Summary
Free flying honeybees were conditioned to moving black and white stripe patterns. Bees learn rapidly to distinguish the direction of movement in the vertical and horizontal plane.
After being trained to a moving pattern bees do not discriminate the moving alternative from a stationary one. There is no significant velocity discrimination for patterns moving in the same direction.
For vertical movements there are clear asymmetries in the spontaneous choice preference and in the learning curves for patterns moving upward or downward.
After bees are trained to a stationary pattern they can discriminate it from an upward moving alternative. Learning curves involving movement are generally biphasic, suggesting different adaptive systems depending on the number of rewards.
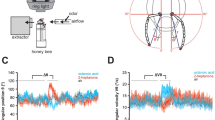
The flight pattern of bees which are trained to movement changes during the process of learning. At the beginning of the learning procedure bees reveal an optokinetic response to the moving patterns, this response is strongly reduced after a number of rewards on a moving pattern.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson AM (1977a) Parameters determining the attractiveness of stripe patterns in the honey bee. Anim Behav 25:80–87
Anderson AM (1977b) The influence of pointed regions on the shape preference of honeybees. Anim Behav 25:88–94
Erber J (1975) The dynamics of learning in the honeybee (Apis mellifica carnica). I. The time dependence of the choice reaction. J Comp Physiol 99:231–242
Erber J (1980) Neural correlates of non-associative and associative learning in the honeybee. Verh Dtsch Zool Ges 1980:250–261
Erber J (1981) Neural correlates of learning in the honeybee. Trends Neurosci 4:270–273
Erber J, Schildberger K (1980) Conditioning of an antennal reflex to visual stimuli in bees (Apismellifera L.). J Comp Physiol 135:217–225
Frisch K von (1965) Tanzsprache und Orientierung der Bienen. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Götz KG, Buchner E (1978) Evidence for one-way movement detection in the visual system ofDrosophila. Biol Cybern 31:243–248
Helversen O von (1972) Zur spektralen Unterschiedsempfindlichkeit der Honigbiene. J Comp Physiol 80:439–472
Kaiser W, Liske E (1974) Die optomotorische Reaktion von fixiert fliegenden Bienen bei Reizung mit Spektrallichtern. J Comp Physiol 89:391–408
Kunze P (1961) Untersuchung des Bewegungssehens fixiert fliegender Bienen. Z Vergl Physiol 44:656–684
Lauer J, Lindauer M (1971) Genetisch fixierte Lerndispositionen bei der Honigbiene. In: Informationsaufnahme und Informationsverarbeitung im lebenden Organismus. Akademie der Wissenschaften und der Literatur, Mainz
Menzel R (1967) Untersuchungen zum Erlernen von Spektralfarben durch die Honigbiene. Z Vergl Physiol 56:22–62
Praagh JP van, Ribi W, Wehrhahn C, Wittmann D (1980) Drone bees fixate the queen with the dorsal frontal part of their compound eyes. J Comp Physiol 136:263–266
Sachs L (1974) Angewandte Statistik. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Wehner R (1967) Zur Physiologie des Formensehens bei der Honigbiene. II. Winkelunterscheidung an Streifenmustern bei variabler Lage der Musterebene im Schwerefeld. Z Vergl Physiol 55:145–166
Wehner R (1972) Dorsoventral asymmetry in the visual field of the bee,Apis mellifca. J Comp Physiol 77:256–277
Wehner R (1975) Pattern recognition. In: Horridge (ed) The compound eye and vision of insects. Clarendon Press, Oxford, pp 77–114
Wehner R (1979) Mustererkennung bei Insekten: Lokalisation und Identifikation visueller Objekte. Verh Dtsch Zool Ges 1979:19–41
Wehner R (1981) Spatial vision in arthropods. In: Autrum (ed) Handbook of sensory physiology, vol VII/6C. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 287–616
Wehner R, Flatt I (1977) Visual fixation in freely flying bees. Z Naturforsch [C] 32:469–471
Wolf E (1933) Das Verhalten der Bienen gegenüber flimmernden Feldern und bewegten Objekten. Z Vergl Physiol 20:151–161
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erber, J. Movement learning of free flying honeybees. J. Comp. Physiol. 146, 273–282 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00610247
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00610247