Summary
Acetylcholine (ACh) contracture of chronically denervated rat diaphragms were studied under different conditions which affect electromechanical coupling.
-
1.
Acetylcholine induced a transient contracture while the membrane potential and the twitch amplitude remained depressed as long as the drug was present.
-
2.
In Tyrode solution with elevated K concentrations, both ACh contractures and twich contractions were diminished or abolished, whereas caffeine was still able to evoke a contracture.
-
3.
In a Ca-free solution, ACh as well as caffeine became ineffective in producing contractures.
-
4.
Manganese depressed both the ACh and caffeine induced contracture, being more effective in the former case.
-
5.
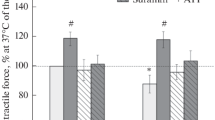
In hypertonic solution and in preparations, in which the T-tubules were disconnected from the plasma membrane by glycerol treatment, acetylcholine failed to initiate contracture, while caffeine could still produce contractures.
These results suggest that ACh induces contracture by release of Ca++ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which is caused by the depolarization of the cell membrane, and that caffein acts directly on this structure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Axelsson, J., Thesleff, S.: Activation of contractile mechanism in striated muscle. Acta physiol. scand.44, 55–66 (1958)
Axelsson, J., Thesleff, S.: A study of super-sensitivity in denervated skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.)147, 178–193 (1959)
Brody, I. A.: Relaxing factor in denervated muscle: a possible explanation for fibrillations. Amer. J. Physiol.211, 1277–1280 (1960)
Ebashi, S., Ebashi, F., Kodama, A.: Troponin as the Ca-receptive protein in the contractile system. J. Biochem.62, 137–138 (1967)
Ebashi, S., Lipmann, F.: Adenosin triphosphate linked concentration of calcium ions in a particulate fraction of rabbit muscle. J. Cell. Biol.14, 389–400 (1962)
Fatt, P., Ginsborg, B. L.: The ionic requirements for the production of action potential in crustacean muscle fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)142, 516–543 (1958)
Frank, G. B.: Effects of changes in extracellular calcium concentration in frog skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.)151, 518–538 (1960)
Frank, G. B.: Utilization of bound calcium in the action of caffeine and certain multivalent cations on skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.)163, 254–268 (1962)
Freeman, S. F., Turner, R. J.: Ionic interactions in acetylcholine contraction of the denervated rat diaphragm. Brit. J. Pharmacol.36, 510–522 (1969)
Fujino, M., Yamaguchi, T., Suzuki, K.: Glycerol effect and the mechanism linking excitation of the plasma membrane with contraction. Nature (Lond.)192, 1159–1161 (1961)
Hagiwara, S., Nakajima, S.: Differences in Na and Ca spikes as examined by application of tetrodotoxin, procaine and manganese ions. J. gen. Physiol.49, 793 to 818 (1966)
Hodgkin, A. L., Horowicz, P.: The differential action of hypertonic solutions on the twitch and action potential of muscle fibre. J. Physiol. (Lond.)136, 17P-18P (1957)
Hodgkin, A. L., Horowicz, P.: Potassium contracture in single muscle fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)153, 386–403 (1960)
Howarth, J. V.: The behaviour of frog muscle in hypertonic solutions. J. Physiol. (Lond.)144, 167–175 (1958)
Howell, J. N.: A lesion of the transvers tubules of skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.)201, 515–533 (1969)
Howell, J. N., Jenden, D. J.: T-tubules of skeletal muscles. Morphological alterations which interrupt excitation-contraction coupling. Fed. Proc.26, 533 (1967)
Jenkinson, D. H., Nicholls, J. G.: Contractures and permeability changes produced by acetylcholine in depolarized denervated muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.)159, 111–129 (1962)
Lorković, H.: Acetylcholine contractures of denervated muscle in sodium-free solutions. Amer. J. Physiol.219, 1496–1504 (1970)
Lorković, H.: Antagonism between calcium and monovalent cations in depolarized denervated muscles. Amer. J. Physiol.222, 1429–1434 (1972)
Lüllmann, H., Muscholl, E.: Über die Wirkung hypotoner Salzlösungen auf das Rattenzwerchfell. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak.,227, 209–214 (1954)
Lüllmann, H., Reis, E.: Über den Zusammenhang zwischen Membranpotential und Kalium bzw. Acetylcholikontraktur an chronisch denervierten Rattenzwerchfell. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.294, 113–118 (1967)
Miledi, R.: The acetylcholine sensitivity of frog muscle fibres after complete and partial denervation. J. Physiol. (Lond.)151, 1–23 (1960)
Nagai, T., Makinose, M., Hasselbach, W.: Der physiologische Erschlaffungsfaktor und die Muskelgrana. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.)43, 223–238 (1960)
Nonomura, Y., Hotta, Y., Ohashi, H.: Tetrodotoxin and managanese ions; effects on electrical activity and tension in taenia coli of guinea pig. Sience152, 97–99 (1966)
Oota, I., Takauji, M., Nagai, T.: Effects of manganese ions on excitation contraction coupling in frog sartorius muscle. Jap. J. Physiol.22, 379–392 (1972)
Portzehl, H. P., Caldwell, P. C., Ruegg, J. C.: The dependence of contraction and relation of muscle fibres from the crab Mia squinado on the internal concentration of free calcium ions. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.)79, 581–591 (1964)
Sakai, T., Geffner, E. S., Sandow, A.: Caffeine contracture in muscle with disrupted transverse tubules. Amer. J. Physiol.220, 712–717 (1971)
Sandow, A.: Excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Pharmacol. Rev.17, 265–320 (1965)
Shibata, S.: Effects of Mn++ on Ca45 content and potassium induced contraction of aortic strips. Canad. J. Physiol. Pharmacol.47, 827–829 (1969)
Stämpfli, R.: A new method for measuring membrane potential with external electrodes. Experientia (Basel)10, 508 (1954)
Weber, A., Herz, R.: The relationship between coffeine contracture of intact muscle and the effect of caffeine on reticulum. J. gen. Physiol.52, 750–759 (1968)
Weber, A., Herz, R., Reiss, I.: On the mechanism of the relaxing effect of fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. gen. Physiol.46, 679–702 (1963)
Weber, A., Herz, R., Reiss, J.: Role of calcium in contraction and relaxation of muscle. Fed. Proc.23, 896–900 (1964)
Yamaguchi, T., Matsushima, F., Fujino, M., Nagai, T.: The excitation-contraction coupling of skeletal muscle and the glycerol effect. Jap. J. Physiol.12, 129–141 (1962)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lüllmann, H., Sunano, S. Acetylcholine contracture and excitation-contraction coupling in denervated rat diaphragm muscle. Pflugers Arch. 342, 271–282 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00586099
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00586099