Abstract
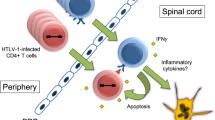
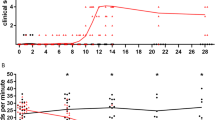
In seropositive HTLV-I carrier rats of the WKAH strain inoculated with 2×107 MT-2 cells at 3–6 months of age, chronic progressive myeloneuropathy, tentatively designated as HTLV-I-associated myelopathy (HAM) rat disease, occurred when the rats were 19–23 months old. Clinical and pathological findings were basically identical to those of seronegative HAM rats of the same strain neonatally inoculated with MT-2 cells. It appears that a high dose of MT-2 cells (108 cells) is more effective for the induction and acceleration of HAM rat disease. Seronegative and seropositive carriers of other strains (F344, ACI, and LEW), WKAH rats inoculated with HUT-78 (a human T cell line without HTLV-I infection), and untreated WKAH rats at comparable ages did not develop HAM rat disease, thereby indicating that development of this disease is caused by HTLV-I infection and is under strict genetic restriction of the host strain. Chronological examination of HAM rat disease induced by 107 MT-2 inoculation into newborn rats showed that the spinal cord lesion began to develop by 12 months of age. T cells were absent in the affected spinal cord throughout the disease process. There was morphological evidence of apoptotic death of oligodendrocytes in the affected spinal cord. Apoptosis was also confirmed by the specific nick end labeling of the nuclear fragmentation in situ, and the apoptotic oligodendrocytes confined to the demyelinating foci, and the number of apoptotic cells positively correlated with severity of the spinal cord lesion. The collective evidence suggests that the major pathogenetic pathway of HAM rat disease appears to be closely related to apoptotic death of the oligodendrocytes, directly or indirectly associated with HTLV-I infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi T, Hoshida Y, Yoshino T, Teramoto N, Kondo E, Hayashi K, Takahashi K (1992) Infectivity of human T lymphotropic virus type I to human nervous tissue cells in vitro. Acta Neuropathol 84:147–152
Claphan P, Nagy K, Cheingsong-Popov R, Exley M, Weiss RA (1983) Productive infection and cell-free transmission of human T-cell leukemia virus in a nonlymphoid cell line. Science 222:1125–1127
Fan N, Gavalchin J, Paul B, Wells KH, Lane MJ, Poiesz BJ (1992) Infection of peripheral blood mononuclear cells and cell lines by cell-free human T-cell lymphoma/leukemia virus type I. J Clin Microbiol 30:905–910
Gavrieli Y, Sherman Y, Ben-Sasson SA (1992) Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol 119:493–501
Gessain A, Barin F, Vernant JC, Gout O, Maurs L, Calender A, De Thé G (1985) Antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type-I in patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Lancet II: 407–409
Gessain A, Saal F, Gout O, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, De Thé G, Peries J, Sigaux F (1990) High human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I proviral DNA load with polyclonal integration in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of French West Indian, Guianese, and African patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Blood 75:428–433
Gessain A, Louie A, Gout O, Gallo RC, Franchini G (1991) Human T-cell leukemia-lymphoma virus type I (HTLV-I) expression in fresh peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with tropical spastic paraparesis/HTLV-I-associated myelopathy. J Virol 65:1628–1633
Hoffman PM, Dhib-Jalbut S, Mikorits JA, Robbins DS, Wolf AL, Bergey GK, Lohrey NC, Weislow OS, Ruscetti FW (1992) Human T-cell leukemia virus type I infection of monocytes and microglial cells in primary human cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:11 784–11 788
