum, New York, 1983) p. 223.
J. Barthel, R. Buchner and H.-J. Wittman,Z. Phys. Chem. 139, 23 (1984).
J. E. Desnoyers, G. Perron, L. Couture, and J.-C. Justice (in preparation).
K. Pitzer, inActivity Coefficients in Electrolyte Solutions, R. M. Pytkowicz, ed., (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1979).
G. Perron, N. Desrosiers and J. E. Desnoyers,Can. J. Chem. 54, 2163 (1976).
D. F.-T. Tuan and R. M. Fuoss,J. Phys. Chem. 67, 1343 (1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perron, G., Hardy, A., Justice, JC. et al. Model system for concentrated electrolyte solutions: Thermodynamic and transport properties of ethylammonium nitrate in acetonitrile and in water. J Solution Chem 22, 1159–1178 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00651697
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00651697