Abstract
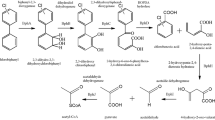
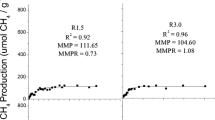
The potential for biological transformation of 23 xenobiotic compounds by microorganisms in municipal solid waste (MSW) samples from a laboratory scale landfill reactor was studied. In addition the influence of these xenobiotic compounds on methanogenesis was investigated. All R11, 1,1 dichloroethylene, 2,4,6 trichlorophenol, dimethyl phthalate, phenol, benzoate and phthalic acid added were completely transformed during the period of incubation (> 100 days). Parts of the initially added perchloroethylene, trichloroethylene, R12, R114, diethyl phthalate, dibutyl phthalate and benzylbutyl phthalate were transformed. Methanogenesis from acetate was completely inhibited in the presence of 2,5 dichlorophenol, whereas 2,4,6 trichlorophenol and R11 showed an initial inhibition, whenafter methane formation recovered. No transformation or effect on the anaerobic microflora occurred for R13, R22, R114, 3 chlorobenzoate, 2,4,6 trichlorobenzoate, bis(2 ethyl)hexyl phthalate, diisodecyl phthalate and dinonyl phthalate. The results indicate a limited potential for degradation, of the compounds tested, by microorganisms developing in a methanogenic landfill environment as compared with other anaerobic habitats such as sewage digestor sludge and sediments.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BBP:
-
benzylbutylphthalate
- DEHP:
-
bis(2 ethylhexyl) phthalate
- 3 CB:
-
3 chlorobenzoate
- R22:
-
chlorodifluoromethane
- CFC:
-
chlorofluorocarbon
- R13:
-
chlorotrifluoromethane
- cis1,2 DCE:
-
cis 1,2 dichloroethylene
- DBP:
-
dibutyl phthalate
- R12:
-
dichlorodifluoromethane
- 1,1 DCE:
-
1,1 dichloroethylenel
- R114:
-
dichlorotetrafluoroethane
- 2,5 DCP:
-
2,5 dichlorophenol
- DEP:
-
diethyl phthalate
- DiDP:
-
diisodecyl phthalate
- DMP:
-
Dimethyl phthalate
- DNP:
-
dinonyl phthalate
- MSW:
-
dunicipal solid waste
- PCE:
-
perchloroethylene
- PA:
-
phthalic acid
- PAE:
-
phthalic acid esters
- R11:
-
trichlorofluoromethane
- 2,4,6 TCB:
-
2,4,6 trichlorobenzoate
- 2,4,6 TCP:
-
2,4,6 trichlorophenol
- VC:
-
vinylchloride
References
Barlaz MA, Schaefer DM & Ham RK (1989) Bacterial population development and chemical characteristics of refuse decomposition in a sanitary landfill. Appl Environ. Microbiol. 55: 55–65
Battersby NS & Wilson V (1989) Survey of the anaerobic biodegradation potential of organic chemicals in digesting sludge. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55: 433–439
Béchard G, Bisaillon J-G, Beaudet R & Sylvestre M (1990) Degradation of phenol by a bacterial consortium under methanogenic conditions. Can. J. Microbiol. 36: 573–578
Christensen TH, Bjerg PL, Rügge K, Albrechtsen HJ, Heron G, Pedersen JK, Foverskov A, Skov B, Würtz S & Refstrup M (1993a) Attenuation of organic leachate pollutants in groundwater. In: Sardinia 93. Proc. 4th Int. Landfill Symposium., Vol 2 (pp 1105–1116) 11–15 Oct. Sardinia, Italy: Imola: Grafiche Galeati
Christensen TH, Albrechtsen HJ, Kromann A, Ludvigsen L & Skov B (1993b) The degradation of chlorinated aliphatic compounds in a sanitary landfill. In: Sardinia 93. Proc. 4th Int. Landfill Symposium., Vol 2 (pp 1087–1092) 11–15 Oct. Sardinia, Italy: Imola: Grafiche Galeati
Christensen TH & Kjeldsen P (1989) Basic biochemical processes in landfills. In: Cristensen TH, Cossu R & Stegmann R (Eds) Sanitary Landfilling: Process, Technology and Environmental Impact (pp 29–49). Academic Press, London
Deipser A & Stegmann R (1994) The origin and fate of volatile trace components in municipal solid waste landfills. Waste Management & Research 12: 129–139
Egli C, Stromeyer S, Cook AM & Leisinger T (1990) Transformation of tetra- and trichloromethane to CO2 by anaerobic bacteria is a non-enzymatic process. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 68: 207–212
Elder DJE & Kelly DJ (1994) The bacterial degradation of benzoid acid and benzenoid compounds under anarobic conditions: Unifying trends and new perspectives. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 13: 441–468
Freedman DL & Gossett JM (1989) Biological reductive dehalogenation of tetrachloroethylene and trichloroethylene to ethylene under methanogenic conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55: 2144–2151
