Summary
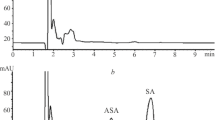
The activity of acetylsalicylic acid-esterase (ASA-esterase) in blood and the degree of protein-salicylate binding were estimated in different age groups. The activity of ASA-esterase was assayed by the amount of salicylate released after incubation with ASA under standard conditions. Lower activity of the enzyme was found in neonates (48–49% of ASA hydrolysed after 60 min) than in older children (60–64% hydrolysed) and male adults (78–83% hydrolysed). The erythrocytes of adult females were less active than those from males. Protein-binding of salicylic acid (SA) was also lower in neonates than in adults (30.7% at SA 68.4 µg/ml, and 52% at 10.28 µg/ml SA, respectively). Even if the protein concentration in adult plasma were reduced to the level of the neonates by dilution, and if bilirubin were added to the mixture, the protein-binding was still greater in plasma from adults than neonates. These observations suggest that in the neonatal period the protein-affinity of certain substances may differ from that in adults.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breddin, K., Scharrer, I., Schepping, M.: Die Hemmung der Plättchenaggregation mit Acetylsalicylsäure. Münch. med. Wschr.113, 1284–1292 (1971)
Chignell, C.F., Vesell, E.S., Berlin, C.M.: The binding of sulphaphenazole to fetal, neonatal and adult plasma albumin. J. clin. Pharmacol. Therap.12, 897–901 (1971)
De Weck, A.L.: Acetylsalicylsäure, ein altes Arzneimittel in neuem Blickwinkel. Dtsch. med. Wschr.96, 1109–1115 (1971)
Ehrnebo, M., Agurell, S., Jalling, B., Boreus, L.O.: Age differences in drug binding by plasma proteins: studies on human fetuses, neonates and adults. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol.3, 189–193 (1971)
Evans, G., Nishizawa, E.E., Packman, M.A.: The effect of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) on platelet function. Blood30, 550–556 (1967)
Ganshorn, A., Kurz, H.: Unterschiede zwischen der Proteinbindung Neugeborener und Erwachsener und ihre Bedeutung für die pharmakologische Wirkung. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmak.260, 117–118 (1968)
Jacobsen, J., Thiessen, H., Brodersen, R.: Effect of fatty acids on the binding of bilirubin to albumin. Biochem. J.126, 7P (1972)
Jobin, F., Delange, J.M.: Aspirin and prednisone in microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia. Lancet1970 II, 208–210
Kucera, J.L., Bullock, F.J.: The binding of salicylates to plasma proteins from several animal species. J. Pharm. Pharmacol.21, 293–296 (1969)
Mac Millan, D.C.: Effect of salicylates on human platelets. Lancet1968 II, 1151–1152
Menguy, R., Desbaillets, L., Masters, Y.F., Okabe, S.: Evidence for sex-linked differences in aspirin metabolism. Nature239, 201–204 (1972)
Menon, J.S.: Aspirin and blood fibrinolysis. Lancet1970 II, 364
O'Brien, J.R.: Salicylates and platelet aggregation. Lancet1968 I, 779
Potter, G.D., Guy, J.L.: A micro method for analysis of plasma salicylates. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.)116, 658–660 (1964)
Quick, A.J.: Bleeding time after aspirin ingestion. Lancet1968 I, 50
Sutor, A.H., Schindera, F., Jacobi, H., Künzer, W.: Haemolytic uremic syndrome: thrombocyturia after treatment with streptokinase and aspirin. Lancet1972 II, 762
Weiss, H.J., Aledort, L.M.: Impaired platelet connective-tissue reaction in man after aspirin ingestion. Lancet1967 I, 495–497
Windorfer, jun., A., Mihailova, K., Pringsheim, W.: Besteht erhöhte Gefahr einer Bilirubinencephalopathie im Neugeborenenalter durch eine medikamentöse Therapie? Dtsch. med. Wschr.98, 1260–1267 (1973)
Zucker, M.B., Peterson: Inhibition of adenosin-diphosphate induced secondary aggregation and other platelet functions by acetylsalicylic acid ingestion. Proc. Sec. exp. Biol. (N.Y.)127, 547–551 (1968)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Windorfer, A., Kuenzer, W. & Urbanek, R. The influence of age on the activity of acetylsalicylic acid-esterase and protein-salicylate binding. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 7, 227–231 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00560385
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00560385