Summary
According to earlier studies on mammalian papillary muscles, Ni and Co ions reduce the Ca dependent mechanical response whilst the action potential persists. In order to clarify the mode of action of these cations together with those of Mn their effects on the transmembrane fast Na and of the slow Ca currents were studied in voltage clamp experiments using the double sucrose gap technique. By a conditioning clamping procedure the Ca current was separated from the Na current. The following results were obtained:
-
1.
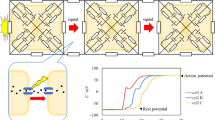
Ni ions (2 mM) and Co ions (2 mM) strongly depress the Ca conductivity of the membrane. The same blockade was observed under the influence of Mn ions (2 mM). Even in the continued presence of Ni, Co or Mn the transmembrane Ca conductivity can be restored to a varying degree by increasing the extracellular Ca concentration.
-
2.
In contrast to this strong inhibitory effect on the transmembrane Ca inward movements the fast transient Na current is only slightly affected if at all.
-
3.
Apart from their selective inhibitory action on the transmembrane Ca current, Co ions show some additional features a) enhancement of its inhibitory action by repeated membrane depolarizations. b) Co-induced replacement of the slow Ca inward current by a transitory fast inward current component, c) synergetic effects of Co with Ca in restricting the fast Na current.
-
4.
The selective inhibition of the transmembrane Ca conductivity clearly demonstrates the existence of a separate channel for Ca which is independent from the fast Na channel of the membrane.
This dual membrane transport system allows the regulation of the Ca dependent process of excitation-contraction coupling independently of a simultaneous influence on excitation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, P. F., Meves, H., Ridgway, E. B.: Phasic entry of calcium in response to depolarization of giant axons of Loligo forbesi. J. Physiol. (Lond.)215, 22 P (1971).
Carmeliet, E., Vereecke, J.: Adrenaline and the plateau phase of the cardiac action potential. Pflügers Arch.313, 300 (1969).
Fleckenstein, A., Tritthart, H., Fleckenstein, B., Herbst, A., Grün, G.: deEine neue Gruppe kompetitiver Ca++-Antagonisten (Iproveratril, D 600, Prenylamin) mit starken Hemmeffekten auf die elektro-mechanische Koppelung im Warmblütermyokard. Pflügers Arch.307, 25 (1969).
Haas, H. G., Kern, R., Einwächter, H. M.: Electrical activity and metabolism in cardiac tissue. An experimental and theoretcial study. J. Membrane Biol.3, 180 (1970).
Kaufmann, R., Fleckenstein, A.: Ca++-kompetitive elektro-mechanische Entkoppelung durch Ni++- und Co++-Ionen am Warmblüter-Myokard. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.282, 290 (1965).
Kohlhardt, M., Bauer, B., Krause, H., Fleckenstein, A.: Differentiation of the transmembrane Na and Ca channels in mammalian cardiac fibres by the use of specific inhibitors. Pflügers Arch.335, 309 (1972).
Ochi, R.: The slow inward current and the action of manganese ions in guinea-pigs myocardium. Pflügers Arch.316, 81 (1970).
Reuter, H., Beeler, G. W.: Calcium current and activation of contraction in ventricular myocardial fibres. Science163, 399 (1969).
Rougier, O., Vassort, G., Garnier, D., Gargouil, Y. M., Coraboeuf, E.: Existence and role of a slow inward current during the frog atrial action potential. Pflügers Arch.308, 91 (1969).
Rougier, O., Vassort, G., Stämpfli, R.: Voltage clamp experiments on frog atrial heart muscle fibres with the sucrose gap technique. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.301, 91 (1968).
Stämpfli, R.: A new method for measuring membrane potential with external electrodes. Experientia (Basel)10, 508 (1954).
Vassort, G., Rougier, O., Garnier, D., Sauviat, M. P., Coraboeuf, E., Gargouil, Y. M.: Effects of adrenaline on membrane inward currents during the cardiac action potential. Pflügers Arch.309, 70 (1969).
Vitek, M., Trautwein, W.: Die Wirkung von Mangan-Ionen auf Aktionpotential und Ionenströme der Purkinje-Faser. Pflügers Arch.319, 113 (1970).
Weidmann, S.: Elektrophysiologie der Herzmuskelfaser. Bern-Stuttgart: Huber 1956.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kohlhardt, M., Bauer, B., Krause, H. et al. Selective inhibition of the transmembrane Ca conductivity of mammalian myocardial fibres by Ni, Co and Mn ions. Pflugers Arch. 338, 115–123 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00592747
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00592747