Summary
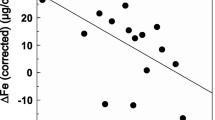
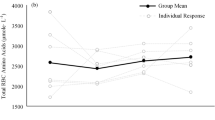
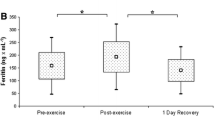
To characterize the so-called pseudoanaemia of endurance-trained athletes, the plasma volume (PV), red cell volume (RCV) and total blood volume (TBV) of 12 male and 12 female athletes and 5 male and 5 female nonexercising controls were measured using125I-la-belled human serum albumin and51Cr-labelled erythrocytes. The mean PV of the male athletes (52.8 ml·kg−1) was 37.5% higher than that of the controls (38.4 ml·kg−1), while the 18.1% increase measured in the female runners (51.5 ml·kg−1) over the controls (43.6 ml·kg−1) was a novel observation. Although the RCV was significantly greater (34.7%) in male athletes (32.6 ml·kg−1 vs 24.2 ml·kg−1 in the controls), a similar elevation (3.6%) was not found in the female athletes (25.9 ml·kg−1) compared to the sedentary women (22.8 ml·kg−1). This could have been due to iron-limited erythropoiesis because the RCV of the female athletes defined as clinically anaemic was markedly lower that of the nonanaemic women (P<0.05). The elevated plasma protein mass and concentration measured in the athletes partly accounted for their expanded PV. It was concluded that the decreased blood haemoglobin levels reported in the endurance athletes was largely a dilutional effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addison GM, Beamish MR, Hales CN, Hodgkins M, Jacobs A, Llewellin P (1972) An immunoradiometric assay for ferritin in the serum of normal subjects and patients with iron deficiency and iron overload. J Clin Pathol 25:326–329
Cary NC (Ed) (1985) Statistical Analysis Systems Users Guide. 5 edn. DMDP Statistical Software Inc, Los Angeles, p 956
Brotherhood J, Brozovic B, Pugh LGC (1975) Haematological status of middle- and long-distance runners. Clin Sci Mol Med 48:139–145
Clement DB, Asmundsen RC (1982) Nutritional intake and haematological parameters in endurance runners. Physician Sportsmed 10:37–43
Convertino VA, Keil LC, Bernauer EM, Greenleaf JE (1981) Plasma volume, osmolality, vasopressin and renin activity during graded exercise in man. J Appl Physiol 50:123–128
Costill DL, Branam G, Fink W, Nelson R (1976) Exercise induced sodium conservation: changes in plasma renin and aldosterone. Med Sci Sports Exerc 8:209–213
Eichner RE (1986) The anaemias of athletes. Physician Sportsmed 14:122–130
Greenleaf JE, Sciaraffa D, Shvartz E, Keil LC, Brock PJ (1981) Exercise-training hypotension: implications for plasma volume, renin and vasopressin. J Appl Physiol 51:293–305
Hallberg L, Magnusson B (1984) The etiology of “sports anaemia”: a physiological adaptation of the oxygen — dissociation curve of hemoglobin to an unphysiological exercise load. Acta Med Scand 216:145–148
Haralambie G (1969) Changes in serum glycoproteins after long lasting exercise. Clin Chim Acta 26:287–291
International Committee on Radiation Protecion (1960) Report of Committee 11 on permissible dose of internal radiation, 1959. ICRP publications no. 2. Pergamon Press, Oxford
International Committee for Standardization in Haematology (1980) Recommended methods for measurement of red-cell and plasma volume. J Nucl Med 21:793–800
Johansson L, Mattson S, Nosslin B (1984) Effective dose equivalents for radiopharmaceuticals. Eur J Nucl Med 9:485–489
Koch G, Röcker L (1977) Plasma volume in trained boys and fit young men. J Appl Physiol 43:1085–1088
Magnusson B, Hallberg L, Rossander L, Swolin B (1984) Iron metabolism and ‘sports anaemia’. I. A study of several iron parameters in elite athletes with differences in iron status. Acta Med Scand 216:149–156
McArdle WD, Katch FI, Katch VL (1986) Exercise physiology: energy, nutrition and exercise performance, 2nd edn. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, pp 507–508
Oscai LB, Williams BT, Hertig BA (1968) Effect of exercise on blood volume. J Appl Physiol 24:622–624
Poortmans JR, Haralambie G (1979) Biochemical changes in a 100 km run: protein in serum and urine. Eur J Appl Physiol 40:245–254
Röcker L, Kirsch KA, Stoboy H (1976) Plasma volume, albumin and globulin concentrations and their intravascular protein masses. Eur J Appl Physiol 36:57–64
Rodkey FL (1965a) Separation and determination of globulins of human serum. Clin Chim Acta 11:488–494
Rodkey FL (1965b) Direct spectrophotometric method for the determination of albumin in human serum. Clin Chim Acta 11:478–487
Rowan RM, Fraser C, Gray JH, McDonald GA (1979) The Coulter Counter Models S Plus — the shape of things to come. Clin Lab Haematol 1:29–40
SAS users, guide (1985) Statistics, version 5 edn. SAS Institute, Cary, N. C. p 1290
Sherwood JB (1984) The chemistry and physiology of erythropoietin. Vitam Horm 41:161–210
Teitz TW (Ed) (1976) Fundamentals of Clinical Chemistry. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 302–304
Terjung R (1979) Endocrine responses to exercise. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 7:6–11
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weight, L.M., Darge, B.L. & Jacobs, P. Athletes' pseudoanaemia. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 62, 358–362 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00634973
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00634973