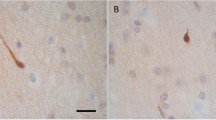
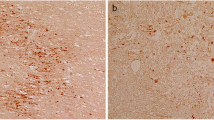
Abstract
β-Amyloid precursor protein immunostaining has recently been shown to be a reliable method for detecting the damage to axons associated with fatal head injury. In an attempt to compare the efficacy of this technique with conventional histological detection of axonal damage, we have reanalysed sections from a large well-characterised series of head-injured and control patients. The results indicate that the frequency of axonal injury has been vastly underestimated using conventional silver techniques, and that axonal injury may in fact be an almost universal consequence of fatal head injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe K, Tanzi RE, Kogure K (1991) Selective induction of kunitz type protease inhibitor domain containing mRNA after persistent focal ischaemia in rat cerebral cortex. Neurosci Lett 125: 172–174
Adams JH (1992) Head injury. In: Adams JH, Duchen LW (eds) Greenfield's neuropathology. Arnold, London, pp 106–152
Adams JH, Mitchell DE, Graham DI, Doyle D (1977) Diffuse brain damage of immediate impact type. Brain 100: 489–502
Adams JH, Doyle D, Ford I, Gennarelli TA, Graham DI, McLellan DR (1989) Diffuse axonal injury and head injury: definition, diagnosis and grading. Histopathology 15: 49–59
Blumbergs PC, Jones NR, North JB (1989) Diffuse axonal injury and head trauma. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 52: 838–841
Blumbergs PC, Scott G, Manavis J, Wainwright H, Simpson DA, McLean AJ (1994) Staining of amyloid precursor protein to study axonal darnage in mild head injury. Lancet 344: 1055–1056
Crooks DA (1991) A method to quantitate axonal injury. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 17: 421–424
Erb DE, Povlishock JT (1988) Axonal damage in severe traumatic brain injury: an experimental study in the cat. Acta Neuropathol 76: 347–358
Gennarelli TA (1983) Head injury in man and experimental animals: clinical aspects. Acta Neurochir [Suppl] (Wien), pp 1–13
Gennarelli TA (1993) Cerebral concussion and diffuse brain injuries. In: Cooper PR (ed) Head injury, 3rd edn. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 137–158
Gennarelli TA, Spielman GM, Langfitt TW, Gildenberg PL, Harrington T, Jane JA, Marshall LF, Miller JD, Pitts LH (1982) Influence of the type of intracranial lesion on outcome from severe head injury. J. Neurosurg 56: 26–36
Gennarelli TA, Adams JH, Graham DI (1986) Diffuse axonal injury: a new conceptual approach to an old problem. In: Baethmans A, Go KG, Unterberg A (eds) Mechanisms of secondary brain damage. Plenum, New York, pp 15–28
Gennarelli TA, Thibault LE, Tipperman R, Tomel G, Sergot R, Brown MD, Maxwell WL, Graham DI, Adams JH, Irvine A, Gennarelli LM, Duhaime AC, Broock R, Greenberg J (1989) Axonal injury in the optic nerve: a model simulating diffuse axonal injury in the brain. J Neurosurg 71: 244–253
Gentleman SM, Nash MJ, Sweeting CJ, Graham DI, Roberts GW (1993) β-Amyloid precursor protein (β-APP) as a marker of axonal injury after head injury. Neurosci Lett 160: 139–144
Grady MS, McLaughlin MR, Christman CW, Valadka AB, Fligner CL, Povlishock JT (1993) The use of antibodies targeted against the neurofilament subunits for the detection of diffuse axonal injury in humans. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 52: 143–152
Grcevic N (1982) Topography and pathogenic mechanisms of lesions in “inner cerebral trauma”. Rad Jugosl Akad Znan Umjet 402: 265–331
Gultekin SH, Smith TW (1994) Diffuse axonal injury in craniocerebral trauma. A comparative histologic and immunohistochemical study. Arch Pathol Lab Med 118: 168–171
Jellinger K (1973) Neuroaxonal dystrophy: its natural history and related disorders. Prog Neuropathol 2: 129–180
Kawarabayashi T, Shoji M, Harigaya Y, Yamaguchi H, Hirai S (1991) Expression of APP in the early stages of brain damage. Brain Res 563: 334–338
Maxwell WL, Irvine A, Graham DI, Adams JH, Gennarelli TA, Tipperman R, Sturatis M (1991) Focal axonal injury: the early axonal response to stretch. J Neurocytol 20: 157–164
McLellan DR, Adams JH, Graham DI, Kerr AE, Teasdale GM (1986) The structural basis of the vegetative state and prolonged coma after non-missile head injury. In: Papo I, Cohadon F, Massarotti M (eds) Le coma traumatique. Liviana, Padova, pp 165–185
Ng HK, Mahaliyana RD, Poon WS (1994) The pathological spectrum of diffuse axonal injury in blunt head trauma: assessment with axon and myelin stains. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 96: 24–31
Ohgami T, Kitamoto T, Tateishi J (1992) Alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein accumulates within axonal swellings in human brain lesions. Neurosci Lett 136: 75–78
Peerless SJ, Rewcastle NB (1967) Shear injuries of the brain. Can Med Assoc J 96: 577–582
Pilz P (1983) Axonal injury in head injury. Acta Neurochir [Suppl] (Wien) 32: 119–123
Povlishock JT (1986) Traumatically induced axonal change without concomitant change in focally related neuronal somata and dendrites. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 70: 53–79
Povlishock JT (1992) Traumatically induced axonal injury: pathogenesis and pathobiological implications. Brain Pathol 2: 1–12
Povlishock JT, Becker DP, Cheng CLY, Vaughan CW (1983) Axonal change in minor head injuries. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 42: 225–242
Roberts GW, Gentleman SM, Lynch A, Murray L, Landon M, Graham DI (1994) β-Amyloid protein deposition in the brain after severe head injury: implication for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 57: 419–425
Sherriff FB, Bridges LR, Sivaloganathan S (1994) Early detection of axonal injury after human head trauma using immunocytochemistry for β-amyloid precursor protein. Acta Neuropathol 87: 55–62
sherriff FE, Bridges LR, Gentleman SM, Sivaloganathan S, Wilson S (1994) Markers of axonal injury in post mortem human brain. Acta Neuropathol 88: 433–439
Strich SJ (1956) Diffuse degeneration of the cerebral white matter in severe dementia following head injury. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 19: 163–185
Strich SJ (1961) Shearing of nerve fibres as a cause of brain damage due to head injury. Lancet II: 443–448
Yaghmai A, Povlishock J (1992) Traumatically induced reactive changes as visualised through the use of monolonal antibodies targeted to neurofilament subunits. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 51: 158–176
Zimmerman RA, Larissa T, Bilaniuk LT, Gennarelli TA (1978) Corputerised tomography of shearing injuries of the cerebral white matter. Radiology 127: 393–396
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gentleman, S.M., Roberts, G.W., Gennarelli, T.A. et al. Axonal injury: a universal consequence of fatal closed head injury?. Acta Neuropathol 89, 537–543 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00571509
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00571509