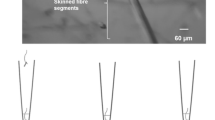
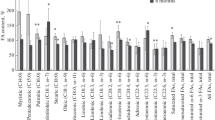
Abstract
The activities of β-glucuronidase, β-N-acetylglucosaminidase, arylsulphatase, ribonuclease,p-nitrophenylphosphatase, and malate dehydrogenase together with protein content were assayed from representative mixed (m. rectus femoris), predominantly red (proximal heads ofm. vastus lateralis, m.v. medius andm. v. intermedius), and predominantly white (distal head ofm. vastus lateralis) muscle homogenates of mice during a two-week period following one single exposure to exhausting intermittent running on a treadmill. The activities of cathepsin D and β-glycerophosphatase were assayed from mixed muscle only. In all three muscle types, particularly in red muscle, the activities of β-glucuronidase, β-N-acetylglucosaminidase, arylsulphatase, and ribonuclease progressively increased between one to five days after the exercise; thereafter the activities began to decrease, being near the control values 15 days after the exercise. In mixed muscle, cathepsin D activity increased. No corresponding changes were observed in the activities of acid phosphatases.
The time course of the activity changes closely resembled that earlier found to be caused by ischaemia in rabbit muscles. It is tentatively concluded that the two treatments, exhaustive exercise and temporary ischaemia, cause similar cell injuries, and that the lysosomal system involved seems to function similarly in the post-stress recovery of the fibres from these injuries.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arstila, A. U., Hirsimäki, P., Hirsimäki, Y.: Lysosomal reaction in chronic cell injury. In: Proceedings of the 9. Congress of the Nordic Society for Cell Biology, (F. Bierring, ed.), pp. 65–76. Odense: University Press 1976
Barrett, A. J.: Lysosomal enzymes. In: Lysosomes, a laboratory handbook, (J. T. Dingle, ed.), pp. 46–126. Amsterdam: North-Holland 1972
Bird, J. W. C.: Skeletal muscle lysosomes. Front. Biol.43, 75–109 (1975)
Canonico, P. G., Bird, J. W. C.: Lysosomes in skeletal muscle tissue. Zonal centrifugation evidence for multiple cellular sources. J. Cell Biol.45, 321–333 (1970)
Digiesi, V., Nassi, P., Cicchi, P., Castigli, E., Ramponi, G., Arcangeli, P.: Changes in enzyme levels in human skeletal muscle during obstructive arteriopathy of the lower limbs. Angiology26, 511–517 (1975)
Fidzianska, A., Strugalska, H., Badurska, B.: Histochemical and ultrastructural studies of the rat muscles after denervation. Folia Histochem. Cytochem.12, 321–328 (1974)
Gollnick, P. D., King, D. W.: Effect of exercise and training on mitochondria of rat skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol.216, 1502–1509 (1969)
Gydikov, A., Kosarov, D.: Some features of different motor units in humanbiceps brachii. Pflügers Arch.347, 75–88 (1974)
Hanzlikova, V., Schiaffino, S.: Mitochondrial changes in ischemic skeletal muscle. J. Ultrastruct. Res.60, 121–133 (1977)
Hecht, H. J., Schumann, H. J., Kunde, D.: Histologische und enzymhistochemische Befunde am Skelettmuskel der untrainierten Ratte nach intensiver physischer Belastung. Med. Sport (Berl.)15, 270–274 (1975)
Lojda, Z., Gutmann, E.: Histochemistry of some acid hydrolases in striated muscle of the rat. Histochemistry49, 337–342 (1976)
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., Randall, R. J.: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem.193, 265–275 (1951)
Maskrey, P., Pluskal, M. G., Harris, J. B., Pennington, R. J.: Studies on increased acid hydrolase activities in denervated muscle. J. Neurochem.28, 403–409 (1977)
Max, S. R., Mayer, R. F., Vogelsang, L.: Lysosomes and disuse atrophy of skeletal muscle. Arch. Biochem. Biophys.146, 227–232 (1971)
Mäkitie, J., Teräväinen, H.: Histochemical studies of striated muscle after temporary ischemia in the rat. Acta Neuropathol. (Berl.)37, 101–110 (1977)
