Summary
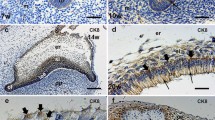
The results of an immunohistological study of the normal human nasal mucosa show that there are frequently vimentin-positive cells detectable in addition to cytokeratins in the respiratory epithelium. The vimentin cells are probably ciliated and/or goblet type in origin. Furthermore, some co-expressing cells were found in basal parts of the submucous glands.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando S, Tanabe K, Gonda Y, Sato C, Inagaki M (1989) Domain- and sequence-specific phosphorylation of vimentin induces disassembly of the filament structure. Biochemistry 28: 2974–2979
Ben-Ze'ev A (1984) Differential control of cytokeratins and vimentin synthesis by cell-cell contact and cell spreading in cultured epithelial cells. J Cell Biol 99:1424–1433
Boysen M (1985) Histopathology of the nasal mucosa in furniture workers. Rhinology 23:109–113
Coggi G, Dell'Orto P, Braidotti P, Coggi A, Viale G (1989) Coexpression of intermediate filaments in normal and neoplastic tissues: a reappraisal. Ultrastruct Pathol 13:501–514
Dabbs PJ, Geisinger KR, Norris HT (1986) Intermediate filaments in endometrial and endocervical carcinomas. Am J Surg Pathol 10:568–576
Franke WW, Jahn L, Knapp AC (1989) Cytokeratins and desmosomal proteins in certain epithelioid and nonepithelial cells. In: Osborn M, Weber K (eds) Cytoskeletal proteins in tumor diagnosis. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, pp 151–172
Gröne H-J, Weber K, Gröne E, Heimchen U, Osborn M (1987) Coexpression of keratin and vimentin in damaged and regenerating tubular epithelia of the kidney. Am J Pathol 129:1–8
Havenith MG, Cleutjens JPM, Beek C, Linden E, De Goeij AFPM, Bosman FT (1987) Human specific anti-type IV collagen monoclonal antibodies, characterization and immunohistochemical application. Histochemistry 87:123–128
Karsten U, Widmaier R, Kunde D (1983) Monoclonal antibodies against antigens of the human mammary carcinomas cell line MCF-7. Arch Geschwulstforsch 53:529–536
Kasper M, Karsten U (1988) Coexpression of cytokeratin and vimentin in Rathke's cysts of the human pituitary gland. Cell Tissue Res 253:419–424
Kasper M, Stosiek P, Varga A, Karsten U (1987) Immunohistochemical demonstration of the co-expression of vimentin and cytokeratin(s) in the guinea pig cochlea. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 244:66–68
Kasper M, Karsten U, Stosiek P, Moll R (1989) Distribution of intermediate-filament proteins in the human enamel organ: unusually complex pattern of coexpression of cytokeratin polypeptides and vimentin. Differentiation 40:207–214
Kasper M, Stosiek P, Van Muijen GNP, Moll R (1989) Cell type heterogeneity of intermediate filament expression in epithelia of the human pituitary gland. Histochemistry 93:93–103
Klein-Szanto AJP, Boysen M, Reith A (1987) Keratin and involucrin in preneoplastic and neoplastic lesions. Arch Pathol Lab Med 111:1057–1061
Moll R (1986) Epitheliale Tumormarker. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol 70:28–50
Nomori H, Kameya T, Shimosato Y, Saito H, Ebihara S, Ono J (1985) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: immunohistochemical study for keratin, secretory component and leukocyte common antigen. Jpn J Clin Oncol 15:95–105
Osborn M, Weber K (1983) Biology of disease. Tumor diagnosis by intermediate filament typing a novel tool for surgical pathology. Lab Invest 48:372–394
Page M (1989) Changing patterns of cytokeratins and vimentin in the early chick embryo. Development 105:97–107
Shi S-R, Goodman ML, Bhan AK, Pilch BZ, Chen LB, Sun TT (1984) Immunohistochemical study of nasophyngeal carcinoma using monoclonal keratin antibodies. Am J Pathol 117:53–63
Spruill WA, Zysk JR, Tres LL, Kierszenbaum AL (1983) Calcium/calmodulin-dependent phosphorylation of vimentin in rat Sertoli cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:760–764
Stosiek P, Kasper M (1988) Zytokeratin-Vimentin-Koexpression in Zystenepithelien. Pathologe 9:330–333
Ternynck T, Gregoire J, Avrameas S (1983) Enzyme/anti-enzyme monoclonal antibody soluble immune complexes (EMAC): their use in quantitative immunoenzymatic assays. J Immunol Methods 58:109–118
Traub P (1985) Intermediate filaments: a review. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Van Muijen GNP, Ruiter DJ, Warnaar SO (1987) Coexpression of intermediate filament polypeptides in human fetal and adult tissues. Lab Invest 57:359–369
Viale G (1988) Cytokeratin immunocytochemistry in the practice of diagnostic histopathology. Ultrastruct Pathol 12:3–7
Viebahn C, Lane EB, Ramaekers FCS (1988) Keratin and vimentin expression in early organogenesis of the rabbit embryo. Cell Tissue Res 253:553–562
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kasper, M., Stosiek, P. The expression of vimentin in epithelial cells from human nasal mucosa. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 248, 53–56 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00634782
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00634782