Hoshino H, Tanaka H, Shimotohno K, Miwa M, Nagai M, Shimoyama M, Sugimura T (1984) Immortalization of peripheral blood lymphocytes of cats by human T-cell leukemia virus. Int J Cancer 34:513–517
Hoxie JA, Matthews DM, Cines DB (1984) Infection of human endothelial cells by human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:7591–7595
Ishiguro N, Abe M, Seto K, Sakurai H, Ikeda H, Wakisaka A, Togashi T, Tateno M, Yoshiki T (1992) A rat model of human T lymphocyte virus type I (HTLV-I) infection. 1. Humoral antibody response, provirus integration, and HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis-like myelopathy in seronegative HTLV-I carrier rats. J Exp Med 176:981–989
Itoyama Y, Minato S, Kira J, Goto I, Sato H, Okochi K, Yamamoto N (1988) Spontaneous proliferation of peripheral blood lymphocytes increased inpatients with HTLV-I associated myelopathy. Neurology 38:1302–1307
Jacobson S, Shida H, McFarlin DE, Fauci AS, Koenig S (1990) Circulating CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for HTLV-I pX in patients with HTLV-I associated neurolgical disease. Nature 348:245–248
Kannagi M, Harada S, Maruyama I, Inoko H, Igarashi H, Kuwashima G, Sato S, Morita M, Kidokoro M, Sugimoto M, Funahashi S, Osame M, Shida H (1991) Predominant recognition of human T cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-I) pX gene product by human CD8+ cytotoxic T cells directed against HTLV-I-infected cells. Int Immunol 3:761–767
Kitajima I, Yamamoto K, Sato K, Nakajima Y, Nakajima T, Maruyama I, Osame M, Nishioka K (1991) Detection of human T cell lymphotropic virus type I proviral DNA and its gene expression in synovial cells in chronic inflammatory arthropathy. J Clin Invest 88:1315–1322
Koenig S, Woods RM, Brewah YA, Newell AJ, Jones GM, Boone E, Adelsberger JW, Baseler MW, Robinson SM, Jacobson S (1993) Characterization of MHC class I restricted cytotoxic T cell responses to Tax in HTLV-I infected patients with neurologic disease. J Immunol 151:3874–3883
Kushida S, Matsumura M, Tanaka H, Ami Y, Hori M, Kobayashi M, Uchida K, Yagami K, Kameyama T, Yoshizawa T, Mizusawa H, Iwasaki Y, Miwa M (1993) HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis-like rats by intravenous injection of HTLV-I-producing rabbit or human T-cell line into adult WKA rats. Jpn J Cancer Res 84:831–833
Louis J-C, Magal E, Takayama S, Varon S (1993) CNTF protection of oligodendrocytes against natural and tumor necrosis factor-induced death. Science 259:689–692
Markham PD, Salahuddin SZ, Macchi B, Robert-Guroff M, Gallo RC (1984) Transformation of differnt phenotypic types of human bone marrow T-lymphocytes by HTLV-I. Int J Cancer 33:13–17
Maruyama I, Tihara J, Sakashita I, Mizoguti R, Mori S, Usuku K, Jonosono M, Tara M, Matsumoto M, Niina S, Sonoda S, Yasaki S, Osame M (1988) HTLV-I associated bronchopneumonopathy — A new clinical entity? Am Rev Res Dis 137:46
Matsuura A, Ishii Y, Yuasa H, Narita H, Kon S, Takami T, Kikuchi K (1984) Rat T lymphocyte antigens comparable with mouse Lyt-1 and Lyt-2, 3 antigenic systems: characterization by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol 132:316–322
Miyoshi I, Kubonishi I, Yoshimoto S, Akagi T, Ohtsuki Y, Shiraishi Y, Nagata K, Hinuma Y (1981) Type C virus particles in a cord T-cell line derived by co-cultivating normal human cord leukocytes and human leukemic T-cells. Nature 294:770–771
Miyoshi I, Taguchi H, Fujishita M, Yoshimoto S, Kubonishi I, Ohtsuki Y, Shiraishi Y, Akagi T (1983) Transformation of monkey lymphocytes with adult T-cell leukaemia virus. Lancet I:1016
