Summary
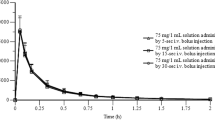
The bioavailabilities of a conventional and two slow release 20 mg isosorbide dinitrate (ISDN) formulations were compared after oral administration in a three way cross-over study in 8 male volunteers. In a further group of 6 male volunteers the pharmacokinetics and metabolism of ISDN were investigated after intravenous infusion of a median dose of 14.1 mg for 2.5 h. A new analytical procedure was developed for the determination of isosorbide-5-mononitrate-2-glucuronide (IS-5-MN-2-Glu) and of isosorbide (IS). Kinetic data analysis on a molar basis was performed by the program package KINPAK providing model independent parameters. The median elimination half-lives of ISDN, IS-5-MN, IS-2-MN and IS-5-MN-2-Glu were 0.7, 5.1, 3.2 and 2.5 h, respectively. The systemic clearance of ISDN was 3.7 l/min and the distribution volume 2521 (3.1 l/kg). Apart from IS-5-MN-2-Glu, with a renal clearance of 5.9 l/min which suggested substantial glucuronidation in the kidney, the renal clearances of ISDN, IS-5-MN, IS-2-MN and the corresponding amounts excreted were negligible. 27.8% of the administered ISDN was excreted as IS-5-MN-2-Glu (8.7%) and IS (19.1%). Calculations based on the two mononitrate metabolites formed from ISDN showed an incomplete recovery of 84.1%, leading to the assumption that a simultaneous denitration to IS must have occurred. The rate of denitration at each nitro group in ISDN was almost twice as high as for the same position in the corresponding mononitrate. The bioavailability of the conventional ISDN formulation was 19%, although complete absorption was indicated by comparison of the percentages of mononitrate metabolites formed after the different routes of administration. On the same basis the absorption of the two sustained release formulations was found to be poor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abshagen U, Betzien G, Endele R, Kaufmann B (1981) Pharmacokinetics of intravenous and oral isosorbide-5-mononitrate. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 20: 269–275
Assinder DF, Chasseaud LF, Taylor T (1977) Plasma isosorbide dinitrate concentrations in human subjects after administration of standard and sustained-release formulations. J Pharm Sci 66: 775–778
Betzien G, Kaufmann B, Schneider B, Ritschel WA (1985a) Evaluating blood level curves: a comprehensive approach with KINPAK. Harvey Whitney Books, Cincinnati, OH, USA (in press)
Betzien G, Kaufmann B, Schneider B (1985b) KINPAK: a new program for standardized evaluation of kinetic parameters. Arzneimittelforsch/Drug Res (in press)
Bruyneel K, Rosseel MT, Bogaert MG (1982) Plasma concentrations of isosorbide dinitrate and mononitrates after acute and chronic oral administration of isosorbide dinitrate in man. Arzneimittelforsch/Drug Res 32: 769–772
Chasseaud LF, Down WH, Grundy RK (1975) Concentrations of the vasodilator isosorbide dinitrate and its metabolites in the blood of human subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 8: 157–160
Chasseaud LF, Taylor T (1981) Pharmacokinetics of isosorbide mononitrates in human subjects. In: Lichtlen PR, Engel HJ, Schrey A, Swan HJC (eds) Nitrates III. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, p 47
Down WH, Chasseaud LF, Grundy RK (1974) Biotransformation of isosorbide dinitrate in humans. J Pharm Sci 63: 1147–1149
Doyle E, Chasseaud LF, Taylor T (1980) Measurement of plasma concentrations of isosorbide dinitrate. Biopharm Drug Dispos 1: 141–147
Endele R, Senn M (1983) MS/MS in pharmacokinetic studies. Int J Mass Spectrom Ion Physics 48: 81–84
Frydman A, Levenson J, Simon A, Safar M, Bieder A, Bertharion J, Gaillor J (1982) Pharmacocinetique du dinitrate d'isosorbide. Nouv Presse Med 11: 2049–2056
Fung HL, McNiff EF, Ruggirello D, Darke A, Thadani U, Parker JO (1981) Kinetics of isosorbide dinitrate and relationships to pharmacological effects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 11: 579–590
Fung HL, Parker JO (1983) Prolonged plasma half-life after oral isosorbide dinitrate in patients with angina pectoris. Br J Clin Pharmacol 15: 746–748
Geigenberger A, Degen J, Maier-Lenz H (1982) Vergleichende Pharmakokinetik und Bioverfügbarkeit von Isosorbiddinitrat und seiner Metaboliten 5- und 2-Isosorbidmononitrat aus zwei Retardpräparaten. Arzneimittelforsch/Drug Res 32: 1138–1140
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1982) Pharmacokinetics (2nd edn). Marcel Dekker, New York Basel, p 17
Gladigau V, Neurath G, Dünger M, Schnelle K, Johnson KI (1981) Plasma levels of isosorbide dinitrate and its main metabolites following oral administration of two sustained release formulations in normal man. Arzneimittelforsch/Drug Res 31: 835–840
Laufen H, Scharpf F, Bartsch G (1978) Improved method for the rapid determination of isosorbide dinitrate in human plasma and its application in pharmacokinetic studies. J Chromatogr 146: 457–464
McNiff EF, Yacobi A, Young-Chang FM, Golden LH, Goldfarb A, Fung HL (1981) Nitroglycerin pharmacokinetics after intravenous infusion in normal subjects. J Pharm Sci 70: 1054–1058
Morrison RA, Wiegand UW, Jähnchen E, Höhmann D, Bechthold H, Meinertz T, Fung HL (1983) Isosorbide dinitrate kinetics and dynamics after intravenous, sublingual, and percutaneous dosing in angina. Clin Pharmacol Ther 33: 747–756
Needleman P, Hunter FE Jr (1965) The transformation of glyceryl trinitrate and other nitrates by glutathione-organic nitrate reductase. Mol Pharmacol 1: 77–86
Pang KS, Kwan KC (1983) A commentary: methods and assumptions in the kinetic estimation of metabolite formation. Drug Metab Dispos 11: 79–84
Platzer R, Reutemann G, Galeazzi RL (1982) Pharmacokinetics of intravenous isosorbide-dinitrate. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 10: 575–585
Reed DE, Akester JM, Prather JF, Tuckosh JR, McCurdy DH, Yeh C (1977) Blood and tissue levels of [14C] isosorbide dinitrate after oral and intravenous administration to rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 202: 32–37
Rosseel MT, Bogaert MG (1979) Simultaneous determination of isosorbide dinitrate and its mononitrates in human plasma by capillary column GLC. J Pharm Sci 68: 659–660
Sisenwine SF, Ruelius HW (1971) Plasma concentrations and urinary excretion of isosorbide dinitrate and its metabolites in the dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 176: 296–301
Spörl-Radun S, Betzien G, Kaufmann B, Liede V, Abshagen U (1980) Effects and pharmacokinetics of isosorbide dinitrate in normal man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 18: 237–244
Taylor T, Chasseaud LF, Doyle E, Bonn R, Darragh A, Lambe RF (1982) Isosorbide dinitrate pharmacokinetics. Arzneimittelforsch/Drug Res 32: 1329–1333
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abshagen, U., Betzien, G., Endele, R. et al. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of isosorbide-dinitrate after intravenous and oral administration. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 27, 637–644 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00547041
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00547041