Abstract
The knee joints of one hind limb of male Wistar rats (250–300 g) were immobilised in a plaster cast for up to 3 weeks with the limb in either the fully extended or flexed position Serial frozen sections ofvastus intermedius muscle were stained histochemically for myosin ATPase, succinic dehydrogenase, phosphorylase and capillaries. Muscle fibres were classified as either slow twitch oxidative (SO), fast twitch oxidative glycolytic (FOG) or fast twitch glycolytic (FG).
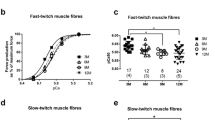
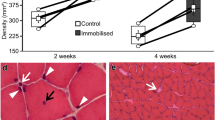
Fibre area of SO fibres (3019 μ2) decreased by 50% following 3 weeks' immobilisation in the stretched (1532 μ2) and shortened (1517 μ2) positions. Atrophy of FOG fibres (2456 μ2) was greater in muscles immobilised in the stretched (750 μ2) than shortened (1185 μ2) positions. Evidence has been obtained that muscle fibre number remained unchanged following immobilisation. Control muscles contained 70.4% SO fibres, 29.6% FOG fibres and >0.5% FG fibres. Immobilisation produced an increased proportion of high myosin ATPase staining fibres. The percentage occurrence of FOG fibres increased to 65% and 83% respectively, in muscles immobilised for 3 weeks in the stretched and shortened positions. Mechanisms for the transformation of muscle fibre types and the influence of muscle length on the properties of immobilised muscle are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen, P.: Capillary density in skeletal muscle of man. Acta Physiol. Scand.95, 203–205 (1975)
Andersen, P., Henriksson, J.: Capillary supply of the quadriceps femoris muscle of man: adaptive response to exercise. J. Physiol. (Lond.)270, 677–690 (1977)
Andersen, P., Kroese, A. J.: Capillary supply in soleus and gastrocnemius muscles of man. Pflügers Arch.375, 245–249 (1978)
Ariano, M. A., Armstrong, R. B., Edgerton, V. R.: Hindlimb muscle fibre populations of five mammals. J. Histochem. Cytochem.21, 51–55 (1973)
Booth, F. W., Kelso, J. R.: Effect of hindlimb immobilisation on contractile and histochemical properties of skeletal muscle. Pflügers Arch.342, 231–238 (1973)
Brown, M. D., Cotter, M. A., Hudlickza, O., Vrbova, G.: The effects of different patterns of muscle activity on capillary density, mechanical properties and structure of slow and fast rabbit muscle. Pflügers Arch.361, 241–250 (1976)
Buller, A. J., Eccles, J. C., Eccles, R. M.: Interaction between motorneurones and muscles in respect of the characteristic speed of their responses. J. Physiol. (Lond.)150, 417–439 (1960)
Carrow, R. E., Brown, R. E., Van Huss, W. D.: Fiber sizes and capillary to fibre ratios in skeletal muscle of exercised rats. Anat. Rec.159, 33–40 (1967)
Davies, A. S., Gunn, H. M.: Histochemical fibre types in the mammalian diaphragm. J. Anat.112, 41–60 (1972)
Edgerton, V. R., Barnard, R. J., Peter, J. B., Maier, A., Simpson, D. R.: Properties of immobilised hindlimb muscles of the Galago senegalesis. Exp. Neurol.46, 115–131 (1975)
Fischbach, G. D., Robbins, N.: Changes in contractile properties of disused soleus muscle. J. Physiol.201, 305–320 (1969)
Godlewski, H. G.: Are active and inactive phosphorylases histochemically distinguishable? J. Histochem. Cytochem.11, 108–112 (1963)
Goldspink, D. F.: The influence of immobilisation and stretch on protein turnover in rat skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.)264, 267–282 (1977)
Gutmann, E., Schiaffine, S., Hanzlikova, V.: Mechanism for compensatory hypertrophy in skeletal muscle of the rat. Exp. Neurol.31, 451–464 (1971)
Head, J. F., Weeks, R. A., Perry, S. V.: Affinity chromatographic isolation and some properties of troponin c from different muscle types. Biochem. J.161, 465–471 (1977)
Hermansen, L., Wachtlova, M.: Capillary density of skeletal muscle in well-trained and untrained men. J. Appl. Physiol.30, 860–863 (1971)
Hudlicka, D., Brown, M., Cotter, M., Smith, M., Vrbova, G.: The effect of long term stimulation of fast muscles on their blood flow, metabolism and ability to withstand fatique. Pflügers Arch.369, 141–149 (1977)
Lömo, T.: The role of activity in the control of membrane and contractile properties of skeletal muscle. In: Motorinnervation of skeletal muscle. (S. Thesleff, ed.) pp. 289–321. London: Academic Press 1976
Lömo, T., Rosenthal, J.: Control of ACh sensitivity by muscle activity in the rat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)221, 493–513 (1972)
Lömo, T., Wesgaard, R. H., Dahl, H. A.: Contractile properties of muscle: Control by pattern of muscle activity in the rat. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Biol.187, 99–103 (1974)
Luff, A. R.: Dynamic properties of fast and slow skeletal muscles in the cat and rat following cross-reinnervation. J. Physiol. (Lond.)248, 83–96 (1975)
Mai, J. V., Edgerton, V. R., Barnard, R. J.: Capillarity of red, white and intermediate muscle fibers in trained and untrained guinea-pigs. Experientia26, 1222–1223 (1970)
Melichna, J., Gutman, E.: Stimulation and immobilisation effects on contractile and histochemical properties of denervated muscle. Pflügers Arch.352, 165–178 (1974)
Nelson, P. G.: Functional consequences of tenotomy in hindlimb muscles of the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)201, 321–333 (1969)
Pearse, A. G.: Histochemistry 3rd edn. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingston (1972)
Reis, D. J., Wooten, G. F.: The relationship of blood flow in myoglobin, capillary density and twitch characteristics in red and white muscles in the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)210, 121–135 (1970)
Romanul, F. C. A.: Capillary supply and metabolism of muscle fibres. Arch. Neurol.12, 497–509 (1965)
Saltin, B., Blomqvist, B., Mitchell, J. H., Johnson, R. L., Jr., Wildenthal, K., Chapman, C. B.: Response to exercise after bed rest and training. Circulation, Suppl.7, 37–38 (1968)
Tabary, T. C., Tabary, C., Tardieu, C., Tardieu, G., Goldspink, G.: Physiological and structural changes in the cat soleus muscle due to immobilisation at different lengths by plaster casts. J. Physiol.224, 231–244 (1972)
Weeds, A. G., Trentham, D. R., Kean, C. J. C., Buller, A. J.: Myosin from cross-reinnervated cat muscles. Nature247, 135–139 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boyes, G., Johnston, I. Muscle fibre composition of ratvastus intermedius following immobilisation at different muscle lengths. Pflugers Arch. 381, 195–200 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00583249
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00583249