Horowitz A, Shelton DR, Cornell CP & Tiedje JM (1982) Anaerobic degradation of aromatic compounds in sediments and digested sludge. Dev. Indust. Microbiol. 23: 435–444
KEMI (1990) Swedish National Chemicals Inspectorate. Appendix to Report 10/90. Descriptions of Compounds. Print Graf, Stockholm (In Swedish)
Knoll G & Winter J (1989) Degradation of phenol via carboxylation to benzoate by a defined, obligate syntrophic consortium of anaerobic bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 30: 318–324
Krone UE & Thauer RK (1992) Dehalogenation of trichlorofluoromethane (CFC-11) byMethanosarcina barkeri. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 90: 201–204
Krone UE, Thauer RK, Hogenkamp HPC & Steinbach K (1991) Reductive formation of carbon monoxide from CCl4 and freons 11, 12, and 13 catalysed by corrinoids. Biochem. 30: 2713–2719
Lagerkvist A & Chen H (1993) Control of two step anaerobic degradation of municipal solid waste (MSW) by enzyme addition. Wat. Sci. Tech. 27: 47–56
Laugwitz R (1990) Deponiegase als Quelle halogenierter Kohlenwasserstoffe. Müll und Abfall 3: 142–151
Lovley DR & Woodward JC (1992) Consumption of freons CFC-11 and CFC-12 by anaerobic sediments and soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 26: 925–929
Madsen J & Aamand J (1992) Anaerobic transformation and toxicity of trichlorophenols in a stable enrichment culture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58: 557–561
Mohn WW & Tiedje JM (1992) Microbial reductive dehalogenation. Microbiol. Rev. 56: 482–507
O'Connor OA, Rivera MD & Young LY (1989) Toxicity and biodegradation of phthalic acid esters under methanogenic conditions. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 8: 569–576
Öman C & Hynning P-Å (1993) Identification of organic compounds in municipal landfill leachates. Environ. Pollut. 80: 265–271
Örlygsson J, Houwen FP & Svensson BH (1993) Anaerobic degradation of proteins and the role of methane formation in steady state thermophilic enrichment cultures. Swedish J. agric. Res. 23: 45–54
Pohland FR (1991). Fundamental principles and management strategies for landfill codisposal practices. In: Sardinia 91. Proc. 3rd Int. Landfill Symposium., Vol 1 (pp. 1445–1460) 14–18 Oct. Sardinia, Italy: Imola: Grafiche Galeati
Reinhart DR & Pohland FG (1991) The assimilation of organic hazardous wastes by municipal solid waste landfills. J. Indust. Microbiol. 8: 193–200
Shelton DR, Boyd SA & Tiedje JM (1984) Anaerobic biodegradation of phthalic acid esters in sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 18: 93–97
Shelton DR & Tiedje JM (1984) General method for determining anaerobic biodegradation potential. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 47: 850–857
Stegmann R (1981) Beschreibung eines Verfahrens zur Untersuchung anaerober Umsetzungsprozesse von Festen Abfallstoffen im Labormaßstab. Müll und Abfall 2.
Vogel TM & McCarty PL (1985) Biotransformation of tetrachloroethylene to trichloroethylene, dichloroethylene, vinylchloride and carbondioxide under methanogenic conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 49: 1080–1083
Willumsen HC, Burian-Hanssen P & Jensen PE (1988) Toxic components in biogas extracted from landfills. In: Hall ER & Hobson PN (Eds) Anaerobic Digestion, 5th Int. Symposium on Anaerobic Digestion (pp 507–512). Pergamon Press, Bologna
Zehnder AJB, Huser BA, Brock TD & Wuhrmann K (1980) Characterization of an acetate-decarboxylating, non-hydrogen-oxidizing methane bacterium. Arch. Microbiol. 124: 1–11
Zhang X & Wiegel J (1990) Sequential anaerobic degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol in freshwater sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56: 1119–1127
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ejlertsson, J., Johansson, E., Karlsson, A. et al. Anaerobic degradation of xenobiotics by organisms from municipal solid waste under landfilling conditions. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 69, 67–74 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00641613
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00641613