Summary
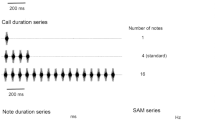
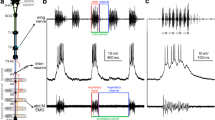
The activity of the external (motor) branch of the superior laryngeal nerve (SLN), innervating the cricothyroid muscle, was recorded in the greater horseshoe bat,Rhinolophus ferrumequinum. The bats were induced to change the frequency of the constant frequency (CF) component of their echolocation signals by presenting artificial signals for which they Doppler shift compensated. The data show that the SLN discharge rate and the frequency of the emitted CF are correlated in a linear manner.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SLN :
-
Superior laryngeal nerve
- RLN :
-
Recurrent laryngeal nerve
- DCS :
-
Doppler compensation system
- CF :
-
Constant frequency
- FM :
-
Frequency modulation
References
Griffiths TA (1978) Modification of M. cricothyroideus and the larynx in the mormoopidae, with reference to amplification of high frequency pulses. J Mammal 59:724–730
Novick A, Griffin DR (1961) Laryngeal mechanisms in bats for the production of orientation sounds. J Exp Zool 148:125–145
Roberts LH (1972) Variable resonance in constant frequency bats. J Zool 166:337–348
Roberts LH (1973) Cavity resonances in the production of orientation cries. Period Biol 75:27–32
Schnitzler H-U (1968) Die Ultraschall-Ortungslaute der Hufeisenfledermäuse (Chiroptera — Rhinolophidae) in verschiedenen Orientierungssituationen. Z Vergl Physiol 57:376–408
Schnitzler H-U (1978) Die Detektion von Bewegung durch Echoortung bei Fledermäusen. Verh Dtsch Zool Ges 1978:16–33
Schuller G, Beuter K, Schnitzler H-U (1974) Response to frequency shifted artificial echoes in the batRhinolophus ferrumequinum. J Comp Physiol 89:275–286
Schuller G, Beuter K, Rübsamen R (1975) Dynamic properties of the compensation system for Doppler shifts in the bat,Rhinolophus ferrumequinum. J Comp Physiol 97:113–125
Schuller G, Suga N (1976) Laryngeal mechanisms for the emission of CF-FM sounds in the Doppler-shift compensating bat,Rhinolophus ferrumequinum. J Comp Physiol 107:253–262
Simmons JA (1974) Response of the Doppler echolocation system in the bat,Rhinolophus ferrumequinum. J Acoust Soc Am 56:672–682
Suthers RA, Fattu JM (1973) Mechanism of sound production by echolocating bats. Am Zool 13:1215–1226
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by grants of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG), Az.: Schu 390/1, /2 and SFB 45
We are indebted to Dipl.-Ing. H. Zöller for providing the computer programs. We want to thank H. Hahn and A. Polotzek for technical help.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schuller, G., Rübsamen, R. Laryngeal nerve activity during pulse emission in the CF-FM bat,Rhinolophus ferrumequinum . J. Comp. Physiol. 143, 317–321 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00611168
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00611168