Summary
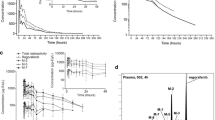
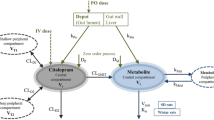
Plasma and urinary levels of chlorpheniramine (CPM) and its 2 demethylated metabolites were measured by HPLC after i.v. and oral dosing. In 5 mg (maleate) i.v. bolus studies in 2 subjects, plasma CPM levels were fitted to triexponential equations with terminal half-lives (t 1/2) of 23 and 22 h and area of 3.6 and 3.21/kg, respectively. Intravenous data predicted hepatic blood extraction ratios for the 2 subjects to be 0.06 and 0.07, respectively. Absolute bioavailability from oral solution (10 mg) was 59 and 34%, and from tablets (8 mg) 44 and 25%, respectively, indicating extensive gut first-pass metabolism. Mean t 1/2 from 7 oral fasting studies in 5 subjects was 28 h (19–43 h). Mean absorption lag time was 0.7 h (0.4–1.3 h), and mean peak time was 2.8 h (2–4 h). In 2 subjects, 6 mg solutions were given every 12 h for 9 doses; good correlation between single and multiple dose kinetics was found. Significant accumulation was demonstrated in simulation studies with frequent daily dosing. Estimated accumulation ratios vary from 4.1 to 9.4 (mean 6.5). The t 1/2 from urinary data (collected for 12 days) was consistent with plasma data. The above results suggest the need to reexamine the current practice of frequent daily dosing and the use of sustained or controlled release dosage forms of this drug. The possible cause of reduced plasma clearance of CPM in renal patients is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Athanikar NK, Peng GW, Nation RL, Huang SM, Chiou WL (1979) Chlorpheniramine I. Rapid quantitative analysis of chlorpheniramine in plasma, saliva and urine by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr 162: 367–376
Athanikar NK, Chiou WL (1979) Chlorpheniramine II. Effect of the first-pass metabolism on the oral bioavailability in dogs. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 7: 383–396
Barhart W, Johnson JD (1977) Simplified gas chromatographic method for the determination of chlorpheniramine in serum. Anal Chem 49: 1085–1086
Beckett AH, Wilkinson GR (1965) Influence of urine pH and flow rate on the renal excretion of chlorpheniramine in man. J Pharm Pharmacol 17: 256–257
Breimer DD, Honhoff C, Zilly W, Richter E, von Rossum JM (1975) Pharmacokinetics of hexobarbital in man after intravenous infusion. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 3: 1–11
Chiou WL (1978) Critical evaluation of the potential error in pharmacokinetic studies of using the linear trapezoidal rule method for the calculation of the area under the plasma leve-time curve. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 6: 539–546
Chiou WL (1979) Rapid compartment- and model- independent estimation of times required to attain various fractions of steadystate plasma level during multiple dosing of drugs obeying superposition principle and having various absorption or infusion kinetics. J Pharm Sci 68: 1546–1547
Chiou WL, Athanikar NK, Huang SM (1979) Long half-life of chlorpheniramine. N Engl J Med 300: 501
Cook TJ, MacQueen DM, Witting HJ, Thornby JI, Lantos RL, Virtue CM (1973) Degree and duration of skin test suppression and side effects with antihistamines. J Allergy Clin Immunol 51: 71–77
Dube LM, Block R, Warner RN, Hyslop, RM, Popvich NG, Gonzalez MA (1980) Pharmacokinetics of chlorpheniramine maleate in chronic renal failure: Effect of hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Abstract No. 46 American Pharmaceutical Association 127th Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, p 84
Eckart CG, McCorkle T (1978) Analytical profiles of drug substances, Vol 7. Academic Press, New York, p 63
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1975) Pharmacokinetics. Marcel Dekker, New York
Grollman (1962) Pharmacology and therapeutics, 5th ed. Lea & Fiebiger, Philadelphia, p 420–427
Haefelfinger P (1976) Determination of nanogram amounts of aromatic compounds by spectrophotometry on thin-layer chromatograms. J Chromatogr 124: 351–358
Hanna S, Tang A (1974) GLC determination of chlorpheniramine in human plasma. J Pharm Sci 63: 1954–1957
Huang SM, Chiou WL (1981) Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of chlorpheniramine in rabbits after intravenous administration. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 9: 711–723
Huang SM, Huang YC, Chiou WL (1981) Oral absorption and presystemic first-pass effect of chlorpheniramine in rabbits. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 9: 725–738
Lai CM, Stoll RG, Look ZM, Yacobi A (1979) Urinary excretion of chlorpheniramine and pseudoephedrine in humans. J Pharm Sci 68: 1243–1246
Lange WE, Theodore JM, Pruyn FJ (1968) In vivo determination of certain aralkylamines. J Pharm Sci 57: 124–127
Metzler CM, Elfring GL, McEwan AJ (1974) A package of computer programs for pharmacokinetic modeling. Biometrics 30: 562
Peets EA, Weinstein R, Billard W, Symchowicz L (1972) Metabolism of chlorpheniramine maleate in man. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 180: 304–374
Sanders SW, Warner RN, Georgitis JW, Eigen H, Gonzalez MA (1980) Dexchlorpheniramine disposition in man. Abstract No.45 American Pharmaceutical Association 127th Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, p 84
Thompson JA, Leffert FH (1980) Sensitive GLC-Mass spectrometric determination of chlorpheniramine in serum. J Pharm Sci 60: 707–710
The United States Pharmacopeia (1975) nineteenth revision, US Pharmacopeia, Rockville, MD, pp 85–86
Wagner JG (1976) Fundamentals of clinical pharmacokinetics. Drug Intelligence Publications, Hamilton, IL
Wagner JG (1967) Drug accumulation. J Clin Pharmacol 84–88
Yacobi A, Stoll RG, Chao GC, Cater JE, Baaske DM, Kamath BL, Amann AH, Lai CM (1980) Evaluation of sustained-action chlorpheniramine-pseudoephedrine dosage form in humans. J Pharm Sci 69: 1077–1081
Yamaoka K, Nakagawa T, Uno T (1978) Application of Akaike's Information Criterion (AIC) in the evaluation of linear pharmacokinetic equations. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 6: 165–175
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, S.M., Athanikar, N.K., Sridhar, K. et al. Pharmacokinetics of chlorpheniramine after intravenous and oral administration in normal adults. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 22, 359–365 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00548406
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00548406