Summary
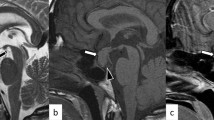
Two cases of pseudohypoparathyroidism were examined with a superconductive 1.5 T MR imaging system. High signal intensities were seen in both putamina, pulvinars and dentate nuclei on T1-weighted images.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vaughan VC III, Mckay RJ, Nelson WE (1975) Textbook of pediatrics, 10th edn. Saunders, Philadelphia
Illum F, Dupont E (1985) Prevalences of CT detected calcification in the basal ganglia in idiopathic hypoparathyroidism and pseudohypoparathyroidism. Neuroradiology 27: 32–37
Scotti G, Scialfa G, Tampieri D, Landoni L (1985) Case report: NMR imaging in Fahr's disease. J Comput Assist Tomogr 9: 790–792
Lang C, Huk W, Pichl J (1989) Comparison of extensive brain calcification in post operative hypoparathyroidism on CT and NMR scan. Neuroradiology 31: 29–32
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Araki, Y., Furukawa, T., Tsuda, K. et al. High field MR imaging of the brain in pseudohypoparathyroidism. Neuroradiology 32, 325–327 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00593055
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00593055