Ochoa, S.: Malic dehydrogenase from pig heart. In: Methods of enzymology, (S. P. Colowick, N. O. Kaplan, eds.), Vol. I, pp. 737–739. New York-London: Academic Press 1955
Peter, J. B., Kar, N. C., Barnard, R. J., Pearson, C. M., Edgerton, V. R.: Distribution of acid hydrolases in guinea pig skeletal muscle. Biochem. Med.6, 257–261 (1972)
Pilström, L., Vihko, V., Åström, E., Arstila, A. U.: Activities of acid hydrolases in skeletal muscle of untrained, trained and detrained mice of different ages. Acta Physiol. Scand.104, 217–224 (1978)
Pollack, M. S., Bird, J. W. C.: Distribution and particle properties of acid hydrolase in denervated muscle. Am. J. Physiol.215, 716–722 (1968)
Reddy, M. K., Etlinger, J. D., Rabinowitz, M., Fischman, D. A., Zak, R.: Removal of Z-lines and α-actinin from isolated myofibrils by a calcium-activated neutral protease. J. Biol. Chem.250, 4278–4284 (1975)
Ruth, G. R., Van Vleet, J. F.: Experimentally induced seleniumvitamin E deficiency in growing swine: Selective destruction of type I skeletal muscle fibers. Am. J. Vet. Res.35, 237–244 (1974)
Schiaffino, S., Hanzlikova, V.: Studies on the effect of denervation in developing muscle. II. The lysosomal system. J. Ultrastruct. Res.39, 1–14 (1972)
Sembrowich, W. L., Gollnick, P. D.: Calcium uptake by heart and skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum from exercised rats. Med. Sci. Sports9, 64 (1977)
Shannon, A. D., Adams, E. P., Courtice, F. C.: The lysosomal enzymes acid phosphatase and β-glucuronidase in muscle following a period of ischaemia. Austr. J. Exp. Biol. Med. Sci.52, 157–171 (1974)
Stauber, W. T., Bird, J. W. C.: S-ϱ zonal fractionation studies of rat skeletal muscle lysosome-rich fractions. Biochem. Biophys. Acta338, 234–245 (1974)
Tate, B. F., Bonner, H. W., Leslie, S. W.: Effects of longterm chronic and acute exercise on mitochondrial calcium and magnesium of rat skeletal muscle. Med. Sci. Sports9, 66 (1977)
Trump, B. F., Berezesky, I. K., Collan, Y., Kahng, M. W., Mergner, W. J.: Recent studies on pathophysiology of ischemic cell injury. Beitr. Pathol.158, 363–388 (1976)
Vihko, V., Arstila, A. U.: Ultrastructural mitochondrial changes in mouse skeletal muscle after forced running exercise. Int. Res. Commun. Syst.2, 1144 (1974)
Vihko, V., Hirsimäki, Y., Arstila, A. U.: Effects of acute and prolonged exercise on the activities of acid hydrolases in mouse skeletal muscle. In: Physical performance and muscle metabolism. Publication no. 57, (O. Hänninen, M. Harri, eds.), pp. 112–120. Somero: The Finnish Society for Research in Sport and Physical Education 1978
Vihko, V., Rantamäki, J., Salminen, A.: Exhaustive physical exercise and acid hydrolase activity in skeletal muscle. A histochemical study. Histochemistry57, 237–249 (1978)
Warburton, M. J., Wynn, C. H.: The turnover of hamster fibroblast β-D-glucuronidase. Biochem. J.162, 201–203 (1977)
Weinstock, I. M., Iodice, A. A.: Acid hydrolase activity in muscular dystrophy and denervation atrophy. In: Lysosomes in biology and pathology. (J. T. Dingle, H. B. Fell, eds.), pp. 450–468. Amsterdam: North-Holland 1969
Wrogeman, K., Pena, S. D. J.: Mitochondrial calcium overload: A general mechanism for cell-necrosis in muscle diseases. Lancet1976, 672–674
Yarom, R.: Role of calcium in cell necrosis in muscle disease. Lancet1976, 1242–1243
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by grants from the Ministry of Education (Finland) and the Emil Aaltonen Foundation
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vihko, V., Salminen, A. & Rantamäki, J. Acid hydrolase activity in red and white skeletal muscle of mice during a two-week period following exhausting exercise. Pflugers Arch. 378, 99–106 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584441
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584441