Abstract
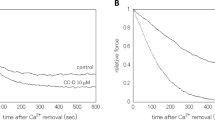
The effects of physiological concentrations of cGMP and cAMP on tension development in skinned coronary arteries (Triton X-100) were studied. cGMP inhibited tension elicited at intermediate Ca2+ concentrations at pH 7.0 but not at more acidic or alkaline pH values. cAMP, on the other hand, decreased submaximal tension development independent of pH (from pH 6.5 to pH 7.2). Neither nucleotide affected tension development at maximally activating Ca2+ concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Casteels R (1969) Calculation of the membrane potential in smooth muscle cells of the guinea pig's taenia coli by the Goldman equation. J Physiol (Lond) 205:193–208
Conti MA, Adelstein RS (1980) Phosphorylation by cyclic adenosine 3′:5′-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase regulates myosin light chain kinase. Fed Proc 39:1569–1573
Conti MA, Adelstein RS (1981) The relationship between calmodulin binding and phosphorylation of smooth muscle myosin kinase by the catalytic subunit of 3′:5′ cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem 256:3178–3181
Furchgott RF (1983) Role of endothelium in responses of vascular smooth muscle. Circ Res 53:557–573
Flockerzi V, Speichermann N, Hofmann F (1978) A guanosine 3′:5′-monophosphate dependent protein kinase from bovine heart muscle. J Biol Chem 253:3395–3399
Galvas PE, DiSalvo J (1983) Concentration and time-dependent relationship between isosorbide dinitrate-induced relaxation and formation of cyclic GMP in coronary arterial smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 224:373–378
Gerzer R, Hofmann F, Schultz G (1981) Purification of a soluble, sodium-nitroprusside stimulated guanylate cyclase from bovine lung. Eur J Biochem 116:479–486
Grütter CA, Barry BK, McNamara DB, Gruetter DY, Kadowitz PJ, Ignarro LJ (1979) Relaxation of bovine coronary artery and activation of coronary arterial guanylate cyclase by nitric oxide, nitroprusside, and a carcinogenic nitrosamine. J Cyclic Nucleot Res 5:211–224
Holzmann S (1982) Endothelium-induced relaxation by acetylcholine associated with larger rises in cyclic GMP in coronary arterial strips. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res 8:409–419
Itoh T, Kuriyama H, Ueno H (1983) Mechanisms of the nitroglycerine-induced vasodilation in vascular smooth muscles of the rabbit and pig. J Physiol 343:233–252
Ives HE, Casnellie JE, Greengard P, Jamieson JD (1980) Subcellular localization of cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase and its substrates in vascular smooth muscle. J Biol Chem 255:3777–3785
Janis RA, Diamond J (1979) Relationship between cyclic nucleotide levels and drug induced relaxation of smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 211:480–484
Jones AW, Somlyo AP, Somlyo AV (1973) Potassium accumulation in smooth muscle and associated ultrastructural changes. J Physiol (Lond) 232:247–273
Keith RA, Burkman AM, Sokoloski TD, Fertel RH (1982) Vasclar tolerance to nitroglycerin and cyclic GMP generation in rat aortic smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 221:525–531
Kukovetz WR, Holzmann A, Wurm A, Pöch G (1979) Evidence for cyclic GMP-mediated relaxant effects of nitro-compounds in coronary smooth muscle. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 310:129–138
Marston SB, Rüegg JC, Flockerzi V, Hofmann F (1982) cGMP-dependent protein kinase decreases calcium-sensitivity of skinned cardiac fibers. FEBS Lett 149:171–175
Portzehl H, Caldwell PC, Rüegg JC (1964) The dependence of contraction and relaxation of muscle fibres from the crab maia squinado on the internal concentration of free calcium ions. Biochem Biophys Acta 79:581–591
Rapoport RM, Draznin MB, Murad F (1983) Endothelium-dependent relaxation in rat aorta may be mediated through cyclic GMP-dependent protein phosphorylation. Nature 306:174–176
Rüegg JC, Meisheri K, Pfitzer G, Zeugner C (1983) Skinned coronary smooth muscle: calmodulin, calcium antagonists, and cAMP influence contractility. Basic Res Cardiol 78:462–471
Rüegg JC, Paul RJ (1982) Vascular smooth muscle, calmodulin and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase alter calcium sensitivity in porcine carotid skinned fibers. Circ Res 50:394–399
Saida K (1982) Intracellular Ca release in skinned smooth muscle. J Gen Physiol 80:191–202
Scharma RK, Wang JH (1979) Preparation and assay of the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein. Adv Cyclic Nucl Res 10:187–198
Scheid CR, Honeyman TW, Fay FS (1978) Mechanism of β-adrenergic relaxation of smooth muscle. Nature (Lond) 277:32–36
Schneider M, Sparrow M, Rüegg JC (1981) Inorganic phosphate promotes relaxation of chemically skinned smooth muscle of guinea-pig taenia coli. Experientia 37:980–982
Schultz KD, Schultz K, Schultz G (1977) Sodium nitroprusside and other smooth-muscle-relaxants increase cyclic GMP levels in rat ductus deferens. Nature (Lond) 265:750–751
Schultz KD, Boehme E, Kreye VA, Schultz G (1979) Relaxation of hormonally stimulated smooth muscular tissues by the 8-bromo derivate of cyclic GMP. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 306:1–9
Silver PJ, DiSalvo J (1979) Adenosine 3′:5′-monophosphate mediated inhibition of myosin light chain phosphorylation in bovine aortic actomyosin. J Biol Chem 254:9951–9954
Silver PJ, Schmidt-Silver C, DiSalvo J (1982) β-adrenergic relaxation and cAMP-kinase activation in coronary arterial smooth muscle. Am J Physiol 242:H177-H184
Thomas MV (1982) Techniques in calcium research. Academic Press, London New York, pp 40–45
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pfitzer, G., Hofmann, F., DiSalvo, J. et al. cGMP and cAMP inhibit tension development in skinned coronary arteries. Pflugers Arch. 401, 277–280 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00582596
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00582596