Abstract
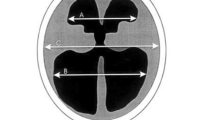
The aim of this study was to quantify the intra- and extraventricular cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) spaces in children with benign enlargement of the frontal subarachnoid space (BE). The infra-and supratentorial CSF compartments were measured in 61 CT examinations of children with BE, 3–27 months old, and compared with those of 96 CT examinations considered normal. Measurements of the ventricular system, and the pontine and chiasmatic cisterns were related to cranial size. In all children with BE the lateral and third ventricles were dilated and the chiasmatic cistern was widened. The subarachnoid space was wider than the upper limits in the control group, in the frontal region (4mm), and the anterior interhemispheric (4mm) and Sylvian (3 mm) fissures. The infratentorial CSF compartments, the occipital subarachnoid space, the posterior part of the interhemispheric fissure and, in most cases, the cortical sulci were normal in size in children with BE. The majority were macrocephalic or had rapid head growth but there were also normocephalic children with normal head growth. The size of the posterior fossa was within the normal range in all children with BE. Idiopathic BE is not uncommon in children up to about 3 years old who are healthy or have minimal neurological disturbance and is characterised by a specific pattern of widening of the supratentorial CSF compartments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maytal J, Alvarez LA, Elkin CM, Shinnar S (1987) External hydrocephalus: radiologic spectrum and differentiation from cerebral atrophy. AJR 148:1223–1230
Yamada H, Nakamura S, Tajima M, Kageyama N (1981) Neurological manifestations of pediatric achondroplasia. J Neurosurg 54:49–57
Kapila A, Trice J, Spies WG, Siegel BA, Gado MH (1982) Enlarged cerebrospinal fluid spaces in infants with subdural hematomas. Radiology 142: 669–672
Odita JC (1992) The widened frontal subarachnoid space. A CT comparative study between macrocephalic, microcephalic, and normocephalic infants and children. Childs Nerv Syst 8:36–39
Nickel RE, Gallenstein JS (1987) Developmental prognosis for infants with benign enlargement of the subarachnoid space. Dev Med Child Neurol 29:181–186
Ment LR, Duncan CC, Geeher R (1981) Benign enlargement of the subarachnoid spaces in the infant. J Neurosurg 54:504–508
De Vries LS, Smet M, Ceulemans B, Marchal G, Wilms G, Roo M de, Plets C, Casaer P (1990) The role of high resolution ultrasound and MRI in the investigation of infants with macrocephaly. Neuropediatrics 21:72–75
Carolan PL, McLaurin RL, Towbin RB, Towbin JA, Egelhaff JC (1986) Benign extra-axial collections of infancy. Pediatr Neurosci 12:140–144
Wilms G, Vanderschueren G, Demaerel PH, Smet MH, Van Calenbergh F, Plets C, Goffin J, Casaer P (1993) CT and MR in infants with pericerebral collections and macrocephaly: benign enlargement of the subarachnoid spaces versus subdural collections. AJNR 14:855–860
Prassopoulos P, Cavouras D (1994) CT evaluation of normal CSF spaces in children: relationship to age, gender and cranial size. Eur J Radiol 18:22–25
Alvarez LA, Maytal J, Shinnar S (1986) Idiopathic external hydrocephalus: natural history and relationship to benign familiar macrocephaly. Pediatrics 77: 901–907
Barkovich AJ (1990) Pediatric neuroimaging. Raven Press, New York, pp 205–226
Chapman PH (1983) External hydrocephalus. Concepts Pediatr Neurosurg 4:102–118
Briner S, Bodensteiner J (1980) Benign subdural collections of infancy. Pediatries 67:802–804
Hahn FJ, Chu WK, Cheung JV (1984) CT measurements of cranial growth: normal subjects. AJR 142:1253–1255
Mori K, Handa H, Masatoshi I, Okino Y (1981) Benign subdural effusion in infants. J Comput Assit Tomogr 4:466–471
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prassopoulos, P., Cavouras, D., Golfinopoulos, S. et al. The size of the intra- and extraventricular cerebrospinal fluid compartments in children with idiopathic benign widening of the frontal subarachnoid space. Neuroradiology 37, 418–421 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00588027
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00588027