Abstract
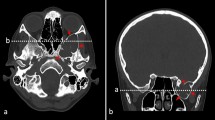
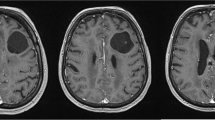
Because of the extreme rarity of intradiploic arachnoid cysts, their pathogenesis is unknown; congenital or traumatic origins are suggested. We report an intradiploic arachnoid cyst in a 57-year-old woman, without a history of trauma, in whom a forgotten injury might play a significant role.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cook PG, Norman PF (1988) Intradiploic leptomeningeal cyst of the frontal bone occurring as a complication of head injury in an adult. Clin Radiol 39: 214–215
D'Almeida ACG, King RB (1981) Intradiploic cerebrospinal fluid fistula. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg 54: 84–88
Halliday AL, Chapman PH (1990) Leptomeningeal cyst resulting from adulthood trauma: case report. Neurosurgery 26: 150–153
Hande AM, Karapurkar P (1991) Hemorrhage into an intradiploic arachnoid cyst. Case report. J Neurosurg 75: 969–971
Lunardi P, Missori P, Artico M, Fortuna A (1991) Posttraumatic intradiploic leptomeningeal cyst in an adult: case report. Surg Neur 35: 475–477
Numerow LM, Kreck JP, Wellece CJ, Tramner BI, Auer RN, Fong TC (1991) Growing skull fractures simulating a rounded lytic calvarial lesion. AJNR 12: 783–784
Rabimizadesh A, Haddiadian K (1986) Bilateral traumatic leptomeningeal cysts. Neurosurgery 18: 386–387
Sartawi M, Schwartz FT, Fox JL (1973) An unusual osteolytic lesion of the skull due to a traumatic arachnoid cyst. Neuroradiology 6: 180–181
Lende R, Erickson T (1961) Growing skull fractures of childhood. J Neurosurg 18: 479–489
Taveras J, Ransohoff J (1953) Leptomeningeal cyst of the brain following trauma with erosion of the skull. A study of seven cases treated by surgery. J Neurosurg 10: 233–241
Ito H, Miwa J, Onowa Y (1977) Growing skull fracture of childhood. Child's Brain 1: 116–126
Kingsley D, Till K, Hoare R (1978) Growing fracture of the skull. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 41: 312–318
Soule A, Whitcomb B (1946) Extensive erosion of the base of the skull from a leptomeningeal cyst. Report of a case. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 55: 382–387
Weinand ME, Rengachary SS, McGregor DH, Watanabe I (1989) Intradiploic arachnoid cysts. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg 70: 954–958
Kaufman B, Nulsen F, Weiss MH, Brodkey JS, White RJ, Sykora GF (1977) Acquired spontaneous, nontraumatic normal-pressure cerebrospinal fluid fistulas originating from the middle fossa. Radiology 122: 379–387
Kaufman B, Yonas H, White RJ, Miller CF (1979) Acquired middle cranial fossa fistulas: normal pressure and non traumatic in origin. Neurosurgery 5: 466–472
Shapiro R, Janzen AH The normal skull. A roentgenogram study. Hoeber, Philadelphia, p 130
Nugent GR, Odom GL, Woodhall B (1959) Spinal extradural cyst. Neurology 9: 379–406
Atlas SW (1991) Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and spine. Raven Press, New York, p 365
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alfieri, A., Zona, G., Cirillo, S. et al. Intradiploic arachnoid cyst: case report. Neuroradiology 38, 569–571 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00626101
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00626101