Miyoshi I, Yoshimoto S, Taguchi H, Kubonishi I, Fujishita M, Ohtsuki Y, Shiraishi Y, Akagi T (1983) Transformation of rabbit lymphocytes with adult T-cell leukemia virus. Jpn J Cancer Res 74:1–4
Mochizuki M, Watanabe T, Yamaguchi K, Takatsuki K, Yoshimura K, Shirao M, Nakashima S, Mori S, Araki S, Miyata N (1992) HTLV-I uveitis: a distinct clinical entity caused by HTLV-I. Jpn J Cancer Res 83:236–239
Nishioka K, Maruyama J, Sato K, Kitajima I, Nakajima Y, Osame M (1989) Chronic inflammatory arthropathy associated with HTLV-I. Lancet I:441
Osame M, Usuku K, Izumo S, Ijichi N, Amitani H, Igata A, Matsumoto M, Tara M (1986) HTLV-I associated myelopathy, a new clinical entity. Lancet I:1031–1032
Osame M, Matsumoto M, Usuku K, Izumo S, Ijichi N, Amitani H, Tara M, Igata A (1987) Chronic progressive myelopathy associated with elevated antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type I and adult T-cell leukemia like cells. Ann Neurol 21:117–122
Poiesz BJ, Ruscetti FW, Gazdar AF, Bunn PA, Minna JD, Gallo RC (1980) Detection and isolation of type-C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:7415–7419
Selmaj KW, Raine CS (1988) Tumor necrosis factor mediates myelin and oligodendrocyte damage in vitro. Ann Neurol 23:339–346
Selmaj KW, Raine CS, Farooq M, Norton WT, Brosman CF (1991) Cytokine cytotoxicity against oligodendrocytes. Apoptosis induced by lymphotoxin. J Immunol 147:1522–1529
Tateno M, Kondo N, Itoh T, Chubachi T, Togashi T, Yoshiki T (1984) Rat lymphoid cell lines with human T cell leukemia virus production. I. Biological and serological characterization. J Exp Med 159:1105–1116
Tendler CL, Greenberg SJ, Burton JD, Danielpour D, Kim S-J, Blattner WA, Manns A, Waldmann TA (1991) Cytokine induction in HTLV-I associated myelopathy and adult T-cell leukemia: alternate molecular mechanisms underlying retroviral pathogenesis. J Cell Biochem 46:302–311
Vernant JC, Maurs L, Gessain A, Barin F, Gout O, Delaporte JM, Sanhadji K, Buisson G, De Thé G (1987) Endemic tropical spastic paraparesis associated with human T-lymphotropic virus type I: a clinical and seroepidemiological study of 25 cases. Ann Neurol 21:123–130
Vernant JC, Buisson G, Magdelaine J, DeThore J, Jouannelle A, Neisson-Vernant C, Monplaisir N (1988) T-lymphocyte alveolitis, tropical spastic paresis, and Sjögren syndrome. Lancet I:177
Watabe K, Saida T, Kim SU (1989) Human and simian glial cells infected by human T-lymphotropic virus type I in culture. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 48:610–619
Williams GT, Smith CA (1993) Molecular regulation of apoptosis: genetic controls on cell death. Cell 74:777–779
Yamaki T, Uede T, Sugawara Y, Wada T, Yamaguchi A, Kokai Y, Kikuchi K (1987) Characterization of rat T cell subset antigen by monoclonal antibody. Microbiol Immunol 31: 793–807
Yoshida M, Miyoshi I, Hinuma Y (1982) Isolation and characterization of retrovirus from cell lines of human adult T-cell leukemia and its implication in the disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:2031–2035
Yoshida M, Osame M, Kawai H, Toita M, Kuwasaki N, Nishida Y, Hiraki Y, Takahashi K, Nomura K, Sonoda S, Eiraku N, Ijichi S, Usuku K (1989) Increased replication of HTLV-I in HTLV-I-associated myelopathy. Ann Neurol 26:331–335
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seto, K., Abe, M., Ohya, O. et al. A rat model of HTLV-I infection: development of chronic progressive myeloneuropathy in seropositive WKAH rats and related apoptosis. Acta Neuropathol 89, 483–490 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00571502
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00571502